Clin Endosc.
2024 Jan;57(1):89-95. 10.5946/ce.2022.288.
Stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation in endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Kitasato University School of Medicine, Sagamihara, Japan
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Isehara Kyodo Hospital, Isehara, Japan
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Japan Community Health Care Organization Sagamino Hospital, Sagamihara, Japan
- KMID: 2551197
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.288
Abstract
- Background/Aims
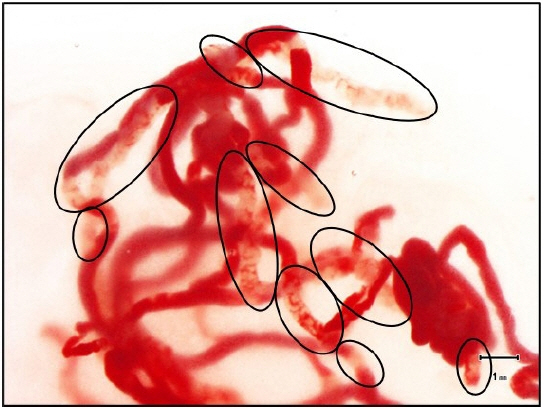
In stereomicroscopic sample isolation processing, the cutoff value (≥4 mm) of stereomicroscopically visible white cores indicates high diagnostic sensitivity. We aimed to evaluate endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) using a simplified stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions (SELs).
Methods
In this multicenter prospective trial, we performed EUS-TA using a 22-gauge Franseen needle in 34 participants with SELs derived from the upper gastrointestinal muscularis propria, requiring pathological diagnosis. The presence of stereomicroscopically visible white core (SVWC) in each specimen was assessed using stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation. The primary outcome was EUS-TA’s diagnostic sensitivity with stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation based on the SVWC cutoff value (≥4 mm) for malignant upper gastrointestinal SELs.
Results
The total number of punctures was 68; 61 specimens (89.7%) contained stereomicroscopically visible white cores ≥4 mm in size. The final diagnoses were gastrointestinal stromal tumor, leiomyoma, and schwannoma in 76.5%, 14.7%, and 8.8% of the cases, respectively. The sensitivity of EUS-TA with stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation based on the SVWC cutoff value for malignant SELs was 100%. The per-lesion accuracy of histological diagnosis reached the highest level (100%) at the second puncture.
Conclusions
Stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation showed high diagnostic sensitivity and could be a new method for diagnosing upper gastrointestinal SELs using EUS-TA.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang KX, Ben QW, Jin ZD, et al. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with EUS-guided FNA: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:283–290.2. Klapman JB, Logrono R, Dye CE, et al. Clinical impact of on-site cytopathology interpretation on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1289–1294.3. Hocke M, Topalidis T, Braden B, et al. "Clinical" cytology for endoscopists: a practical guide. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6:83–89.4. Lopes CV, Dedavid E, Silva TL, et al. The value of endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle aspiration in the suspicion of pancreatic hydatid cyst in endemic areas with negative serology (with video). Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6:350–351.5. Wang Y, Chai N, Feng J, et al. A prospective study of endoscopic ultrasonography features, cyst fluid carcinoembryonic antigen, and fluid cytology for the differentiation of small pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:335–342.6. Biermann K, Lozano Escario MD, Hébert-Magee S, et al. How to prepare, handle, read, and improve EUS-FNA and fine-needle biopsy for solid pancreatic lesions: the pathologist's role. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017; 6(Suppl 3):S95–S98.7. van Riet PA, Cahen DL, Poley JW, et al. Mapping international practice patterns in EUS-guided tissue sampling: outcome of a global survey. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E360–E370.8. Masutani H, Okuwaki K, Kida M, et al. On-site stereomicroscope quality evaluations to estimate white core cutoff lengths using EUS-FNA biopsy sampling with 22-gauge needles. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 90:947–956.9. Okuwaki K, Masutani H, Kida M, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of white core cutoff lengths obtained by EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy using a novel 22G Franseen biopsy needle and sample isolation processing by stereomicroscopy for subepithelial lesions. Endosc Ultrasound. 2020; 9:187–192.10. Okuwaki K, Imaizumi H, Kida M, et al. Usefulness of the automated multiband imaging system for EUS-FNA biopsy specimen evaluation in patients with upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions. Endosc Ultrasound. 2022; 11:283–290.11. Watanabe M, Okuwaki K, Kida M, et al. Multicenter prospective study of the efficacy of stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation in endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition in patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2022; 22:311–316.12. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.13. Kida M, Kawaguchi Y, Miyata E, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography diagnosis of subepithelial lesions. Dig Endosc. 2017; 29:431–443.14. Polkowski M. Endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of malignant submucosal tumors. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:635–645.15. Goettsch WG, Bos SD, Breekveldt-Postma N, et al. Incidence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours is underestimated: results of a nation-wide study. Eur J Cancer. 2005; 41:2868–2872.16. Ishigaki K, Nakai Y, Oyama H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition by 22-gauge Franseen and standard needles for solid pancreatic lesions. Gut Liver. 2020; 14:817–825.17. Hedenström P, Marschall HU, Nilsson B, et al. High clinical impact and diagnostic accuracy of EUS-guided biopsy sampling of subepithelial lesions: a prospective, comparative study. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:1304–1313.18. Bang JY, Hebert-Magee S, Navaneethan U, et al. Randomized trial comparing the Franseen and Fork-tip needles for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:1432–1438.19. Conti CB, Cereatti F, Grassia R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of solid pancreatic masses: the fine needle aspiration or fine needle biopsy dilemma. Is the best needle yet to come? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 11:454–471.20. Hébert-Magee S, Bae S, Varadarajulu S, et al. The presence of a cytopathologist increases the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a meta-analysis. Cytopathology. 2013; 24:159–171.21. Matynia AP, Schmidt RL, Barraza G, et al. Impact of rapid on-site evaluation on the adequacy of endoscopic-ultrasound guided fine-needle aspiration of solid pancreatic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:697–705.22. Hewitt MJ, McPhail MJ, Possamai L, et al. EUS-guided FNA for diagnosis of solid pancreatic neoplasms: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:319–331.23. Kong F, Zhu J, Kong X, et al. Rapid on-site evaluation does not improve endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration adequacy in pancreatic masses: a meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0163056.24. Polkowski M, Jenssen C, Kaye P, et al. Technical aspects of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) technical guideline: March 2017. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:989–1006.25. Yang F, Liu E, Sun S. Rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) with EUS-FNA: the ROSE looks beautiful. Endosc Ultrasound. 2019; 8:283–287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- What method can we choose if rapid on-site evaluation is not available for the endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions?
- The Diagnosis of Subepithelial Lesions in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration versus Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subepithelial Tumors
- Effectiveness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition with stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation for preoperative diagnosis of resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: a prospective study
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?