Ann Clin Microbiol.
2023 Sep;26(3):41-50. 10.5145/ACM.2023.26.3.1.
Progress and potential of group B Streptococcus vaccines: a narrative review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Medical Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
- KMID: 2550654
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2023.26.3.1
Abstract
- Group B Streptococcus (GBS, Streptococcus agalactiae) is a pathogen that causes sepsis and meningitis, particularly in newborns, as well as severe infections in the elderly and those at high risk. For many years, the administration of intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis (IAP) has been a standard method to prevent neonatal GBS infection. However, IAP may be unsuitable in low-income settings due to its high cost and difficult accessibility to medical institutions. Additionally, IAP may lead to the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Hence, an alternative method for the control of GBS, such as a vaccine, is needed. An effective vaccine will likely prevent the further spread of GBS and be cost-effective compared with IAP. GBS vaccines have been under development for the past two decades, and several candidates have shown potential. In this review, we discuss the current development of GBS vaccines, including types and their implementation in different target populations.
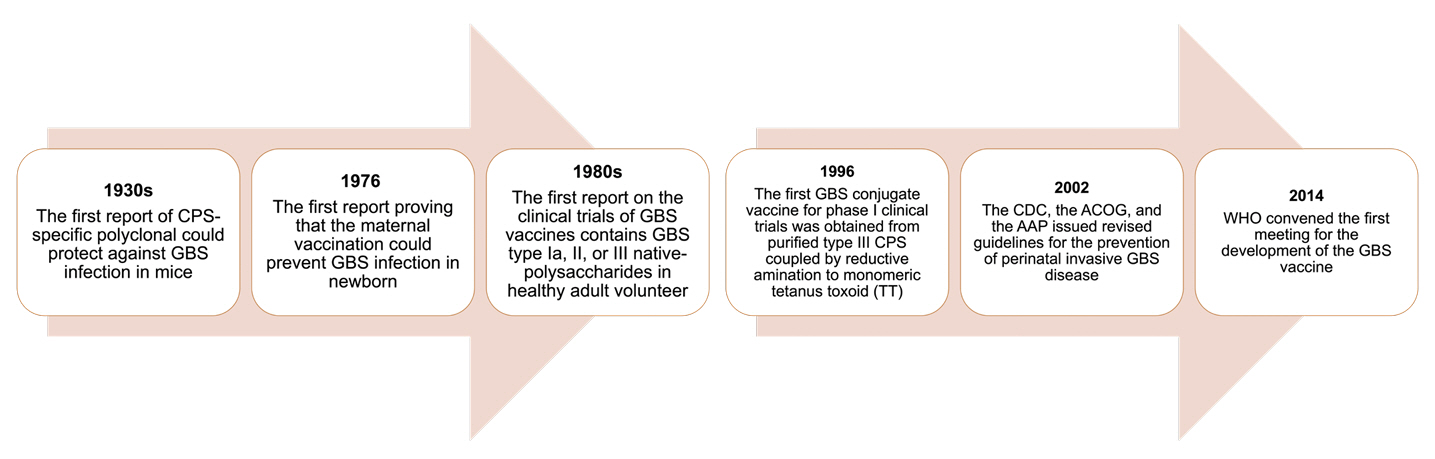
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kong F, Gowan S, Martin D, James G, Gilbert GL. Serotype identification of group B streptococci by PCR and sequencing. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:216-26. .2. Hanna M and Noor A. Streptococcus group B. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL); StatPearls Publishing, 2020. .3. Russell NJ, Seale AC, O’Driscoll M, O’Sullivan C, Bianchi-Jassir F, Gonzalez-Guarin J, et al. Maternal colonization with group B StreStreptococcusptococcus and serotype distribution worldwide: systematic review and meta-analyses. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:S100-11. .4. Blencowe H, Cousens S, Jassir FB, Say L, Chou D, Mathers C, et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of stillbirth rates in 2015, with trends from 2000: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2016;4:e98-108. .5. Lawn JE, Blencowe H, Oza S, You D, Lee AC, Waiswa P, et al. Every newborn: progress, priorities, and potential beyond survival. Lancet 2014;384:189-205. .6. Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Perin J, Rudan I, Lawn JE, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015;385:430-40. .7. Seale AC, Bianchi-Jassir F, Russell NJ, Kohli-Lynch M, Tann CJ, Hall J, et al. Estimates of the burden of group B streptococcal disease worldwide for pregnant women, stillbirths, and children. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:S200-19. .8. CDC. Group B Strep (GBS). https://www.cdc.gov/groupbstrep/index.html [Online] (last visited on 28 August 2023). .9. Braye K, Foureur M, de Waal K, Jones M, Putt E, Ferguson J. Group B streptococcal screening, intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis, and neonatal early-onset infection rates in an Australian local health district: 2006-2016. PLoS One 2019;14:e0214295. .10. Horsley L. CDC updates guidelines for the prevention of perinatal GBS disease. Am Fam Physician 2011;83:1106-10. .11. Fairlie T, Zell ER, Schrag S. Effectiveness of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal disease. Obstet Gynecol 2013;121:570-7. .12. Pintye J, Saltzman B, Wolf E, Crowell CS. Risk factors for late-onset group B streptococcal disease before and after implementation of universal screening and intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc 2016;5:431-8. .13. Carreras-Abad C, Ramkhelawon L, Heath PT, Le Doare K. A vaccine against group B Streptococcus: recent advances. Infect Drug Resist 2020:1263-72. .14. Nogacka A, Salazar N, Suárez M, Milani C, Arboleya S, Solís G, et al. Impact of intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis upon the intestinal microbiota and the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in vaginally delivered full-term neonates. Microbiome 2017;5:1-10. .15. Azad MB, Konya T, Persaud RR, Guttman DS, Chari RS, Field CJ, et al. Impact of maternal intrapartum antibiotics, method of birth and breastfeeding on gut microbiota during the first year of life: a prospective cohort study. BJOG: Int J Obstet Gynaecol 2016;123:983-93. .16. Corvaglia L, Tonti G, Martini S, Aceti A, Mazzola G, Aloisio I, et al. Influence of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis for group B Streptococcus on gut microbiota in the first month of life. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2016;62:304-8. .17. CDC. Serotypes and the importance of serotyping Salmonella. https://www.cdc.gov/ salmonella/reportspubs/salmonella-atlas/serotyping-importance.html [Online] (last visited on 28 August 2023). .18. Madrid L, Seale AC, Kohli-Lynch M, Edmond KM, Lawn JE, Heath PT, et al. Infant group B streptococcal disease incidence and serotypes worldwide: systematic review and metaanalyses. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:S160-72. .19. Kang HM, Lee HJ, Lee H, Jo DS, Lee HS, Kim TS, et al. Genotype characterization of group B Streptococcus isolated from infants with invasive diseases in South Korea. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2017;36:e242-7. .20. Yao Z, Jiayin W, Xinyi Z, Ling C, Mingyuan H, Simin M, et al. Identification of group B Streptococcus serotypes and genotypes in late pregnant women and neonates that are associated with neonatal early-onset infection in a South China population. Front Pediatr 2020;8:265. .21. Hannoun A, Shehab M, Khairallah MT, Sabra A, Abi-Rached R, Bazi T, et al. Correlation between group B streptococcal genotypes, their antimicrobial resistance profiles, and virulence genes among pregnant women in Lebanon. Int J Microbiol 2009;2009. .22. Takahashi T, Maeda T, Lee S, Lee DH, Kim S. Clonal distribution of clindamycin-resistant erythromycin-susceptible (CRES) Streptococcus agalactiae in Korea based on whole genome sequences. Ann Lab Med 2020;40:370-81. .23. Udo EE, Boswihi SS, Al-Sweih N. Genotypes and virulence genes in group B Streptococcus isolated in the maternity hospital, Kuwait. Med Princ Pract 2013;22:453-7. .24. Zakerifar M, Kaboosi H, Goli HR, Rahmani Z, Peyravii Ghadikolaii F. Antibiotic resistance genes and molecular typing of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from pregnant women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023;23:1-13. .25. Berner R. Group B Streptococcus vaccines: one step further. Lancet Infect Dis 2021;21:15860. .26. GAVI. Routine vaccines, extraordinary impact: Group B Streptococcus (GBS). https://www. gavi.org/vaccineswork/routine-vaccines-extraordinary-impact-group-b-Streptococcus-gbs [Online] (last visited on 30 August 2023). .27. Baker CJ and Kasper DL. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med 1976;294:753-6. .28. Lin FYC, Philips III JB, Azimi PH, Weisman LE, Clark P, Rhoads GG, et al. Level of maternal antibody required to protect neonates against early-onset disease caused by group B Streptococcus type Ia: a multicenter, seroepidemiology study. J Infect Dis 2001;184:1022-8. .29. Baker CJ, Carey VJ, Rench MA, Edwards MS, Hillier SL, Kasper DL, et al. Maternal antibody at delivery protects neonates from early-onset group B streptococcal disease. J Infect Dis 2014;209:781-8. .30. Johri AK, Paoletti LC, Glaser P, Dua M, Sharma PK, Grandi G, et al. Group B Streptococcus: global incidence and vaccine development. Nat Rev Microbiol 2006;4:932-42. .31. Paoletti LC and Kasper DL. Conjugate vaccines against group B Streptococcus types IV and VII. J Infect Dis 2002;186:123-6. .32. Wessels M, Paoletti L, Kasper D, DiFabio J, Michon F, Holme K, et al. Immunogenicity in animals of a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine against type III group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest 1990;86:1428-33. .33. Kasper DL, Paoletti LC, Wessels MR, Guttormsen HK, Carey VJ, Jennings HJ, et al. Immune response to type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine. J Clin Invest 1996;98:2308-14. .34. Baker CJ, Rench MA, Fernandez M, Paoletti LC, Kasper DL, Edwards MS. Safety and immunogenicity of a bivalent group B streptococcal conjugate vaccine for serotypes II and III. J Infect Dis 2003;188:66-73. .35. Ali MM, Asrat D, Fenta DA, Chaka TE, Woldeamanuel Y. Group B Streptococcus colonization rate and serotype distribution among pregnant women and their newborns at Adama Hospital Medical College, Ethiopia. Sci Rep 2020;10:9301. .36. Baker C and Edwards M. Group B streptococcal conjugate vaccines. Arch Dis Child 2003;88:375-8. .37. Dhar N, Mohamed E, Kirstein F, Williams M, Dorasamy S, van Zyl P, et al. Immune responses against group B Streptococcus monovalent and pentavalent capsular polysaccharide tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccines in Balb/c mice. iScience 2023;26:107380. .38. Dominguez K and Randis TM. Toward the development of a protein-based group B Streptococcus vaccine. Cell Rep Med 2022;3:100536. .39. Fischer P, Pawlowski A, Cao D, Bell D, Kitson G, Darsley M, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a prototype recombinant alpha-like protein subunit vaccine (GBS-NN) against Group B Streptococcus in a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind phase 1 trial in healthy adult women. Vaccine 2021;39:4489-99. .40. Pawlowski A, Lannergård J, Gonzalez-Miro M, Cao D, Larsson S, Persson JJ, et al. A group B Streptococcus alpha-like protein subunit vaccine induces functionally active antibodies in humans targeting homotypic and heterotypic strains. Cell Rep Med 2022;3:100511. .41. CDC. Group B streptococcal infections: the Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases National Center for Infectious Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https:// wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/p0000422/p0000422.asp [Online] (last visited on 26 August 2023). .42. MinervaX. MinervaX commences first phase 1 clinical study of novel GBS vaccine in older adults. https://www.minervax.com/minervax-commences-first-phase-1-clinical-study-ofnovel-gbs-vaccine-in-older-adults/ [Online] (last visited on 30 August 2023). .43. McLaughlin JM, Peyrani P, Furmanek S, Khan FL, Quinn A, Jodar L, et al. The burden of adults hospitalized with group B streptococcal infection. J Infect Dis 2021;224:1170-8. .44. CDC. Active bacterial core surveillance report, emerging infections program network, group B Streptococcus, 2009. https://www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-findings/survreports/gbs09.pdf [Online] (last visited on 31 August 2023). .45. Smith E, Khan M, Reingold A, Watt J. Group B Streptococcus infections of soft tissue and bone in California adults, 1995–2012. Epidemiol Infect 2015;143:3343-50. .46. Lamagni TL, Keshishian C, Efstratiou A, Guy R, Henderson KL, Broughton K, et al. Emerging trends in the epidemiology of invasive group B streptococcal disease in England and Wales, 1991–2010. Clin Infect Dis 2013;57:682-8. .47. Palazzi DL, Rench MA, Edwards MS, Baker CJ. Use of type V group B streptococcal conjugate vaccine in adults 65–85 years old. J Infect Dis 2004;190:558-64. .48. Arena CT. MinervaX initiates Phase I GBS vaccine trial in older people. https://www. clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/minervax-phase-i-gbs-trial-older-people/ [Online] (last visited on 1 September 2023). .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Status of group B streptococcal vaccine development
- Nasal vaccine as a booster shot: a viable solution to restrict pandemic?
- Commentary on "Progress in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a narrative review of telerehabilitation and wearable devices"
- Indirect Effects of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in National Immunization Programs for Children on Adult Pneumococcal Disease
- Progress and hurdles in the development of influenza virus-like particle vaccines for veterinary use