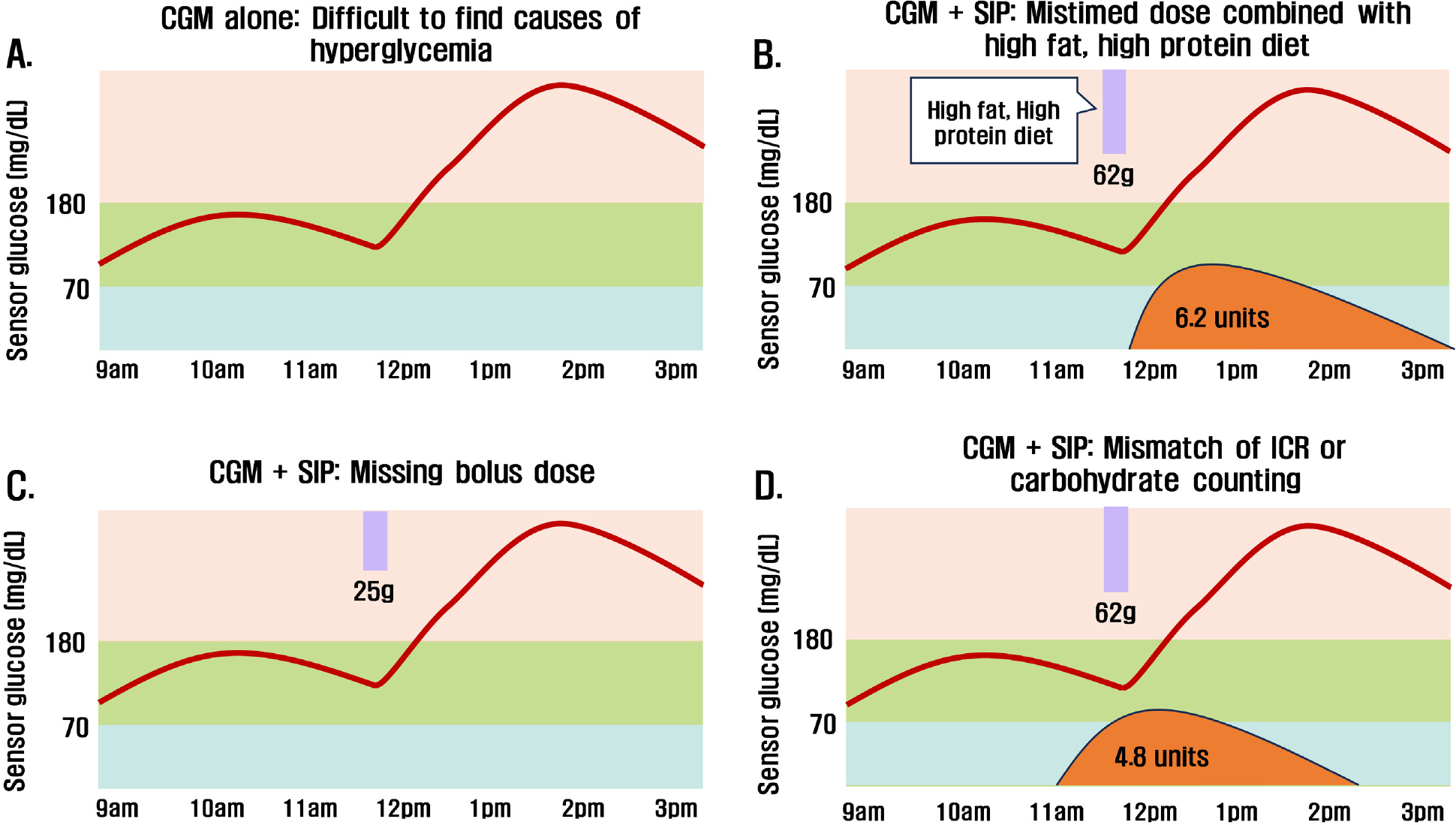
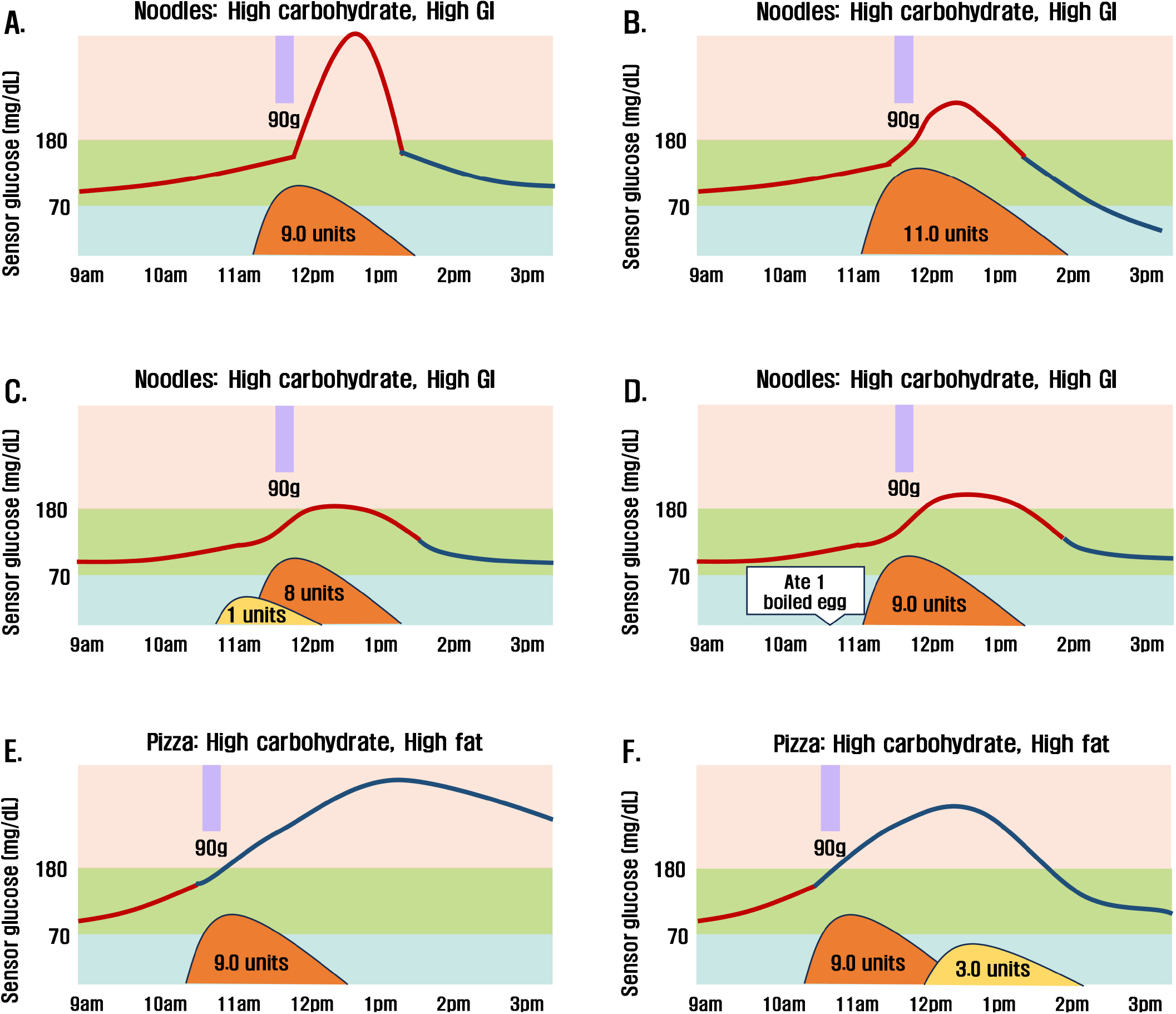
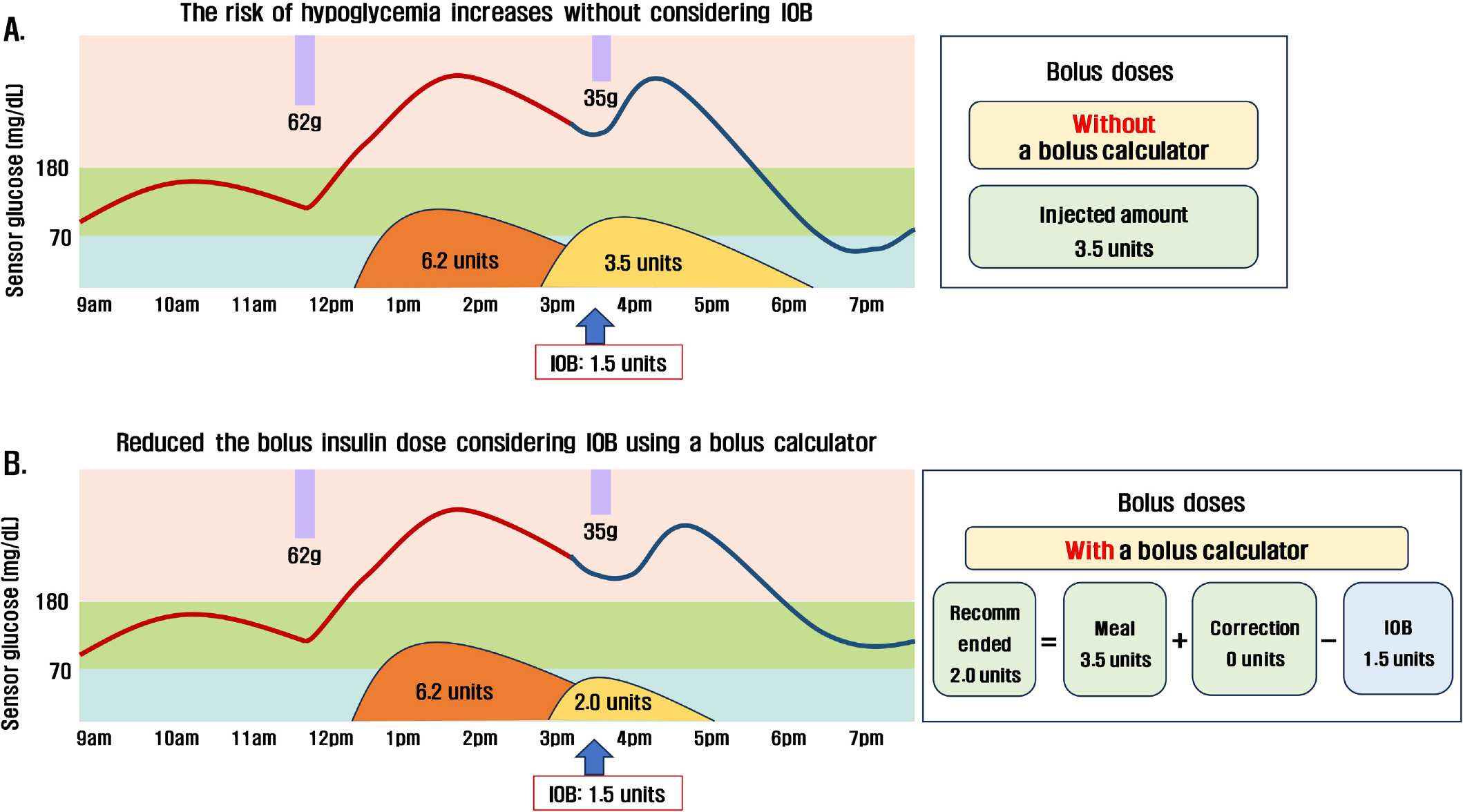
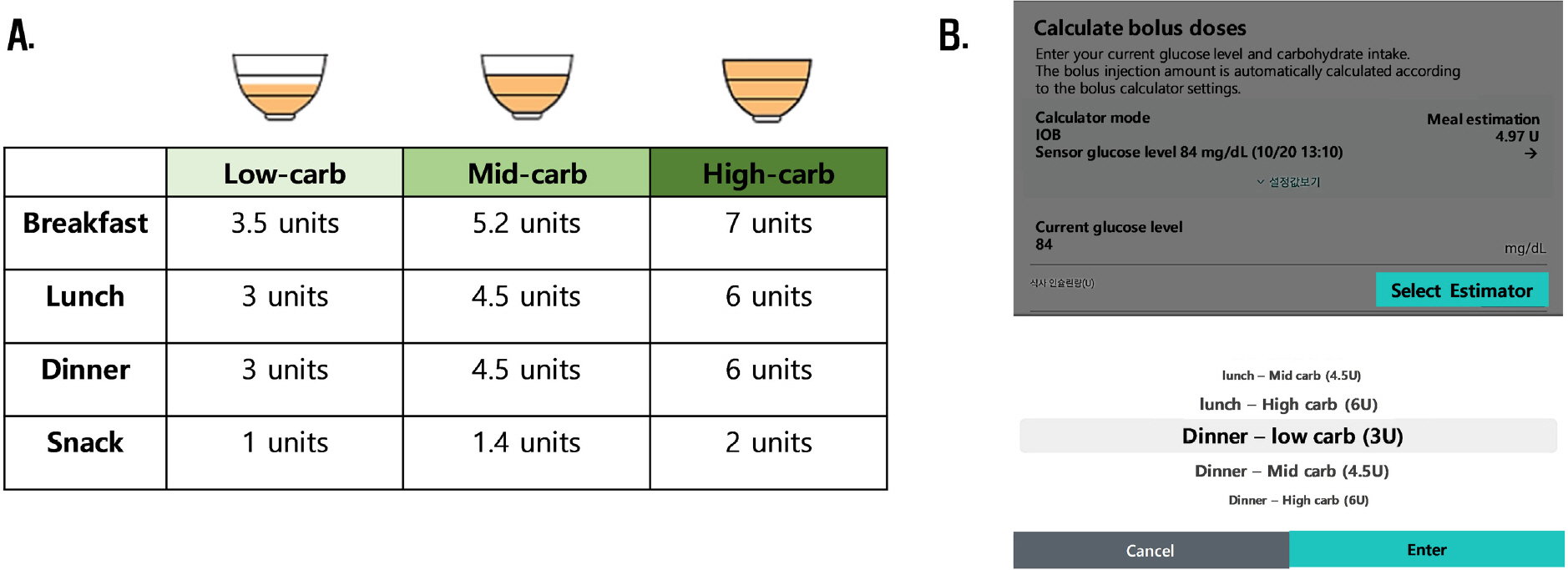
J Korean Diabetes.
2023 Dec;24(4):190-198. 10.4093/jkd.2023.24.4.190.
Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Korea
- 3Department of Clinical Research Design and Evaluation, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550158
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2023.24.4.190
Abstract
- The number of insulin users in Korea has doubled over the past 20 years. Numerous studies have shown the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) on glycemic outcomes in people with diabetes receiving insulin therapy. However, patients often failed to reach the target even with the CGM. Advanced technology, such as automated insulin delivery (AID), can potentially reduce patient burden and improve glycemic status in people on insulin therapy. However, wearing a CGM all day and complex device operation could also burden users. Additionally, since insulin users are often elderly with type 2 diabetes, there is an urgent need for new devices that are more efficient and simpler than AID. In that sense, the smart insulin pen (SIP) is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator integrated with CGM. In this context, we discuss efficient use of SIP as an educational tool.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Park J., Kim G., Kim BS., Han KD., Kwon SY., Park SH, et al. Insulin fact sheet in type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus and trends of anti-diabetic medication use in insulin users with type 2 diabetes mellitus: 2002 to 2019. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. 47:211–9.2.Lee YB., Kim M., Kim JH. Glycemia according to the use of continuous glucose monitoring among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Korea: a real-world study. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. 47:405–14.3.Gerhardsson P., Schwandt A., Witsch M., Kordonouri O., Svensson J., Forsander G, et al. The SWEET project 10-year benchmarking in 19 countries worldwide is associated with improved HbA1c and increased use of diabetes technology in youth with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021. 23:491–9.4.Miller KM., Kanapka LG., Rickels MR., Ahmann AJ., Aleppo G., Ang L, et al. Benefit of continuous glucose monitoring in reducing hypoglycemia is sustained through 12 months of use among older adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2022. 24:424–34.5.Ruedy KJ., Parkin CG., Riddlesworth TD., Graham C; DIAMOND Study Group. Continuous glucose monitoring in older adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes using multiple daily injections of insulin: results from the DIAMOND trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. 11:1138–46.6.Yoo JH., Kim JH. Time in range from continuous glucose monitoring: a novel metric for glycemic control. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. 44:828–39.7.Beck RW., Riddlesworth T., Ruedy K., Ahmann A., Bergenstal R., Haller S, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017. 317:371–8.8.Martens T., Beck RW., Bailey R., Ruedy KJ., Calhoun P., Peters AL, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021. 325:2262–72.9.Heinemann L., Freckmann G., Ehrmann D., Faber-Heine-mann G., Guerra S., Waldenmaier D, et al. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections (HypoDE): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018. 391:1367–77.10.Beck RW., Riddlesworth TD., Ruedy K., Ahmann A., Haller S., Kruger D, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2017. 167:365–74.11.Yoo JH., Kim G., Lee HJ., Sim KH., Jin SM., Kim JH. Effect of structured individualized education on continuous glucose monitoring use in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022. 184:109209.12.Petrovski G., Al Khalaf F., Campbell J., Day E., Almajaly D., Hussain K, et al. Glycemic outcomes of Advanced Hybrid Closed Loop system in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes, previously treated with Multiple Daily Injections (MiniMed 780G system in T1D individuals, previously treated with MDI). BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. 22:80.13.Davis GM., Peters AL., Bode BW., Carlson AL., Dumais B., Vienneau TE, et al. Safety and efficacy of the Omnipod 5 automated insulin delivery system in adults with type 2 diabetes: from injections to hybrid closed-loop therapy. Diabetes Care. 2023. 46:742–50.14.Yoo JH., Kim JH. Advances in continuous glucose monitoring and integrated devices for management of diabetes with insulin-based therapy: improvement in glycemic control. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. 47:27–41.15.Jin SM., Kim JH. Management of adults with type 1 diabetes: current status and suggestions. J Korean Diabetes. 2014. 15:1–6.16.MacLeod J., Vigersky RA. A review of precision insulin management with smart insulin pens: opening up the dig-ital door to people on insulin injection therapy. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023. 17:283–9.17.Donnelly LA., Morris AD., Evans JM; DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. Adherence to insulin and its association with glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. QJM. 2007. 100:345–50.18.Galindo RJ., Ramos C., Cardona S., Vellanki P., Davis GM., Oladejo O, et al. Efficacy of a smart insulin pen cap for the management of patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes: a randomized cross-over trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023. 17:201–7.19.Adolfsson P., Hartvig NV., Kaas A., Møller JB., Hellman J. Increased time in range and fewer missed bolus injections after introduction of a smart connected insulin pen. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020. 22:709–18.20.ElSayed NA., Aleppo G., Aroda VR., Bannuru RR., Brown FM., Bruemmer D, et al. 7. Diabetes technology: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023. 46(Suppl 1):S111–27.21.Ben-Yacov O., Godneva A., Rein M., Shilo S., Kolobkov D., Koren N, et al. Personalized postprandial glucose response-targeting diet versus Mediterranean diet for glycemic control in pre-diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021. 44:1980–91.22.Rein M., Ben-Yacov O., Godneva A., Shilo S., Zmora N., Kolobkov D, et al. Effects of personalized diets by prediction of glycemic responses on glycemic control and metabolic health in newly diagnosed T2DM: a randomized dietary intervention pilot trial. BMC Med. 2022. 20:56.23.Munshi MN. Cognitive dysfunction in older adults with diabetes: what a clinician needs to know. Diabetes Care. 2017. 40:461–7.24.Ekberg NR., Hartvig NV., Kaas A., Møller JB., Adolfsson P. Smart pen exposes missed basal insulin injections and reveals the impact on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022. doi: 10.1177/19322968221104142 [Epub ahead of print].
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
- Using Motivational Interviewing to Overcome Psychological Insulin Resistance
- Is the Indicator Magnifying Window for Insulin Pens Helpful for Elderly Diabetic Patients?
- Insulin Therapy in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity in Women with a Previous Gestational Diabetes: Understanding of Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes