Acute Crit Care.
2023 Nov;38(4):498-506. 10.4266/acc.2023.01354.
Eleven years of experience in operating a pediatric rapid response system at a children’s hospital in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Innovative Medical Technology Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550906
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.01354
Abstract
- Background
Various rapid response systems have been developed to detect clinical deterioration in patients. Few studies have evaluated single-parameter systems in children compared to scoring systems. Therefore, in this study we evaluated a single-parameter system called the acute response system (ARS).
Methods
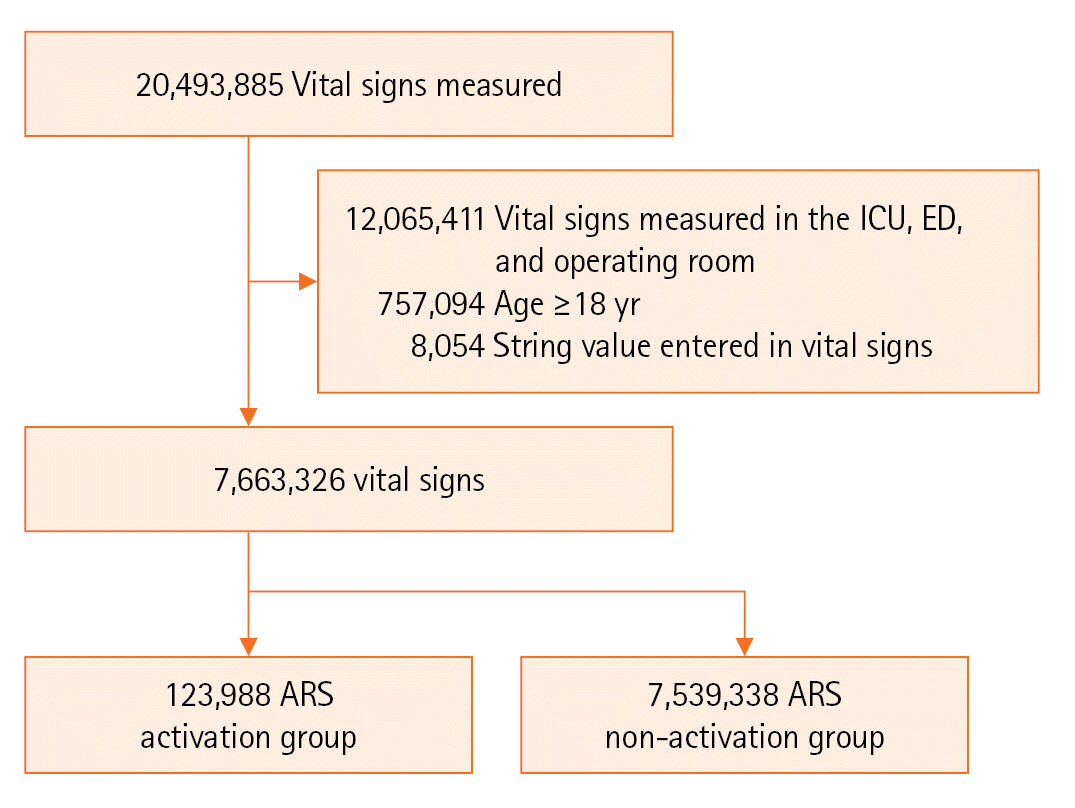
This retrospective study was performed at a tertiary children’s hospital. Patients under 18 years old admitted from January 2012 to August 2023 were enrolled. ARS parameters such as systolic blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and whether the ARS was activated were collected. We divided patients into two groups according to activation status and then compared the occurrence of critical events (cardiopulmonary resuscitation or unexpected intensive care unit admission). We evaluated the ability of ARS to predict critical events and calculated compliance. We also analyzed the correlation between each parameter that activates ARS and critical events.
Results
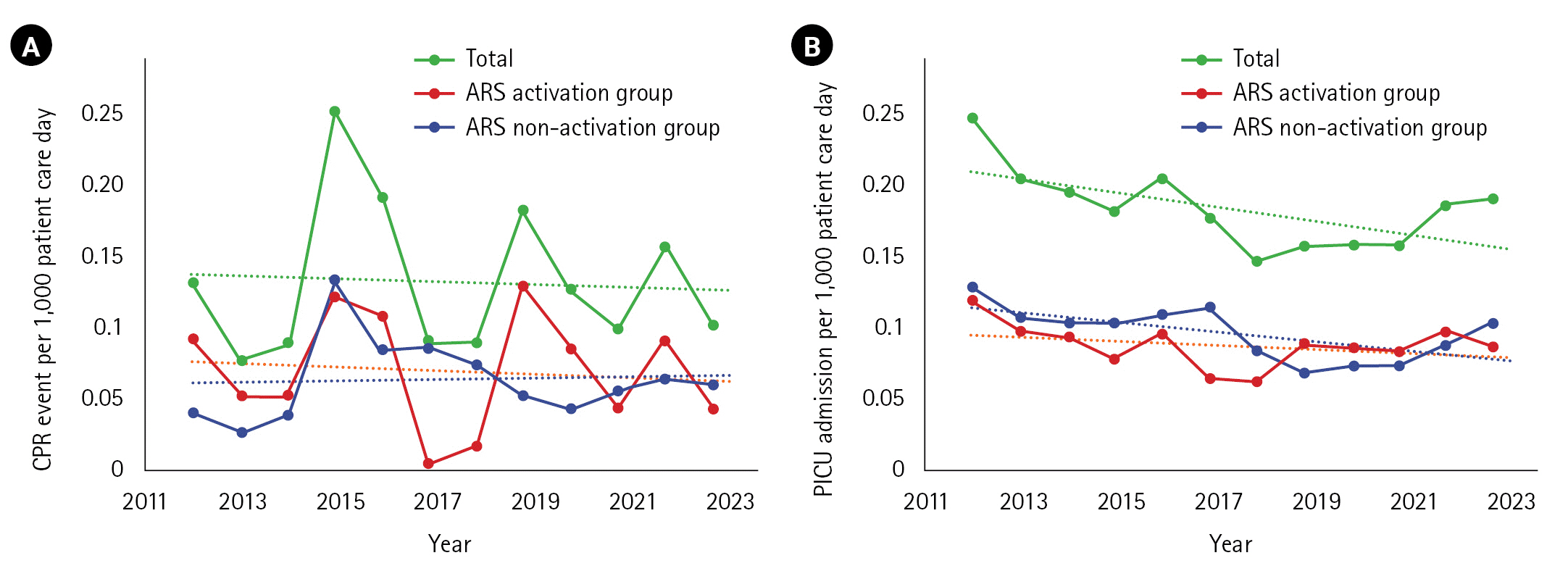
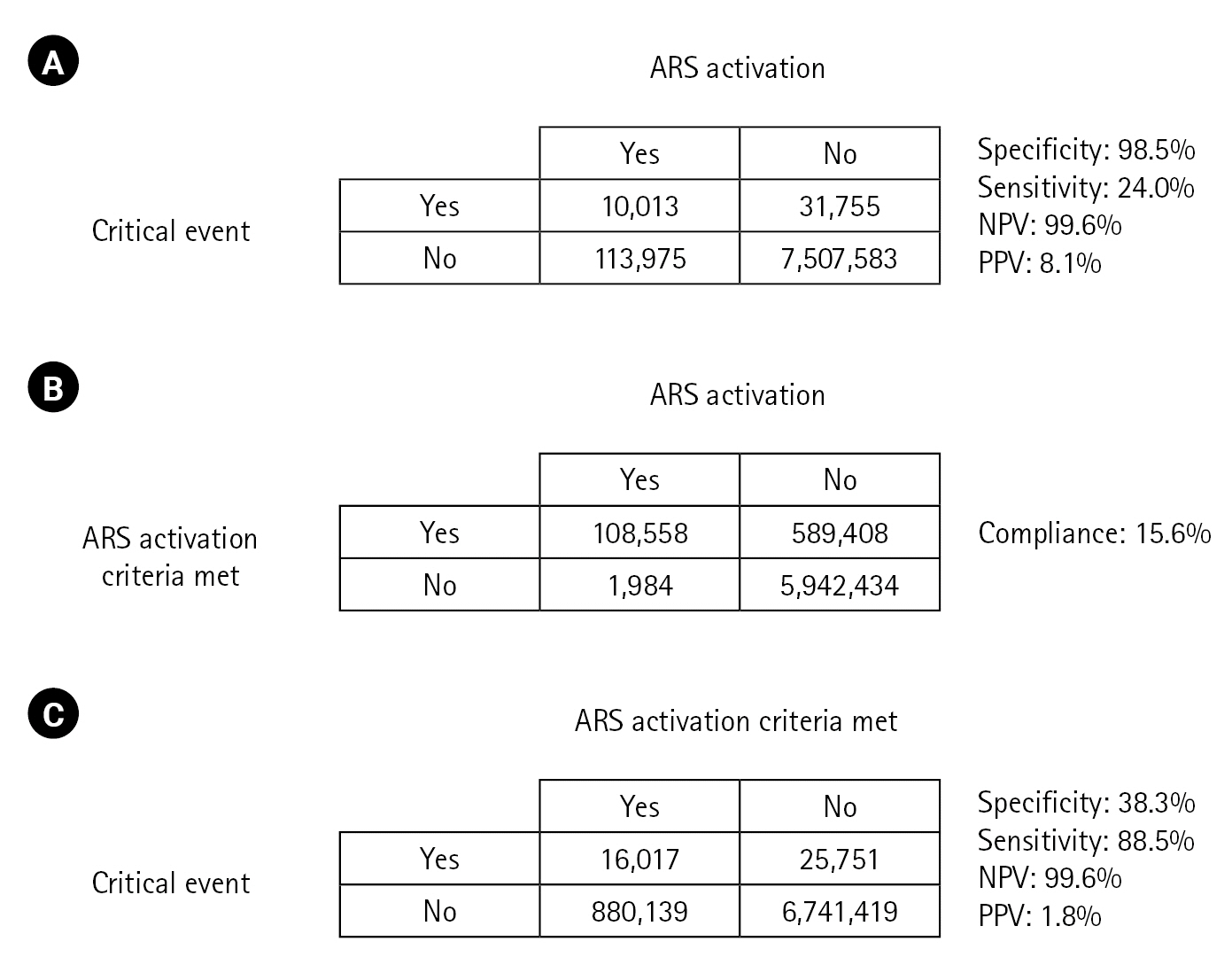
The critical events prediction performance of ARS has a specificity of 98.5%, a sensitivity of 24.0%, a negative predictive value of 99.6%, and a positive predictive value of 8.1%. The compliance rate was 15.6%. Statistically significant increases in the risk of critical events were observed for all abnormal criteria except low heart rate. There was no significant difference in the incidence of critical events.
Conclusions
ARS, a single parameter system, had good specificity and negative predictive value for predicting critical events; however, sensitivity and positive predictive value were not good, and medical staff compliance was poor.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vincent JL, Einav S, Pearse R, Jaber S, Kranke P, Overdyk FJ, et al. Improving detection of patient deterioration in the general hospital ward environment. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018; 35:325–33.
Article2. Tibballs J, Kinney S, Duke T, Oakley E, Hennessy M. Reduction of paediatric in-patient cardiac arrest and death with a medical emergency team: preliminary results. Arch Dis Child. 2005; 90:1148–52.
Article3. Simchen E, Sprung CL, Galai N, Zitser-Gurevich Y, Bar-Lavi Y, Gurman G, et al. Survival of critically ill patients hospitalized in and out of intensive care units under paucity of intensive care unit beds. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32:1654–61.
Article4. Al-Moteri M, Plummer V, Cooper S, Symmons M. Clinical deterioration of ward patients in the presence of antecedents: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. Aust Crit Care. 2019; 32:411–20.
Article5. Parshuram CS, Dryden-Palmer K, Farrell C, Gottesman R, Gray M, Hutchison JS, et al. Effect of a pediatric early warning system on all-cause mortality in hospitalized pediatric patients: the EPOCH Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2018; 319:1002–12.
Article6. Choi YH, Lee HS, Lee BJ, Suh DI, Park JD. Effectiveness of bradycardia as a single parameter in the pediatric acute response system. Korean J Crit Care Med. 2014; 29:297–303.
Article7. Hall KK, Lim A, Gale B. The use of rapid response teams to reduce failure to rescue events: a systematic review. J Patient Saf. 2020; 16(3S Suppl 1):S3–7.
Article8. Trubey R, Huang C, Lugg-Widger FV, Hood K, Allen D, Edwards D, et al. Validity and effectiveness of paediatric early warning systems and track and trigger tools for identifying and reducing clinical deterioration in hospitalised children: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019; 9:e022105.
Article9. Edwards ED, Powell CV, Mason BW, Oliver A. Prospective cohort study to test the predictability of the Cardiff and Vale paediatric early warning system. Arch Dis Child. 2009; 94:602–6.
Article10. Smith GB, Prytherch DR, Schmidt PE, Featherstone PI, Higgins B. A review, and performance evaluation, of single-parameter “track and trigger” systems. Resuscitation. 2008; 79:11–21.
Article11. Bell MB, Konrad D, Granath F, Ekbom A, Martling CR. Prevalence and sensitivity of MET-criteria in a Scandinavian University Hospital. Resuscitation. 2006; 70:66–73.
Article12. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Acutely ill adults in hospital: recognising and responding to deterioration [Internet]. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2007 [cited 2023 Nov 1]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg50.13. Subbe CP, Slater A, Menon D, Gemmell L. Validation of physiological scoring systems in the accident and emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2006; 23:841–5.
Article14. Hillman K, Chen J, Cretikos M, Bellomo R, Brown D, Doig G, et al. Introduction of the medical emergency team (MET) system: a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005; 365:2091–7.
Article15. Skaletzky SM, Raszynski A, Totapally BR. Validation of a modified pediatric early warning system score: a retrospective case-control study. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2012; 51:431–5.
Article16. Parshuram CS, Duncan HP, Joffe AR, Farrell CA, Lacroix JR, Middaugh KL, et al. Multicentre validation of the bedside paediatric early warning system score: a severity of illness score to detect evolving critical illness in hospitalised children. Crit Care. 2011; 15:R184.
Article17. Akre M, Finkelstein M, Erickson M, Liu M, Vanderbilt L, Billman G. Sensitivity of the pediatric early warning score to identify patient deterioration. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:e763–9.
Article18. Tucker KM, Brewer TL, Baker RB, Demeritt B, Vossmeyer MT. Prospective evaluation of a pediatric inpatient early warning scoring system. J Spec Pediatr Nurs. 2009; 14:79–85.
Article19. Duncan H, Hutchison J, Parshuram CS. The Pediatric Early Warning System score: a severity of illness score to predict urgent medical need in hospitalized children. J Crit Care. 2006; 21:271–8.
Article20. Kim L, Yun KS, Park JD, Lee B. Effect of diurnal variation of heart rate and respiratory rate on activation of rapid response system and clinical outcome in hospitalized children. Children (Basel). 2023; 10:167.
Article21. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Winslow C, Hall J, Edelson DP. Differences in vital signs between elderly and nonelderly patients prior to ward cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med. 2015; 43:816–22.
Article22. Rothschild JM, Gandara E, Woolf S, Williams DH, Bates DW. Single-parameter early warning criteria to predict life-threatening adverse events. J Patient Saf. 2010; 6:97–101.
Article23. Chong SL, Goh MS, Ong GY, Acworth J, Sultana R, Yao SH, et al. Do paediatric early warning systems reduce mortality and critical deterioration events among children?: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Resusc Plus. 2022; 11:100262.
Article24. Wee BY, Lee JH, Mok YH, Chong SL. A narrative review of heart rate and variability in sepsis. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8:768.
Article25. Chapman SM, Wray J, Oulton K, Pagel C, Ray S, Peters MJ. ‘The Score Matters’: wide variations in predictive performance of 18 paediatric track and trigger systems. Arch Dis Child. 2017; 102:487–95.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapid Section: A simple technique useful to the practicing pathologist
- Rapid Recovery From SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Immunocompromised Children Despite Limited Neutralizing Antibody Response: A Virologic and Sero-Immunologic Analysis of a Single-Center Cohort
- Analysis and Consideration of Factors for Predicting Cooperation Levels in Pediatric Dentistry
- Perception of Parents Regarding Specialized Pediatric Dentistry
- North Korean Children's Health and the Role of Maternal and Child Health Experts