Child Kidney Dis.
2023 Dec;27(2):117-120. 10.3339/ckd.23.017.
Renal artery stenosis presenting as congenital nephrotic syndrome with hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome in a 2-month-old infant: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 3Kidney Research Institute, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children’s Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2549743
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.23.017
Abstract
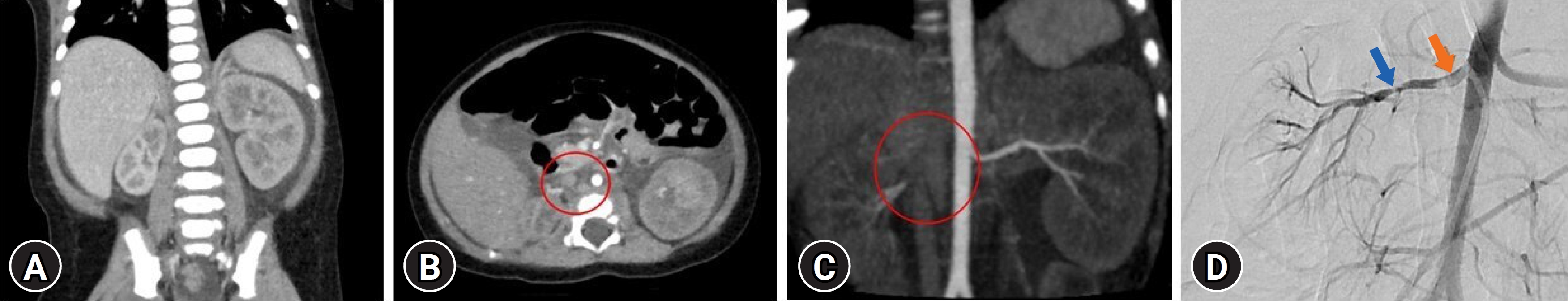
- Here, we present the case of a 2-month-old male infant with hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome resulting from stenosis of the right proximal and mid-renal arteries. The patient exhibited nephrotic-range proteinuria, low serum albumin, increased serum creatinine, and elevated renin and aldosterone levels. Doppler ultrasonography and computed tomography angiography revealed decreased vascular flow in the small right renal artery. Following a successful percutaneous balloon angioplasty, the patient experienced a decrease in blood pressure and normalization of serum electrolyte levels within a few days. However, it took 3 months for the proteinuria to resolve completely. This case is significant as it represents the first reported instance of a neonate presenting with clinical features resembling congenital nephrotic syndrome caused by renal artery stenosis that was successfully treated with percutaneous renal angioplasty.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Peco-Antic A. Pediatric hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome. Therapy. 2005; 2:301–10.
Article2. Kovalski Y, Cleper R, Krause I, Dekel B, Belenky A, Davidovits M. Hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome in pediatric patients: is it really so rare? Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27:1037–40.
Article3. Dixit MP, Hughes JD, Theodorou A, Dixit NM. Hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome (HHS) in an 18-month old-child presenting as malignant hypertension: a case report. BMC Nephrol. 2004; 5:5.
Article4. Oliveira JC, Martins MM, Martins E, Rocha G, Moura C, Pinto H, et al. Hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome secondary to renal ischemia: case report. J Pediatr Neonatal Individualized Med. 2018; 7:e070110.5. van Tellingen V, Lilien M, Bruinenberg J, de Vries WB. The hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome in a preterm infant: a case of severe hyponatremia with neurological sequels. Int J Nephrol. 2011; 2011:406515.
Article6. Boyer O, Schaefer F, Haffner D, Bockenhauer D, Holtta T, Berody S, et al. Management of congenital nephrotic syndrome: consensus recommendations of the ERKNet-ESPN Working Group. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021; 17:277–89.
Article7. Peco-Antic A, Dimitrijevic N, Jovanovic O, Marsenic O, Kostic M. Hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000; 15:286–9.
Article8. Mukherjee D, Sinha R, Akhtar MS, Saha AS. Hyponatremic hypertensive syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. World J Nephrol. 2017; 6:41–4.9. Schiefer J, Chatzikyrkou C, Mertens PR, Liakopoulos V. Remission of nephrotic syndrome after resolution of renal artery stenosis in a patient with a single functional kidney. Clin Nephrol. 2019; 91:265–7.
Article10. Bhardwaj R, Dosani I, Clark BA. Steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome and bilateral renal artery stenosis: a possible role for angiotensin-mediated podocyte injury. Case Rep Nephrol Urol. 2012; 2:59–64.
Article11. Blanc F, Bensman A, Baudon JJ. Renovascular hypertension: a rare cause of neonatal salt loss. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991; 5:304–6.
Article12. Daftary AS, Patole SK, Whitehall J. Hypertension-hyponatremia syndrome in neonates: case report and review of literature. Am J Perinatol. 1999; 16:385–9.
Article13. Seracini D, Pela I, Favilli S, Bini RM. Hyponatraemic-hypertensive syndrome in a 15-month-old child with renal artery stenosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006; 21:1027–30.
Article14. Pandey M, Sharma R, Kanwal SK, Chhapola V, Awasthy N, Mathur A, et al. Hyponatremic-hypertensive syndrome: think of unilateral renal artery stenosis. Indian J Pediatr. 2013; 80:872–4.
Article15. Veldman A, Nold MF, Michel-Behnke I. Thrombosis in the critically ill neonate: incidence, diagnosis, and management. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008; 4:1337–48.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Congenital Syphilitic Nephrotic Syndrome
- A Case of Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome due to Diffuse Mesangial Sclerosis
- A case of Renal Vein Thorombosis Associated with Nephrotic Syndrome
- A case of Congenital Syphilitic Nephrotic Syndrome
- A Case of Noonan Syndrome Presenting with Malignant Hypertension in an Adult