Acute Crit Care.
2023 Nov;38(4):509-512. 10.4266/acc.2021.01452.
Myoclonic status epilepticus after severe hyperthermia in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
- 2Section of Neurology, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA
- KMID: 2550908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.01452
Abstract
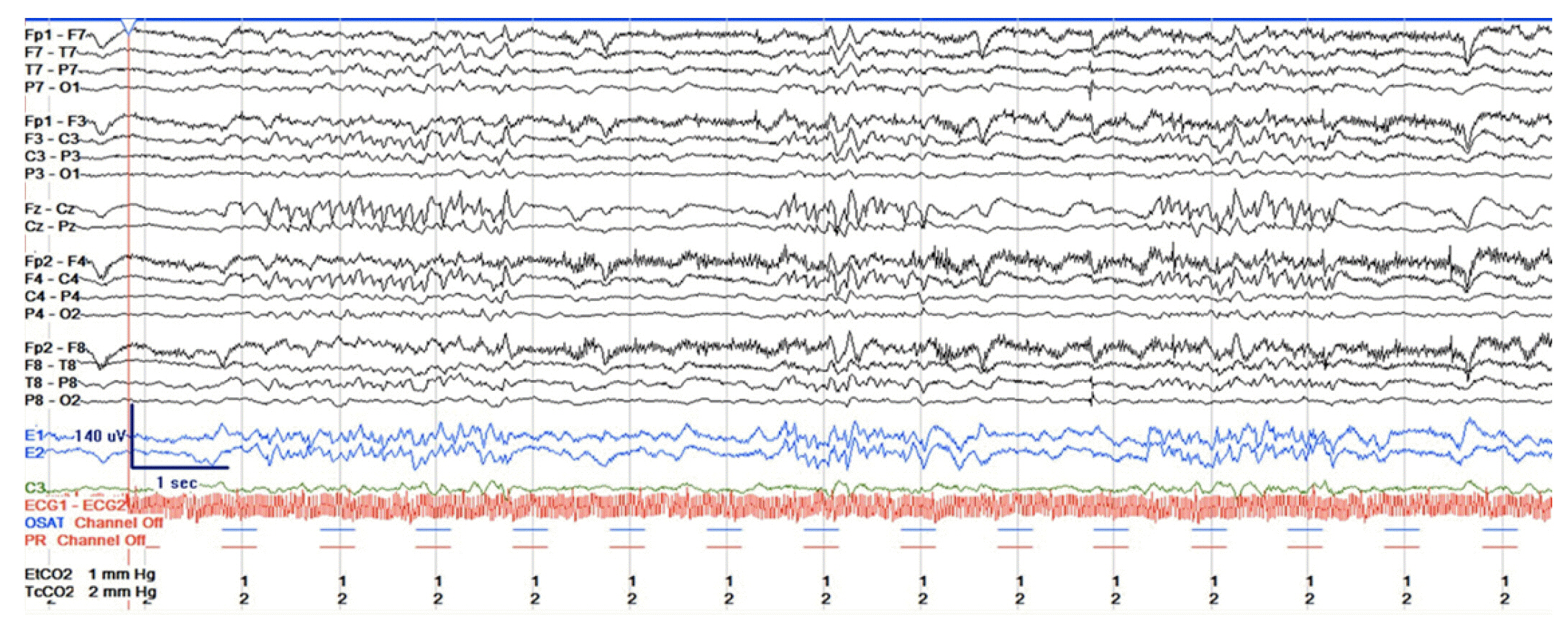
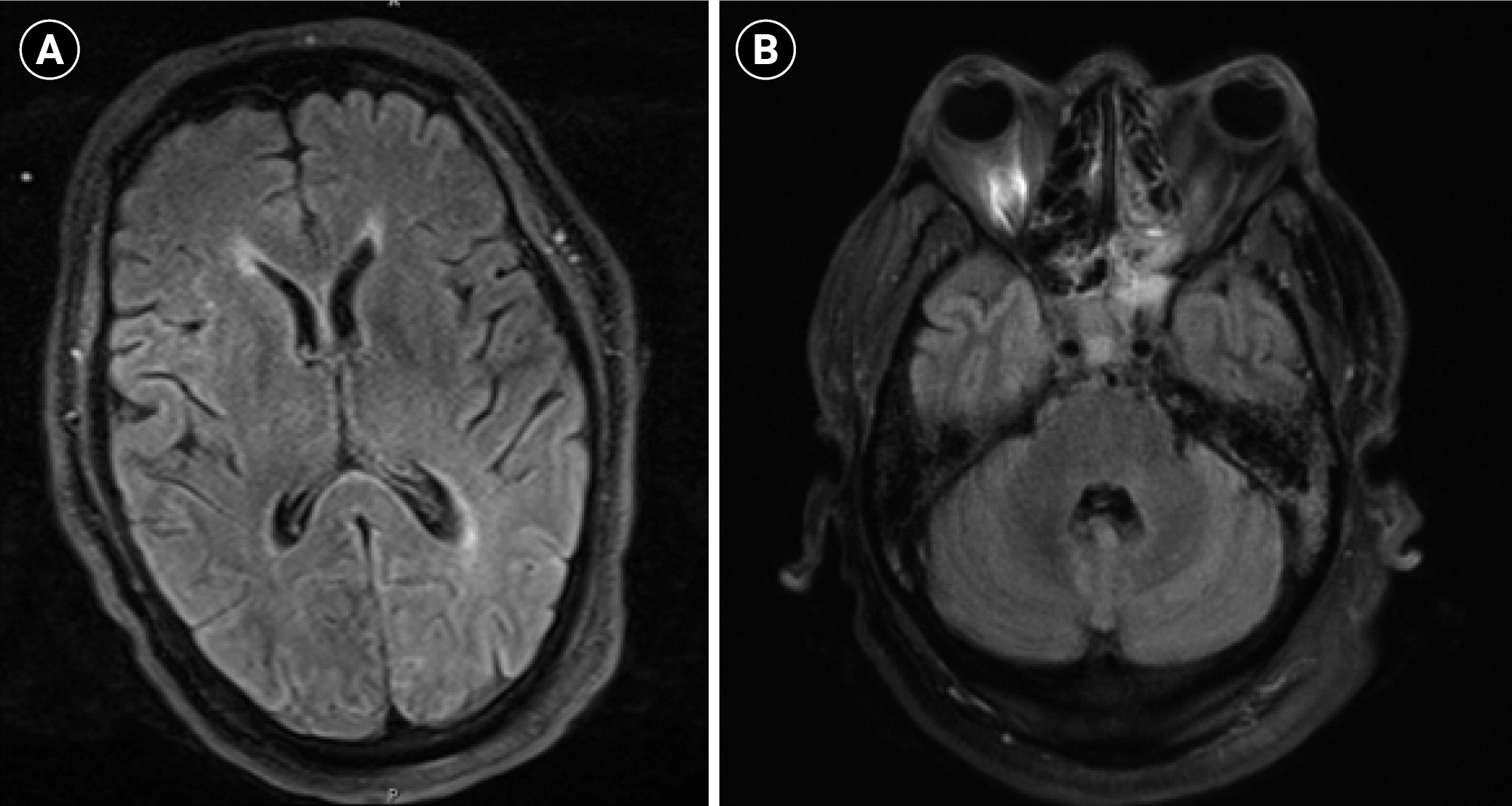
- Myoclonic status epilepticus (MSE) is a sign of severe neurologic injury in cardiac arrest patients. To our knowledge, MSE has not been described as a result of prolonged hyperpyrexia. A 56-yearold man with coronavirus disease 2019 presented with acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic/hypovolemic shock, and presumed community-acquired pneumonia. Five days after presentation, he developed a sustained fever of 42.1°C that did not respond to acetaminophen or ice water gastric lavage. After several hours, he was placed on surface cooling. Three hours after fever resolution, new multifocal myoclonus was noted in the patient’s arms and trunk. Electroencephalography showed midline spikes consistent with MSE, which resolved with 40 mg/kg of levetiracetam. This case demonstrates that severe hyperthermia can cause cortical injury significant enough to trigger MSE and should be treated emergently using the most aggressive measures available. Providers should have a low threshold for electroencephalography in intubated patients with a recent history of hyperpyrexia.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wijdicks EF, Parisi JE, Sharbrough FW. Prognostic value of myoclonus status in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest. Ann Neurol. 1994; 35:239–43.
Article2. Hui AC, Cheng C, Lam A, Mok V, Joynt GM. Prognosis following postanoxic myoclonus status epilepticus. Eur Neurol. 2005; 54:10–3.
Article3. Celesia GG, Grigg MM, Ross E. Generalized status myoclonicus in acute anoxic and toxic-metabolic encephalopathies. Arch Neurol. 1988; 45:781–4.
Article4. Baysal Kirac L, Aydogdu I, Acarer A, Alpaydin S, Bayam FE, Onbasi H, et al. Myoclonic status epilepticus in six patients without epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2012; 1:10–3.
Article5. Chen W, Toprani S, Werbaneth K, Falco-Walter J. Status epilepticus and other EEG findings in patients with COVID-19: a case series. Seizure. 2020; 81:198–200.
Article6. Walter EJ, Carraretto M. The neurological and cognitive consequences of hyperthermia. Crit Care. 2016; 20:199.
Article7. White MG, Luca LE, Nonner D, Saleh O, Hu B, Barrett EF, et al. Cellular mechanisms of neuronal damage from hyperthermia. Prog Brain Res. 2007; 162:347–71.
Article8. Hashim IA, Al-Zeer A, Al-Shohaib S, Al-Ahwal M, Shenkin A. Cytokine changes in patients with heatstroke during pilgrimage to Makkah. Mediators Inflamm. 1997; 6:135–9.
Article9. Hammami MM, Bouchama A, Al-Sedairy S, Shail E, AlOhaly Y, Mohamed GE. Concentrations of soluble tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 receptors in heatstroke and heatstress. Crit Care Med. 1997; 25:1314–9.
Article10. Narula N, Joseph R, Katyal N, Daouk A, Acharya S, Avula A, et al. Seizure and COVID-19: association and review of potential mechanism. Neurol Psychiatry Brain Res. 2020; 38:49–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Severe Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infancy
- Myoclonic Status Epilepticus of Unknown Etiology in an Elderly Patient
- Is the Intensive Anticonvulsant Treatment for Control of Acute Posthypoxic Myoclonic Status Epilepticus Necessary?
- Myoclonic status epilepticus in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy which recurred after somatosensory evoked potential testing
- Non-Convulsive Status with Myoclonic-Astatic Epilepsy: A Case Repot