Cancer Res Treat.
2024 Jan;56(1):61-69. 10.4143/crt.2023.461.
First-Line Alectinib vs. Brigatinib in Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with ALK Rearrangement: Real-World Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2023.461
Abstract
- Purpose
Alectinib and brigatinib are second-generation anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinases (ALKs) that are widely used as first-line therapy for treating ALK-positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Given the lack of a head-to-head comparison of these drugs as first-line therapies, this retrospective observational study aimed to compare the real-world efficacy and safety of alectinib and brigatinib.
Materials and Methods
Patients who received alectinib or brigatinib as the first-line treatment for ALK-positive advanced NSCLC were evaluated for clinical outcomes of objective response rate (ORR), intracranial ORR, time to next treatment (TTNT), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety profiles.
Results
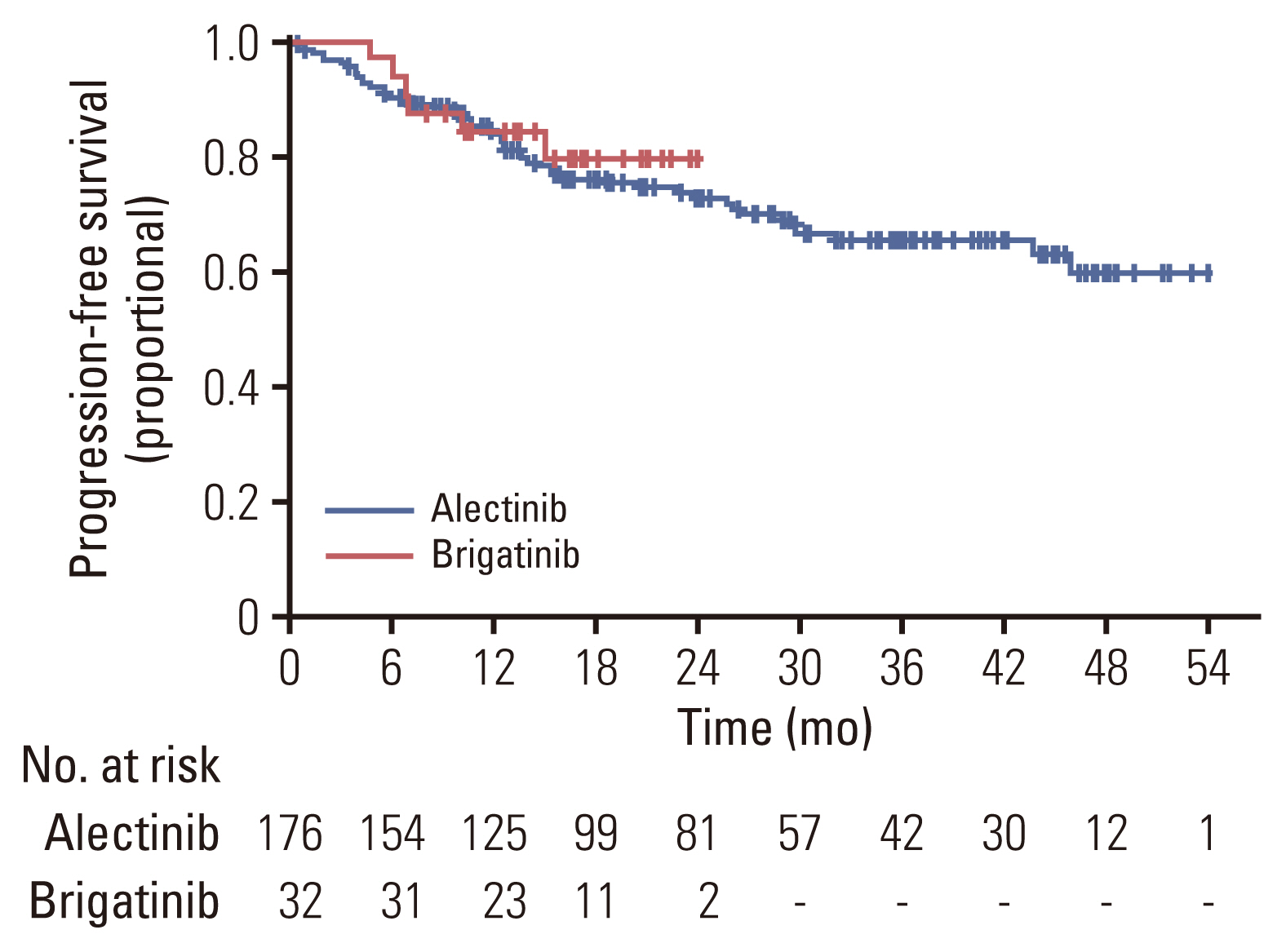
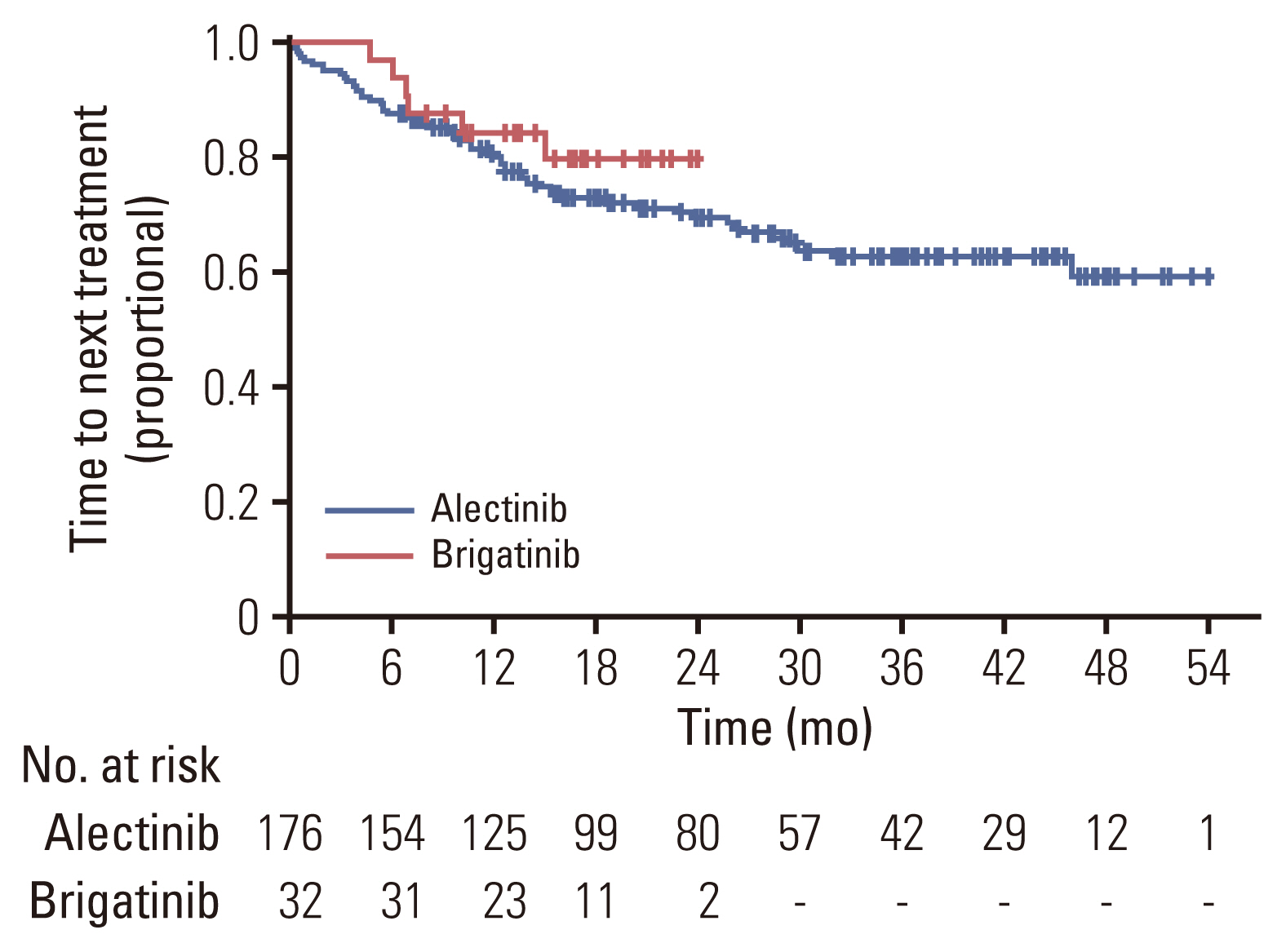
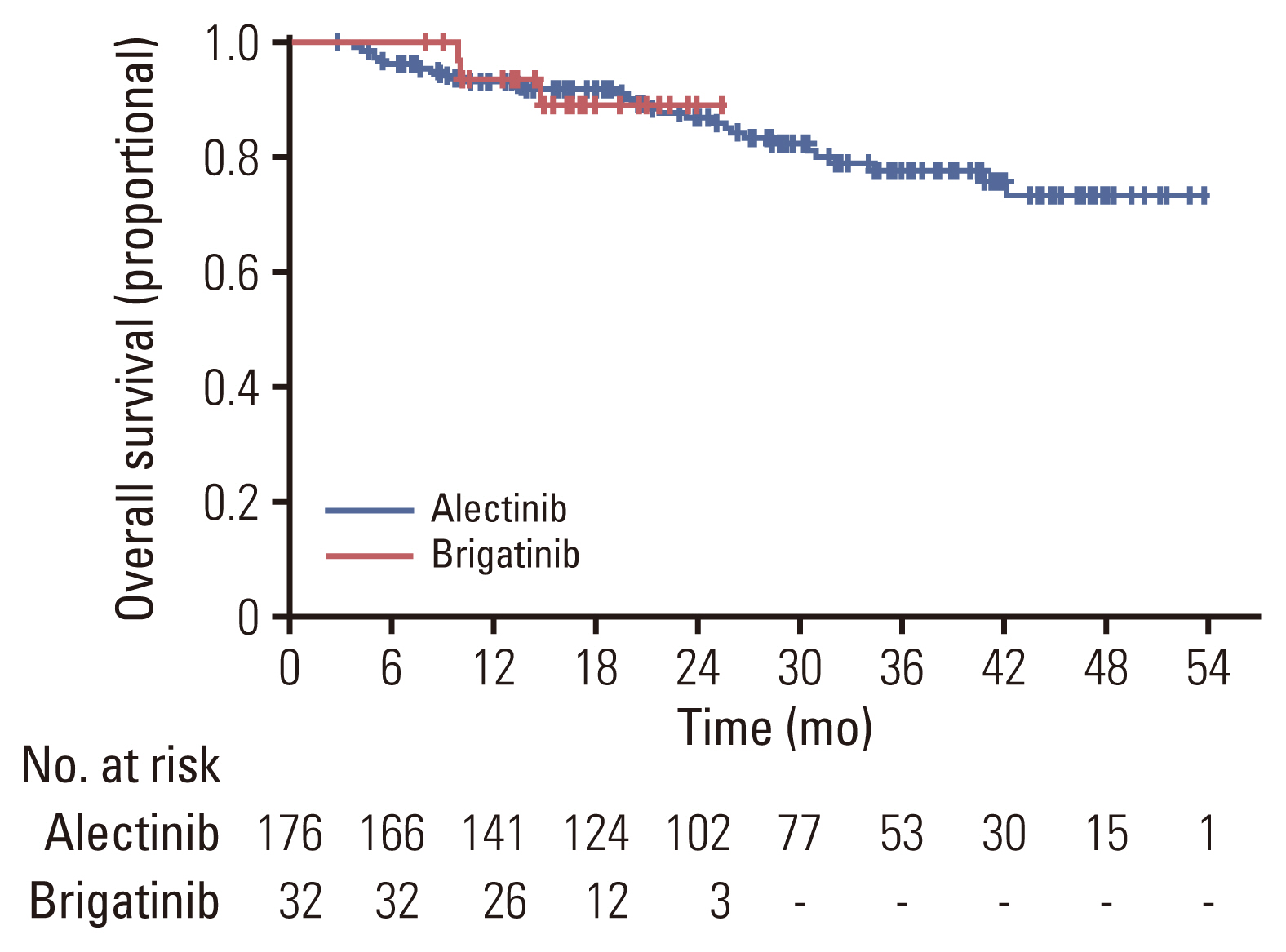
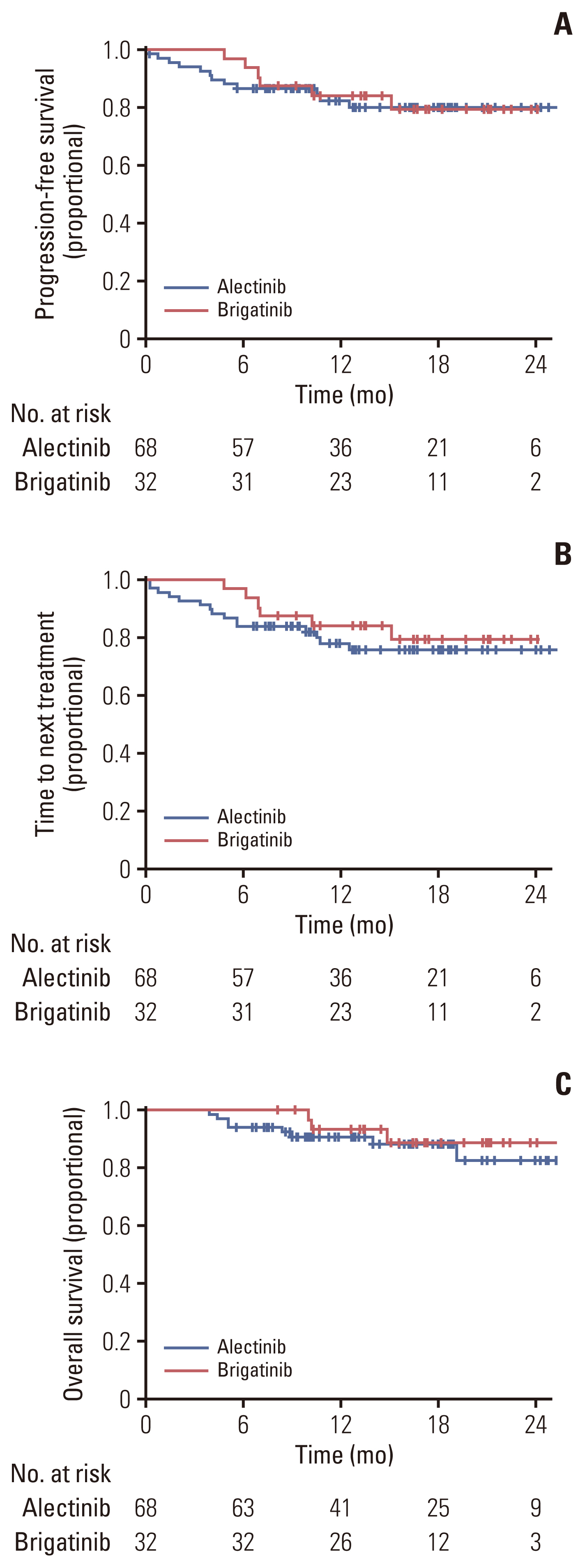
Of 208 patients who received either alectinib or brigatinib as a first-line treatment, 176 received alectinib and 32 received brigatinib. At the data cutoff point, the median follow-up duration was 16.5 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 14.7 to 18.3) in the brigatinib group and 27.5 months (95% CI, 24.6 to 30.4) in the alectinib group. The ORR was 92.5% with alectinib and 93.8% for brigatinib. The intracranial ORR rates were 92.7% (38/41) and 100% (10/10), respectively. The rate of PFS at 12 months was comparable between the alectinib group and the brigatinib groups (84.4% vs. 84.1%, p=0.64), and the median TTNT, PFS, and OS were not reached in either group. Treatment-related adverse events were usually mild, and treatment discontinuation due to adverse events was rare (alectinib 4.5% vs. brigatinib 6.25%).
Conclusion
Alectinib and brigatinib had similar clinical benefits when used as the first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with ALK rearrangement in the real world.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bridging the Gap between Trial Adverse Events and Real-World Data
Sang Hyuk Kim, Hyun Lee, Dong Won Park
Cancer Res Treat. 2024;56(3):972-973. doi: 10.4143/crt.2024.019.
Reference
-
References
1. Global cancer observatory: cancer today [Internet]. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;c2020 [cited 2023 May 1]. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home .2. Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-small cell lungcancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019; 94:1623–40.3. Kalemkerian GP, Narula N, Kennedy EB, Biermann WA, Donington J, Leighl NB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for theselection of patients with lung cancer for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:911–9.4. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1693–703.5. Gambacorti-Passerini C, Messa C, Pogliani EM. Crizotinib inanaplastic large-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:775–6.6. Morris TA, Khoo C, Solomon BJ. Targeting ROS1 rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer: crizotinib and newer generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Drugs. 2019; 79:1277–86.7. Rotow J, Bivona TG. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017; 17:637–58.8. Griesinger F, Roeper J, Pottgen C, Willborn KC, Eberhardt WEE. Brain metastases in ALK-positive NSCLC: time to adjust current treatment algorithms. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:35181–94.9. Johung KL, Yeh N, Desai NB, Williams TM, Lautenschlaeger T, Arvold ND, et al. Extended survival and prognostic factors for patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:123–9.10. Gainor JF, Ou SH, Logan J, Borges LF, Shaw AT. The central nervous system as a sanctuary site in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:1570–3.11. Sullivan I, Planchard D. ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: the latest evidence and developments. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2016; 8:32–47.12. Zhang S, Anjum R, Squillace R, Nadworny S, Zhou T, Keats J, et al. The potent ALK inhibitor brigatinib (AP26113) overcomes mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:5527–38.13. Seto T, Kiura K, Nishio M, Nakagawa K, Maemondo M, Inoue A, et al. CH5424802 (RO5424802) for patients with ALK-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-001JP study): a single-arm, open-label, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:590–8.14. Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Gadgeel S, Ahn JS, Kim DW, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:829–38.15. Camidge DR, Dziadziuszko R, Peters S, Mok T, Noe J, Nowicka M, et al. Updated efficacy and safety data and impact of the EML4-ALK fusion variant on the efficacy of alectinib in untreated ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the global phase III ALEX study. J Thorac Oncol. 2019; 14:1233–43.16. Camidge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, Yang JC, Han JY, Lee JS, et al. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2027–39.17. Camidge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, Yang JC, Han JY, Hochmair MJ, et al. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK inhibitor-naive advanced ALK-positive NSCLC: final results of phase 3 ALTA-1L trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2021; 16:2091–108.18. Carcereny E, Fernandez-Nistal A, Lopez A, Montoto C, Naves A, Segu-Verges C, et al. Head to head evaluation of second generation ALK inhibitors brigatinib and alectinib as first-line treatment for ALK+ NSCLC using an in silico systems biology-based approach. Oncotarget. 2021; 12:316–32.19. Ando K, Akimoto K, Sato H, Manabe R, Kishino Y, Homma T, et al. Brigatinib and alectinib for ALK rearrangement-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer with or without central nervous system metastasis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12:942.20. Reckamp KL, Lin HM, Cranmer H, Wu Y, Zhang P, Walton LJ, et al. Indirect comparisons of brigatinib and alectinib for front-line ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2022; 18:2499–510.21. Yu Y, Zhu F, Zhang W, Lu S. Comparison of efficacy and safety of brigatinib in first-line treatments for patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and indirect treatment comparison. J Clin Med. 2022; 11:2963.22. Nishio M, Nakagawa K, Mitsudomi T, Yamamoto N, Tanaka T, Kuriki H, et al. Analysis of central nervous system efficacy in the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2018; 121:37–40.23. Popat S, Liu G, Lu S, Song G, Ma X, Yang JC. Brigatinib vs. alectinib in crizotinib-resistant advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ALTA-3). Future Oncol. 2021; 17:4237–47.24. Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, Kim YH, Azuma K, Seto T, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017; 390:29–39.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral Ovarian Metastases from ALK Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Simultaneously Diagnosed Lung Adenocarcinoma and Endobronchial Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor with Two Distinct Types of ALK Translocation
- Uterine Cervix Metastasis in Lung Adenocarcinoma with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement
- Alectinib (CH5424802) antagonizes ABCB1- and ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo
- Guideline Recommendations for Testing of ALK Gene Rearrangement in Lung Cancer: A Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group