Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Dec;82(6):269-281. 10.4166/kjg.2023.139.
Infectious Gastric Diseases Other than Helicobacter
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2549794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.139
Abstract
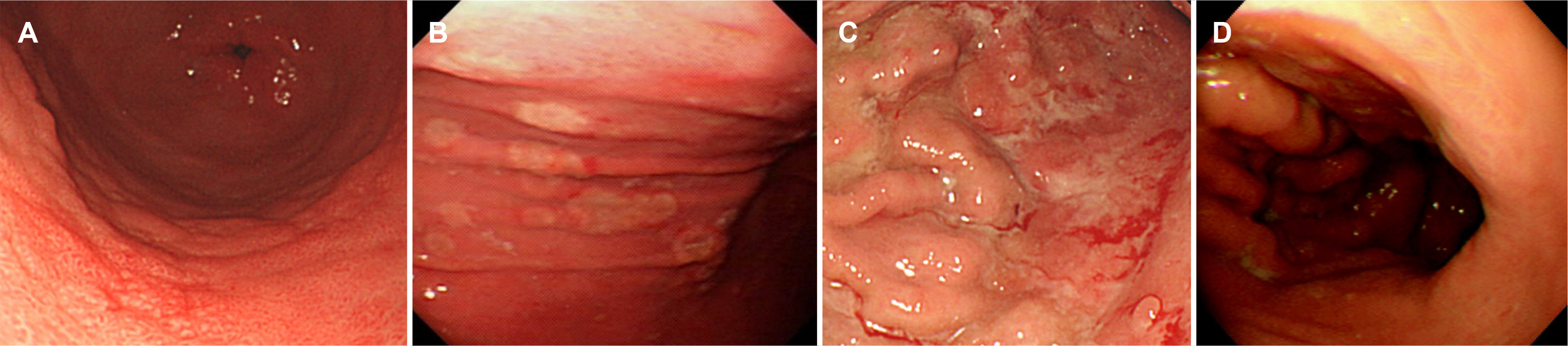
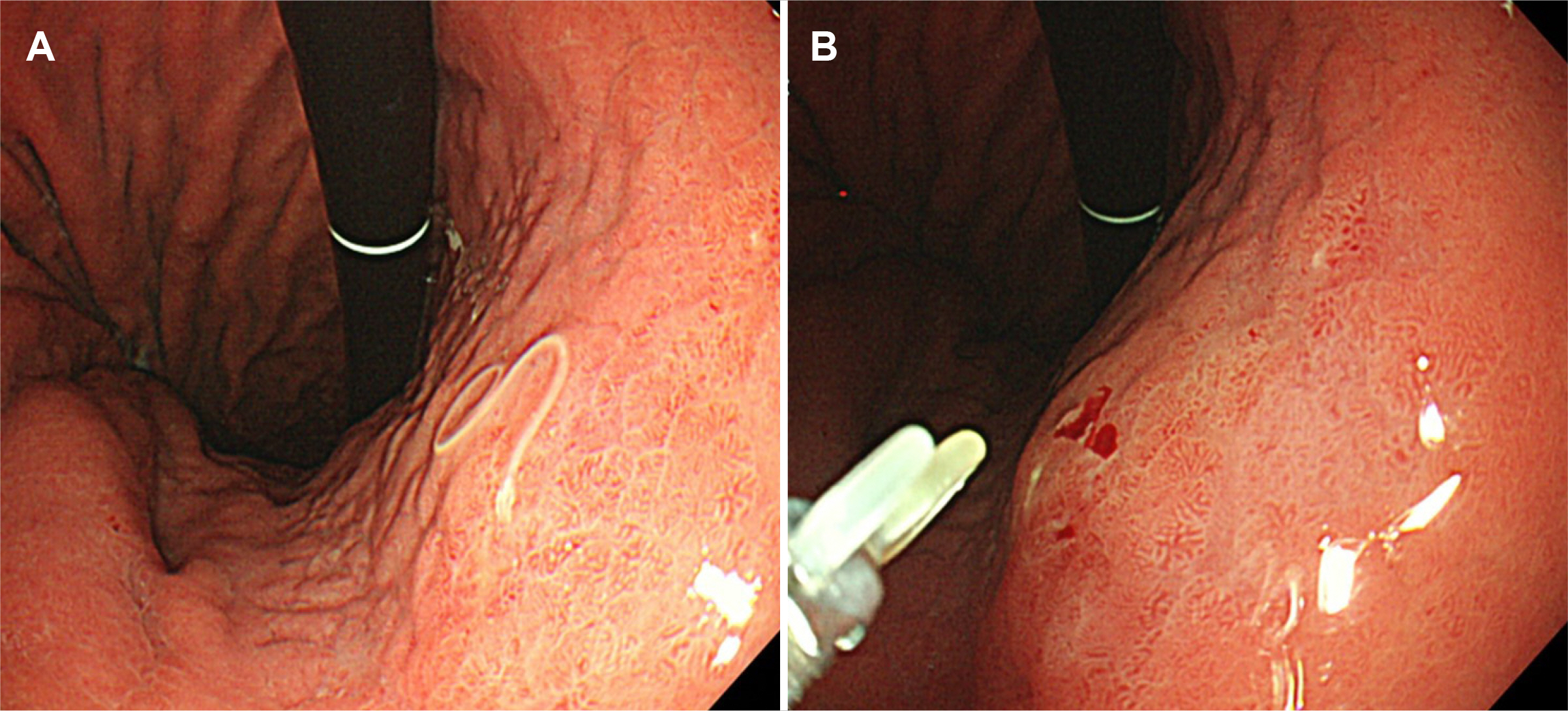
- In addition to Helicobacter pylori, the acute bacterial causes of infectious gastritis, include phlegmonous gastritis, gastric tuberculosis, and gastric syphilis. Bacterial gastritis often improves with appropriate broad-spectrum antibiotics, emphasizing the need for prompt diagnosis and treatment based on the clinical and endoscopic findings. Among viral gastritis, cytomegalovirus gastritis, primarily occurring in immunocompromised patients, necessitates antiviral intervention, while immunocompetent individuals typically achieve amelioration by administering proton pump inhibitors. In contrast, most gastric infections caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are asymptomatic, but an EBV infection is a cause of stomach cancer. EBV-associated gastric cancer exhibits distinct clinical, pathological, genetic, and post-genetic mutation features, making it clinically significant. The colonization of Candida albicans in the stomach is uncommon, and typical antifungal treatment is unnecessary. Candida infections in gastric ulcers can be treated with anti-ulcer treatment alone. Lastly, anisakidosis in the stomach, which occurs when consuming raw seafood, can manifest in various clinical presentations and is typically treated through endoscopic removal of the nematode. This article aims to contribute to the rapid diagnosis and treatment of rare stomach infections beyond Helicobacter pylori in real clinical situations.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SM, Cheung DY. 2019; Infectious diseases of the stomach in immune-compromised patients. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 19:38–41. DOI: 10.7704/kjhugr.2019.19.1.38.2. Nakamura K, Sakuragi N, Takakuwa A, Ayabe T. 2016; Paneth cell α-defensins and enteric microbiota in health and disease. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 35:57–67. DOI: 10.12938/bmfh.2015-019. PMID: 27200259. PMCID: PMC4858879.3. Joo M. 2017; Rare gastric lesions associated with Helicobacter pylori infection: A histopathological review. J Pathol Transl Med. 51:341–351. DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2017.04.03. PMID: 28592787. PMCID: PMC5525039.4. Kim NY, Park JS, Lee KJ, Yun HK, Kim JS. 2011; [A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis causing gastroparesis and cured with medical treatment alone]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 57:309–314. Korean. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.5.309. PMID: 21623140.5. Miller AI, Smith B, Rogers AI. 1975; Phlegmonous gastritis. Gastroenterology. 68:231–238. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(75)80003-5. PMID: 1116671. PMCID: PMC9908034.6. Lee TH, Lee GS, Im EH, et al. 2005; A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis treated with antibiotics alone. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 31:44–48.7. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. 2005; Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 61:168–174. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(04)02217-5. PMID: 15672083.8. Wakayama T, Watanabe H, Ishizaki Y, et al. 1994; A case of phlegmonous esophagitis associated with diffuse phlegmonous gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 89:804–806. PMID: 8172161.9. Joko T, Tanaka H, Hirakata H, et al. 1999; Phlegmonous gastritis in a haemodialysis patient with secondary amyloidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 14:196–198. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/14.1.196. PMID: 10052508.10. Lee BS, Kim SM, Seong JK, et al. 2005; Phlegmonous gastritis after endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 37:490–493. DOI: 10.1055/s-2005-861254. PMID: 15844031.11. Ajibe H, Osawa H, Yoshizawa M, et al. 2008; Phlegmonous gastritis after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 1:91–95. DOI: 10.1177/1756283X08095746. PMID: 21180517. PMCID: PMC3002497.12. Bron BA, Deyhle P, Pelloni S, Krejs GJ, Siebenmann RE, Blum AL. 1977; Phlegmonous gastritis diagnosed by endoscopic snare biopsy. Am J Dig Dis. 22:729–733. DOI: 10.1007/BF01078356. PMID: 879141.13. Itonaga M, Ueda K, Ichinose M. 2012; Phlegmonous gastritis caused by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). Dig Endosc. 24:488. DOI: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01362.x. PMID: 23078457.14. Lee GW, Lee OJ, Jung KW, et al. 2001; Acute phlegmonous gastritis diagnosed early endoscopically and treated successfully with antibiotics. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 23:225–229.15. Kim HS, Jang WI, Lee SS, et al. 1991; Two cases of phlegmonous gastritis secondary to corrosive gastritis caused by formalin. Korean J Intern Med. 40:268–273.16. Waseem S, Moshiree B, Draganov PV. 2009; Gastroparesis: current diagnostic challenges and management considerations. World J Gastroenterol. 15:25–37. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.25. PMID: 19115465. PMCID: PMC2653292.17. Choong NW, Levy MJ, Rajan E, Kolars JC. 2003; Intramural gastric abscess: case history and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 58:627–629. DOI: 10.1067/S0016-5107(03)01967-9. PMID: 14560756.18. Iwakiri Y, Kabemura T, Yasuda D, et al. 1999; A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis successfully treated with antibiotics. J Clin Gastroenterol. 28:175–177. DOI: 10.1097/00004836-199903000-00020. PMID: 10078831.19. Kan-no Y, Irisawa A, Takagi T, et al. 2007; Endosonographic diagnosis and follow-up of phlegmonous gastritis. J Clin Ultrasound. 35:524–526. DOI: 10.1002/jcu.20333. PMID: 17373684.20. López Caleya JF, Martín Rodrigo L, Mohammed Mourad F, de la Iglesia Fanjul I, Martín Sánchez V. 2007; [Gastric tuberculosis. Review apropos of a case]. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 30:334–337. Spanish. DOI: 10.1157/13107571. PMID: 17662216.21. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease E-book: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. Elsevier health sciences;2015.22. Chaudhary P, Khan AQ, Lal R, Bhadana U. 2019; Gastric tuberculosis. Indian J Tuberc. 66:411–417. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2018.10.004. PMID: 31439189.23. Nayyar E, Torres JA, Malvestutto CD. 2016; Tuberculous gastric abscess in a patient with AIDS: A rare presentation. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2016:5675036. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5675036. PMID: 27239353. PMCID: PMC4867059.24. Chung JS, Cho YB, Heo WG, Jo DH, Jeong YH, Seo GS. 2015; [Asymptomatic synchronous tuberculosis involving stomach and small bowel in immunocompetent patient]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 66:345–349. Korean. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.6.345. PMID: 26691192.25. Bandyopadhyay SK, Bandyopadhyay R, Chatterjee U. 2002; Isolated gastric tuberculosis presenting as haematemesis. J Postgrad Med. 48:72–73. PMID: 12082338.26. Wig JD, Vaiphei K, Tashi M, Kochhar R. 2000; Isolated gastric tuberculosis presenting as massive hematemesis: report of a case. Surg Today. 30:921–922. DOI: 10.1007/s005950070046. PMID: 11059734.27. Perez-Piqueras J, Coca S, Silva C, Martinez D, Peralba J, Moreno M. 1993; Isolated gastric tuberculosis: a case report. Endoscopy. 25:376. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1010341. PMID: 8348896.28. Misra RC, Agarwal SK, Prakash P, Saha MM, Gupta PS. 1982; Gastric tuberculosis. Endoscopy. 14:235–237. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1021629. PMID: 7140659. PMCID: PMC10378724.29. Talukdar R, Khanna S, Saikia N, Vij JC. 2006; Gastric tuberculosis presenting as linitis plastica: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:299–303. DOI: 10.1097/00042737-200603000-00013. PMID: 16462546.30. Ecka RS, Wani ZA, Sharma M. 2013; Gastric tuberculosis with outlet obstruction: a case report presenting with a mass lesion. Case Rep Med. 2013:169051. DOI: 10.1155/2013/169051. PMID: 24082885. PMCID: PMC3776544.31. Flores HB, Zano F, Ang EL, Estanislao N. 2011; Duodenal tuberculosis presenting as gastric outlet obstruction: A case report. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 3:16–19. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v3.i1.16. PMID: 21258602. PMCID: PMC3024477.32. Rao YG, Pande GK, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK. 2004; Gastroduodenal tuberculosis management guidelines, based on a large experience and a review of the literature. Can J Surg. 47:364–368. PMID: 15540690. PMCID: PMC3211943.33. Kshirsagar AY, Kanetkar SR, Langade YB, Potwar SS, Shekhar N. 2008; Duodenal stenosis secondary to tuberculosis. Int Surg. 93:265–267. PMID: 19943427.34. Kalpande S, Pandya JS, Tiwari A, Adhikari D. 2017; Gastric outlet obstruction: an unusual case of primary duodenal tuberculosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2017:bcr2016217966. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-217966. PMID: 28343151. PMCID: PMC5372190.35. Padmanabhan H, Rothnie A, Singh P. 2013; An unusual case of gastric outlet obstruction caused by tuberculosis: challenges in diagnosis and treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2013:bcr2012008277. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008277. PMID: 23704423. PMCID: PMC3669768.36. Kim TU, Kim SJ, Ryu H, et al. 2018; Gastric tuberculosis presenting as a subepithelial mass: A rare cause of gastrointestinal bleeding. Korean J Gastroenterol. 72:304–307. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.6.304. PMID: 30642149.37. Choi HY, Lee JW, Lee JS, et al. 2004; A case of tuberculosis affecting stomach and duodenum simultaneously, mimicking malignant tumor. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 29:142–146.38. Elterefi AE, Uwaydah AK, Helal GR, Hassan NMM. 2022; Gastric tuberculosis presenting as a large gastric ulcer. BMJ Case Rep. 15:e248215. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-248215. PMID: 35589270. PMCID: PMC9121417.39. Chaudhary A, Bhan A, Malik N, Dilawari JB, Khanna SK. 1989; Choledocho-duodenal fistula due to tuberculosis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 8:293–294. PMID: 2599567.40. Kim SE, Shim KN, Yoon SJ, et al. 2006; A case of gastric tuberculosis mimicking advanced gastric cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 21:62–67. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2006.21.1.62. PMID: 16646568. PMCID: PMC3891067.41. Puri AS, Sachdeva S, Mittal VV, et al. 2012; Endoscopic diagnosis, management and outcome of gastroduodenal tuberculosis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 31:125–129. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-012-0203-3. PMID: 22711366.42. Roh M, Min YW. 2019; Infectious diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 19:16–22. DOI: 10.7704/kjhugr.2019.19.1.16. PMID: 33382485.43. Crowley JS, Geller AB, Vermund SH, editors. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 2021. Sexually transmitted infections: Adopting a sexual health paradigm. National Academies Press (US);Washington (DC):44. St Cyr S, Barbee L, Workowski KA, et al. 2020; Update to CDC's treatment guidelines for gonococcal infection, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 69:1911–1916. DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6950a6. PMID: 33332296. PMCID: PMC7745960.45. Mylona EE, Baraboutis IG, Papastamopoulos V, et al. 2010; Gastric syphilis: a systematic review of published cases of the last 50 years. Sex Transm Dis. 37:177–183. DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181c0d51f. PMID: 20023597.46. Roh M, Sohn JH, Kim TY, et al. 2015; Gastric syphilis and membranous glomerulonephritis. Clin Endosc. 48:256–259. DOI: 10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.256. PMID: 26064828. PMCID: PMC4461672.47. Shen Y, Nie L, Zhang M, et al. Gastric syphilis mimicking lymphoma. Endoscopy. 2015; 47 Suppl 1 UCTN:E170–171. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1391779. PMID: 25926186. PMCID: PMC10349567.48. Lacerda PN, Campos LM, de Ré MR, Miot HA. 2021; Cutaneous hyperpigmentation and megaloblastic anemia as manifestations of gastric syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 60:e356–e358. DOI: 10.1111/ijd.15535. PMID: 33719066.49. Sinagra E, Macaione I, Stella M, et al. 2023; Gastric syphilis presenting as a nodal inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking a neoplasm: Don't forget the treponema! Case report and scoping review of the literature of the last 65 years. Gastroenterology Insights. 14:178–190. DOI: 10.3390/gastroent14020014.50. Yu HJ, Kim SJ, Oh HH, et al. 2021; Case report of gastric syphilis in Korea: Clinical features, pathology, management, and prognosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e28212. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028212. PMID: 34918682. PMCID: PMC8678019.51. Massironi S, Carmagnola S, Penagini R, Conte D. 2005; Gastric involvement in a patient with secondary syphilis. Dig Liver Dis. 37:368–371. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2004.05.017. PMID: 15843088.52. Facchetti F, Incardona P, Lonardi S, et al. 2009; Nodal inflammatory pseudotumor caused by luetic infection. Am J Surg Pathol. 33:447–453. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318187bfc6. PMID: 19033867.53. Norris SJ, Sell S. 1996; Role of polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of gastric syphilis. Hum Pathol. 27:749–750. DOI: 10.1016/S0046-8177(96)90443-8. PMID: 8760004.54. Chen CY, Chi KH, George RW, et al. 2006; Diagnosis of gastric syphilis by direct immunofluorescence staining and real-time PCR testing. J Clin Microbiol. 44:3452–3456. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00721-06. PMID: 16954299. PMCID: PMC1594693.55. Janssen J. 2009; The impact of EUS in primary gastric lymphoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 23:671–678. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2009.05.008. PMID: 19744632.56. Phelps RG, Knispel J, Tu ES, Cernainu G, Saruk M. 2000; Immunoperoxidase technique for detecting spirochetes in tissue sections: comparison with other methods. Int J Dermatol. 39:609–613. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00029.x. PMID: 10971730.57. Martín-Ezquerra G, Fernandez-Casado A, Barco D, Jucglà A, et al. 2009; Treponema pallidum distribution patterns in mucocutaneous lesions of primary and secondary syphilis: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Hum Pathol. 40:624–630. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2008.10.017. PMID: 19157499.58. Müller H, Eisendle K, Bräuninger W, Kutzner H, Cerroni L, Zelger B. 2011; Comparative analysis of immunohistochemistry, polymerase chain reaction and focus-floating microscopy for the detection of Treponema pallidum in mucocutaneous lesions of primary, secondary and tertiary syphilis. Br J Dermatol. 165:50–60. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10314.x. PMID: 21410678.59. Guerrero AF, Straight TM, Eastone J, Spooner K. 2005; Gastric syphilis in an HIV-infected patient. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 19:281–285. DOI: 10.1089/apc.2005.19.281. PMID: 15916490.60. Park SH, Jang KT, Lee JH. 2008; [A case of gastric syphilis with duodenal involvement]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 51:327–330. Korean. PMID: 18604133.61. Greenstein DB, Wilcox CM, Schwartz DA. 1994; Gastric syphilis. Report of seven cases and review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 18:4–9. DOI: 10.1097/00004836-199401000-00003. PMID: 8113584.62. You DM, Johnson MD. 2012; Cytomegalovirus infection and the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 14:334–342. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-012-0266-4. PMID: 22588614.63. Goodgame RW. 1993; Gastrointestinal cytomegalovirus disease. Ann Intern Med. 119:924–935. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-9-199311010-00010. PMID: 8215005.64. Himoto T, Goda F, Okuyama H, et al. 2009; Cytomegalovirus-associated acute gastric mucosal lesion in an immunocompetent host. Intern Med. 48:1521–1524. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.48.2308. PMID: 19721296.65. Kakugawa Y, Kami M, Matsuda T, et al. 2010; Endoscopic diagnosis of cytomegalovirus gastritis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 16:2907–2912. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2907. PMID: 20556837. PMCID: PMC2887587.66. Gianella S, Letendre S. Cytomegalovirus and HIV: A Dangerous Pas de Deux. J Infect Dis. 2016; 214(Suppl 2):S67–74. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw217. PMID: 27625433. PMCID: PMC5021239.67. Maertens J, Lyon S. 2017; Current and future options for cytomegalovirus reactivation in hematopoietic cell transplantation patients. Future Microbiol. 12:839–842. DOI: 10.2217/fmb-2017-0095. PMID: 28745073.68. Goerig N, Semrau S, Frey B, et al. 2016; Clinically significant CMV (re)activation during or after radiotherapy/chemotherapy of the brain: Correlation with neurological deterioration and improvement upon antiviral treatment. Strahlenther Onkol. 192:489–497. DOI: 10.1007/s00066-016-0987-7. PMID: 27245820.69. Chetty R, Roskell DE. 1994; Cytomegalovirus infection in the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Pathol. 47:968–972. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.47.11.968. PMID: 7829690. PMCID: PMC503052.70. Vachon GC, Brown BS, Kim C, Chessin LN. 1995; CMV gastric ulcer as the presenting manifestation of AIDS. Am J Gastroenterol. 90:319–321. PMID: 7847313.71. Boteon YL, Alves IP, da Silva AP, et al. 2015; Obstructive gastric pseudotumor caused by cytomegalovirus in an AIDS patient: A case report and review of surgical treatment. Am J Case Rep. 16:536–541. DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.894070. PMID: 26277259. PMCID: PMC4542526.72. Ebisutani C, Kawamura A, Shibata N, et al. 2012; Gastric ulcer associated with cytomegalovirus in an immunocompetent patient: method for diagnosis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 6:365–368. DOI: 10.1159/000339714. PMID: 22740812. PMCID: PMC3383304.73. Shin JY, Ko EJ, Bang BW, et al. 2015; A case of cytomegalovirus-associated giant gastric ulcer in a patient who healed by discontinuing immunosuppressive therapy. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 15:44–48. DOI: 10.7704/kjhugr.2015.15.1.44.74. Tapan U, Kutlugun AA, Arici M, Altun B. 2012; Postural epigastric pain: a challenging symptom for cytomegalovirus (CMV) gastritis. Ren Fail. 34:235–236. DOI: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.646883. PMID: 22251042.75. Lee J, Choi SC, Choi CS, Kim TH. 2008; Spontaneous resolving of cytomegalovirus associated gastritis after conservative treatment in immunocompetent patients: A report of two cases. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 37:344–348.76. Kwon MH, Lee CS, Cho SW, Joung CI. 2013; Multiple gastric ulcers as a manifestation of cytomegalovirus infection in a patient with adult-onset Still's disease. J Rheum Dis. 20:172–176. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.3.172.77. Lee HD, Kim NH, Lee KJ, et al. 2011; CMV gastric ulcers healed by supportive therapy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 43:21–24.78. Park SY, Lee EJ, Lee TH, et al. 2011; Cytomegalovirus infectious mononucleosis in a patient with a gastric ulcer. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 42:392–396.79. Kim KH, Park BB, Baek HJ, et al. 2004; Cytomegalovirus-associated gastritis in immunocompetent adult. Korean J Med. 66:326–331.80. Phyun LH, Ko KH, Kim E, Kwak SY. 2004; A case of cytomegalovirus gastric ulcer mimicking gastric cancer in an immunocompetent host. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 28:92–96.81. Rafailidis PI, Mourtzoukou EG, Varbobitis IC, Falagas ME. 2008; Severe cytomegalovirus infection in apparently immunocompetent patients: a systematic review. Virol J. 5:47. DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-47. PMID: 18371229. PMCID: PMC2289809.82. Song IS, Choi KW, Kim CY, et al. 1998; Efficacy of the treatment with antiviral agents in the cytomegalovirus infection of the gastrointestinal test. Korean J Gastroenterol. 32:184–195.83. Ning S. 2011; Innate immune modulation in EBV infection. Herpesviridae. 2:1. DOI: 10.1186/2042-4280-2-1. PMID: 21429244. PMCID: PMC3063194.84. Lee BE. 2021; Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 21:22–28. DOI: 10.7704/kjhugr.2020.0063. PMID: 31836926.85. Hisamatsu A, Nagai T, Okawara H, et al. 2010; Gastritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Intern Med. 49:2101–2105. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.49.3789. PMID: 20930436.86. Cristescu R, Lee J, Nebozhyn M, et al. 2015; Molecular analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes. Nat Med. 21:449–456. DOI: 10.1038/nm.3850. PMID: 25894828.87. Naseem M, Barzi A, Brezden-Masley C, et al. 2018; Outlooks on Epstein-Barr virus associated gastric cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 66:15–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.03.006. PMID: 29631196. PMCID: PMC5964025.88. Kim YS, Nam SC, Han MH, et al. 2008; Predictive factors of Epstein-Barr virus association in gastric adenocarcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 42:193–197.89. Camargo MC, Koriyama C, Matsuo K, et al. 2014; Case-case comparison of smoking and alcohol risk associations with Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 134:948–953. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.28402. PMID: 23904115. PMCID: PMC3961829.90. Cárdenas-Mondragón MG, Carreón-Talavera R, Camorlinga-Ponce M, Gomez-Delgado A, Torres J, Fuentes-Pananá EM. 2013; Epstein Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori co-infection are positively associated with severe gastritis in pediatric patients. PLoS One. 8:e62850. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062850. PMID: 23638154. PMCID: PMC3634751.91. Ryan JL, Shen YJ, Morgan DR, et al. 2012; Epstein-Barr virus infection is common in inflamed gastrointestinal mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 57:1887–1898. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-012-2116-5. PMID: 22410851. PMCID: PMC3535492.92. Choi MG, Jeong JY, Kim KM, et al. 2012; Clinical significance of gastritis cystica profunda and its association with Epstein-Barr virus in gastric cancer. Cancer. 118:5227–5233. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.27541. PMID: 22511405.93. Cheng N, Hui DY, Liu Y, et al. 2015; Is gastric lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma a special subtype of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma? New insight based on clinicopathological features and EBV genome polymorphisms. Gastric Cancer. 18:246–255. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-014-0376-9. PMID: 24771002.94. Tak DH, Jeong HY, Seong JK, Moon HS, Kang SH. 2013; [Comparison of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors between gastric lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma and gastric adenocarcinoma]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 62:272–277. Korean. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.5.272. PMID: 24262592.95. Chen XZ, Chen H, Castro FA, Hu JK, Brenner H. 2015; Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e792. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000792. PMID: 25997049. PMCID: PMC4602887.96. Shin DH, Kim GH, Lee BE, et al. 2017; Clinicopathologic features of early gastric carcinoma with lymphoid stroma and feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 31:4156–4164. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-017-5470-8. PMID: 28409376.97. Cheng Y, Zhou X, Xu K, Huang J, Huang Q. 2020; Very low risk of lymph node metastasis in Epstein-Barr virus-associated early gastric carcinoma with lymphoid stroma. BMC Gastroenterol. 20:273. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01422-9. PMID: 32807085. PMCID: PMC7433105.98. Lim H, Lee IS, Lee JH, et al. 2017; Clinical application of early gastric carcinoma with lymphoid stroma based on lymph node metastasis status. Gastric Cancer. 20:793–801. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-017-0703-z. PMID: 28205059.99. Watanabe H, Enjoji M, Imai T. 1976; Gastric carcinoma with lymphoid stroma. Its morphologic characteristics and prognostic correlations. Cancer. 38:232–243. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(197607)38:1<232::AID-CNCR2820380135>3.0.CO;2-4. PMID: 947518.100. Jo YH, Choi HS, Lee SH, et al. 1998; A case of esophageal and gastroduodenal candidiasis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 18:884–888.101. Trier JS, Bjorkman DJ. 1984; Esophageal, gastric, and intestinal candidiasis. Am J Med. 77:39–43. PMID: 6548606.102. Sari R, Altunbas H, Mahsereci E, Meric M, Gelen T, Karayalcin U. 2003; Multiple gastric ulcers caused by gastric candidiasis in a diabetic patient: a rare cause of upper GI bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 58:309–311. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2003.330. PMID: 12872114.103. Park KB, Chang YW, Kim HJ, et al. 2000; A case of gastric candidiasis presented with massive gastric bleeding. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 20:41–45.104. Nagata N, Nakashima R, Nishimuira S. 2012; Candida associated gastric ulcers in an elderly patient. Intern Med. 51:1433. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.7551. PMID: 22687857.105. Minoli G, Terruzzi V, Butti G, Frigerio G, Rossini A. 1982; Gastric candidiasis: an endoscopic and histological study in 26 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 28:59–61. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(82)72998-0. PMID: 7084642.106. Antonioli A. 1984; Fungal infection of benign gastric ulcer: clinical and endoscopic features. Ital J Gastroenterol. 16:297–299.107. Cronan J, Burrell M, Trepeta R. 1980; Aphthoid ulcerations in gastric candidiasis. Radiology. 134:607–611. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.134.3.7355205. PMID: 7355205.108. Young JA, Elias E. 1985; Gastro-oesophageal candidiasis: diagnosis by brush cytology. J Clin Pathol. 38:293–296. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.38.3.293. PMID: 3973054. PMCID: PMC499127.109. Bougnoux ME, Hill C, Moissenet D, et al. 1990; Comparison of antibody, antigen, and metabolite assays for hospitalized patients with disseminated or peripheral candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 28:905–909. DOI: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.905-909.1990. PMID: 2351733. PMCID: PMC267834.110. Wu CS, Wu SS, Chen PC. 1995; A prospective study of fungal infection of gastric ulcers: clinical significance and correlation with medical treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 42:56–58. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(95)70244-X. PMID: 7557178.111. Neeman A, Avidor I, Kadish U. 1981; Candidal infection of benign gastric ulcers in aged patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 75:211–213. PMID: 7234843.112. Di Febo G, Miglioli M, Calò G, et al. 1985; Candida albicans infection of gastric ulcer frequency and correlation with medical treatment. Results of a multicenter study. Dig Dis Sci. 30:178–181. DOI: 10.1007/BF01308206. PMID: 2857120.113. van Thiel P, Kuipers FC, Roskam RT. 1960; A nematode parasitic to herring, causing acute abdominal syndromes in man. Trop Geogr Med. 12:97–113. PMID: 13776308.114. Bao M, Pierce GJ, Pascual S, et al. 2017; Assessing the risk of an emerging zoonosis of worldwide concern: anisakiasis. Sci Rep. 7:43699. DOI: 10.1038/srep43699. PMID: 28287609. PMCID: PMC5347442.115. Audicana MT, Kennedy MW. 2008; Anisakis simplex: from obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin Microbiol Rev. 21:360–379. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00012-07. PMID: 18400801. PMCID: PMC2292572.116. Sun T. Progress in clinical parasitology: Volume III. Springer Science & Business Media;2012.117. Hochberg NS, Hamer DH. 2010; Anisakidosis: Perils of the deep. Clin Infect Dis. 51:806–812. DOI: 10.1086/656238. PMID: 20804423.118. Chai JY, Darwin Murrell K, Lymbery AJ. 2005; Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: status and issues. Int J Parasitol. 35:1233–1254. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.07.013. PMID: 16143336.119. Audicana MT, Ansotegui IJ, de Corres LF, Kennedy MW. 2002; Anisakis simplex: dangerous--dead and alive? Trends Parasitol. 18:20–25. DOI: 10.1016/S1471-4922(01)02152-3. PMID: 11850010.120. Sohn WM, Na BK, Kim TH, Park TJ. 2015; Anisakiasis: Report of 15 gastric cases caused by anisakis type I larvae and a brief review of Korean anisakiasis cases. Korean J Parasitol. 53:465–470. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2015.53.4.465. PMID: 26323845. PMCID: PMC4566497.121. Muguruma N, Okamura S, Okahisa T, Shibata H, Ito S, Terauchi A. 1999; Anisakis larva involving the esophageal mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc. 49:653–654. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(99)70401-3. PMID: 10228271.122. Nawa Y, Hatz C, Blum J. 2005; Sushi delights and parasites: the risk of fishborne and foodborne parasitic zoonoses in Asia. Clin Infect Dis. 41:1297–1303. DOI: 10.1086/496920. PMID: 16206105.123. Ito Y, Ikematsu Y, Yuzawa H, et al. 2007; Chronic gastric anisakiasis presenting as pneumoperitoneum. Asian J Surg. 30:67–71. DOI: 10.1016/S1015-9584(09)60131-7. PMID: 17337375.124. Céspedes M, Saez A, Rodríguez I, Pinto JM, Rodríguez R. 2000; Chronic anisakiasis presenting as a mesenteric mass. Abdom Imaging. 25:548–550. DOI: 10.1007/s002610000089. PMID: 10931996.125. Namiki M, Yazaki Y. 1989. Endoscopic findings of gastric anisakiasis with acute symptoms. Gastric Anisakiasis in Japan: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment. Springer;p. 47–51. DOI: 10.1007/s002610000089.126. Strickland GT. Hunter's tropical medicine and emerging infectious diseases. WB Saunders;2000. DOI: 10.1007/s002610000089.127. Lee EJ, Kim YC, Jeong HG, Lee OJ. 2009; [The mucosal changes and influencing factors in upper gastrointestinal anisakiasis: analysis of 141 cases]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 53:90–97. Korean. PMID: 19237834.128. Shibata O, Uchida Y, Furusawa T. 1989. Acute gastric anisakiasis with special analysis of the location of the worms penetrating the gastric mucosa. Gastric anisakiasis in Japan: epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment. Springer;p. 53–57.129. Kim HU. 2019; Anisakidosis. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 19:23–37. DOI: 10.7704/kjhugr.2019.19.1.23. PMID: 23863565. PMCID: PMC3811649.130. McClelland G. The trouble with sealworms (Pseudoterranova decipiens species complex, Nematoda): a review. Parasitology. 2002; 124 Suppl:S183–203. DOI: 10.1017/S0031182002001658. PMID: 12396224.131. Sekimoto M, Nagano H, Fujiwara Y, et al. 2011; Two cases of gastric Anisakiasis for which oral administration of a medicine containing wood creosote (Seirogan) was effective. Hepatogastroenterology. 58:1252–1254. DOI: 10.5754/hge11052. PMID: 21937389.