J Stroke.
2024 Jan;26(1):125-128. 10.5853/jos.2023.03349.
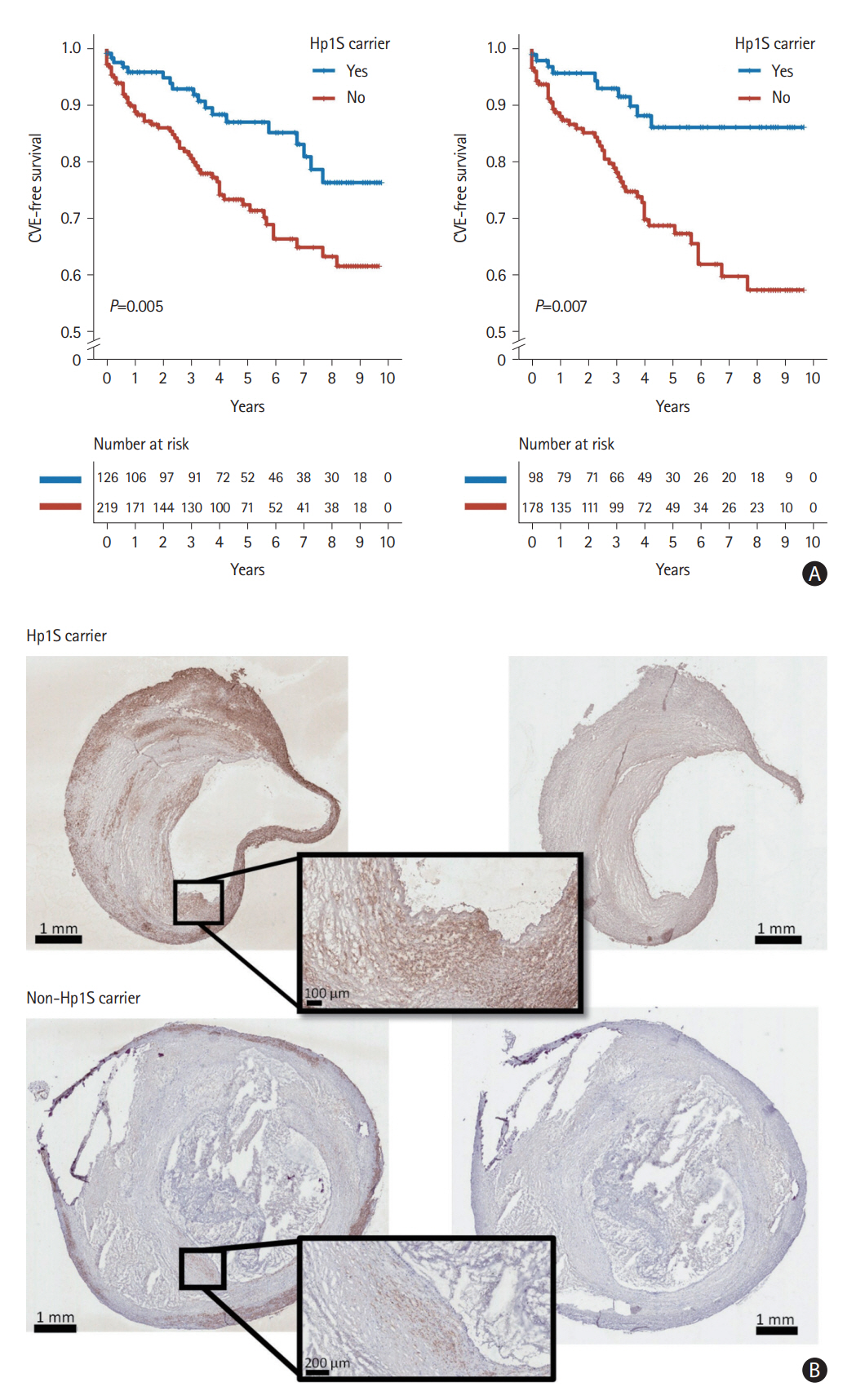
Haptoglobin Gene Polymorphism Is Associated With Lower Postoperative Cardiovascular Risk in Carotid Stenosis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Sciences Malmö, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden
- 2Department of Cardiology, Electrophysiology and Rhythmology, Hospital Porz am Rhein, Cologne, Germany
- 3Department of Cardiology, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden
- 4Wallenberg Center for Molecular Medicine, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
- KMID: 2551357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2023.03349
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Smithies O, Connell GE, Dixon GH. Inheritance of haptoglobin subtypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1962; 14:14–21.2. Boettger LM, Salem RM, Handsaker RE, Peloso GM, Kathiresan S, Hirschhorn JN, et al. Recurring exon deletions in the HP (haptoglobin) gene contribute to lower blood cholesterol levels. Nat Genet. 2016; 48:359–366.3. Merkler A, Sertic´ J, Bazina Martinovic´ A, Križ T, Milicˇic´ I, Šimic´ M, et al. Haptoglobin genotype 2-2 associated with atherosclerosis in patients with ischemic stroke. Gene. 2020; 752:144786.4. Ijäs P, Saksi J, Soinne L, Tuimala J, Jauhiainen M, Jula A, et al. Haptoglobin 2 allele associates with unstable carotid plaque and major cardiovascular events. Atherosclerosis. 2013; 230:228–234.5. Syreeni A, Dahlström EH, Hägg-Holmberg S, Forsblom C, Eriksson MI, Harjutsalo V, et al. Haptoglobin genotype does not confer a risk of stroke in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2022; 71:2728–2738.6. Cahill LE, Jensen MK, Chiuve SE, Shalom H, Pai JK, Flint AJ, et al. The risk of coronary heart disease associated with glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.5% or greater is pronounced in the haptoglobin 2-2 genotype. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:1791–1799.7. Melamed-Frank M, Lache O, Enav BI, Szafranek T, Levy NS, Ricklis RM, et al. Structure-function analysis of the antioxidant properties of haptoglobin. Blood. 2001; 98:3693–3698.8. Carew AS, Levy AP, Ginsberg HN, Coca S, Lache O, Ransom T, et al. Haptoglobin phenotype modifies the influence of intensive glycemic control on cardiovascular outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 75:512–521.9. Naryzny SN, Legina OK. Haptoglobin as a biomarker. Biochemistry Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem. 2021; 15:184–198.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carotid Artery Stenting for Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis: What We Need to Know for Treatment Decision
- Usefulness of carotid ultrasonography and treatment of carotid disease
- Carotid Artery Stenting
- Asymptomatic Bilateral Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion with Ring Finger Protein 213 Gene Polymorphism
- Carotid ultrasound in patients with coronary artery disease