Ann Rehabil Med.
2023 Dec;47(6):511-518. 10.5535/arm.23082.
Prognostic Value of Electroneuronography in Severe Cases of Facial Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center and Konkuk University School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2549732
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.23082
Abstract
Objective
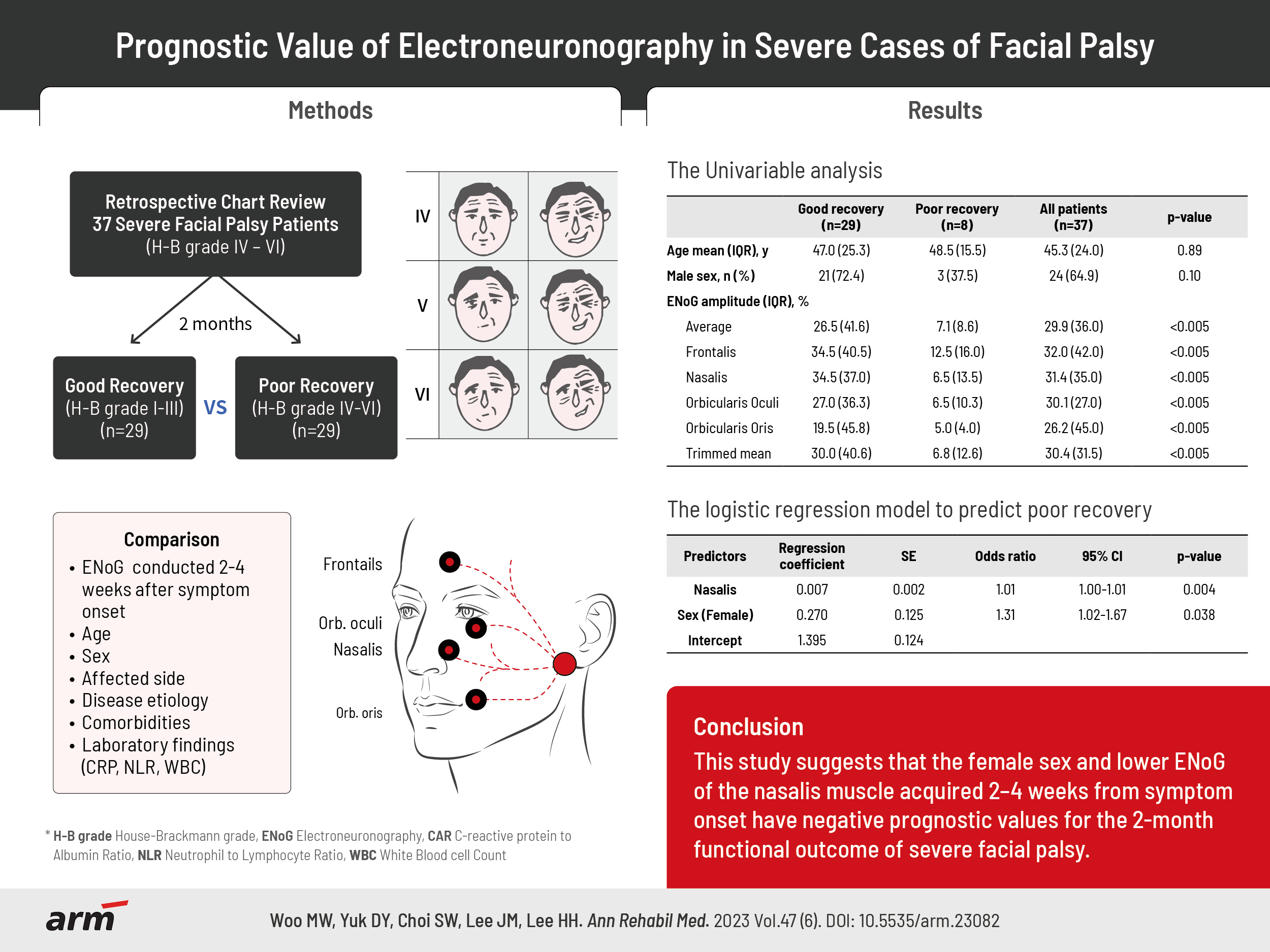
To examine the prognostic value of electroneuronography (ENoG) in predicting functional recovery in severe cases of acute facial palsy.
Methods
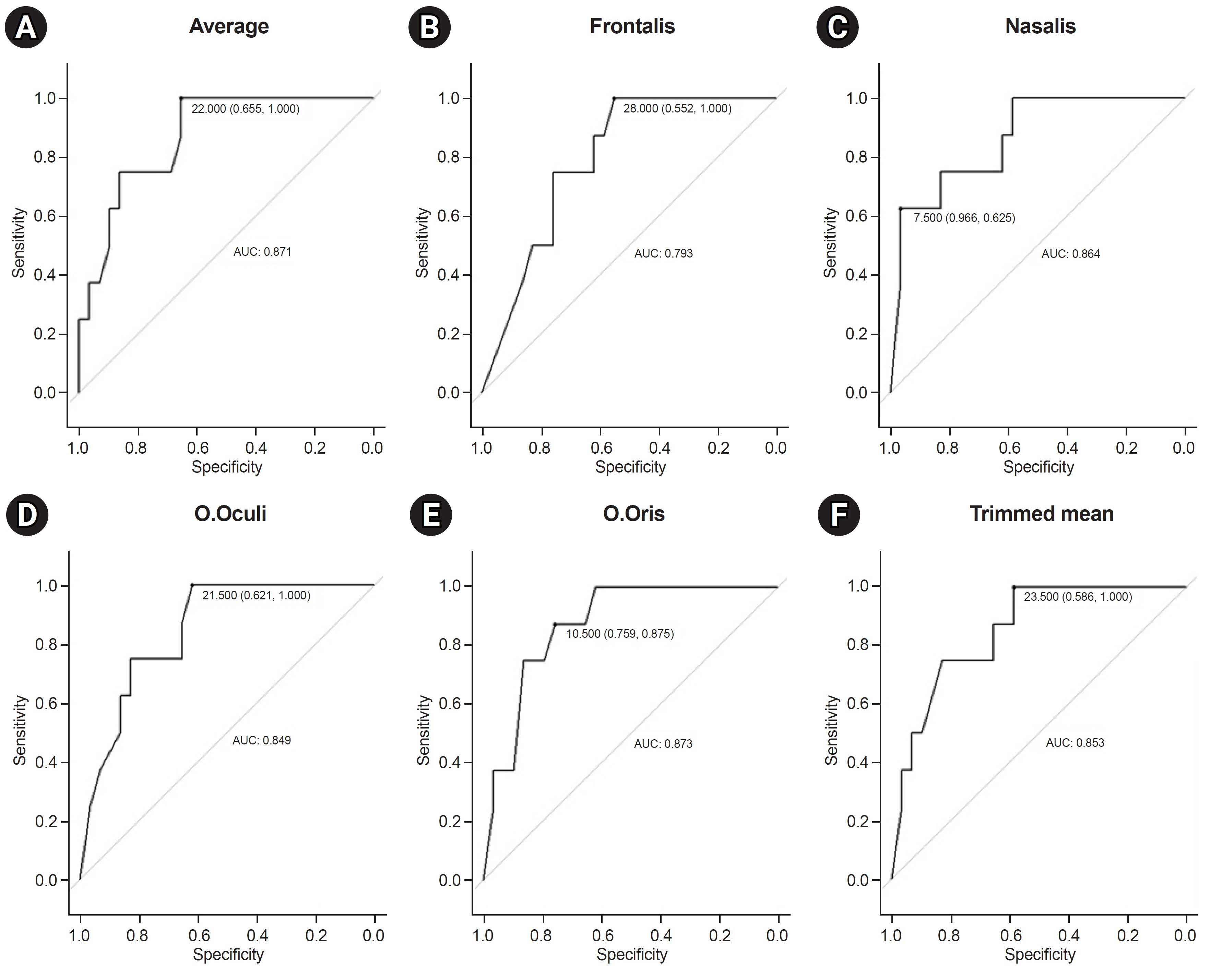
Patients with severe degrees of facial palsy (initial House–Brackmann [HB] grades IV to VI) with available electrodiagnostic studies conducted 2–4 weeks after symptom onset were reviewed retrospectively. The patients were categorized into “good recovery” and “poor recovery” groups, with the former showing mild to no dysfunction (HB I to III) and the latter exhibiting moderate to severe dysfunction (HB IV to VI) on follow-up evaluation, 2 months after onset. ENoG amplitudes in four facial muscles (frontalis, nasalis, orbicularis oculi, and orbicularis oris), as well as age, sex, affected side, disease etiology, comorbidities, and laboratory findings, were compared between the two groups.
Results
Thirty-seven patients were included. Twenty-nine of the patients showed “good recovery,” and eight showed “poor recovery” at 2 months after symptom onset. Univariate analysis yielded no significant difference in age, sex, affected side, disease etiology, comorbidities, and laboratory findings between the two groups. Preserved ENoG amplitudes (individual, average, and trimmed means) were significantly higher in the good recovery group than in the poor recovery group (p<0.005). Sex (p=0.038) and the ENoG of the nasalis muscle, acquired 2–4 weeks from symptom onset (p=0.004), showed significant differences in multivariate regression analysis.
Conclusion
This study suggests that the female sex and lower ENoG of the nasalis muscle, acquired 2–4 weeks from symptom onset, have negative prognostic value for the 2-month functional outcome of severe facial palsy cases.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fu L, Bundy C, Sadiq SA. Psychological distress in people with disfigurement from facial palsy. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:1322–6.
Article2. Esslen E. Electrodiagnosis of facial palsy. In : Miehlke A, editor. Surgery of the facial nerve. W.B. Saunders;1973. p. 45–51.3. Guntinas-Lichius O, Volk GF, Olsen KD, Mäkitie AA, Silver CE, Zafereo ME, et al. Facial nerve electrodiagnostics for patients with facial palsy: a clinical practice guideline. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; 277:1855–74.
Article4. Lee DH. Clinical efficacy of electroneurography in acute facial paralysis. J Audiol Otol. 2016; 20:8–12.
Article5. Yasukawa M, Yasukawa K, Ohnuma H. [Prognostic diagnosis of facial palsy with electroneuronography]. Masui. 1995; 44:378–87. Japanese.6. May M, Blumenthal F, Klein SR. Acute Bell's palsy: prognostic value of evoked electromyography, maximal stimulation, and other electrical tests. Am J Otol. 1983; 5:1–7.7. Wang Y, Zhang S, Xu H. [A report of 164 cases of Bell's palsy]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 1996; 31:334–7. Chinese.8. House JW, Brackmann DE. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985; 93:146–7.
Article9. Fisch U. Prognostic value of electrical tests in acute facial paralysis. Am J Otol. 1984; 5:494–8.10. Prakash KM, Raymond AA. The use of nerve conduction studies in determining the short-term outcome of Bell's palsy. Med J Malaysia. 2003; 58:69–78.11. Cayir S, Hizli O, Kayabasi S. Is C-reactive protein to albumin ratio an indicator of poor prognosis in Bell's palsy? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; 277:115–9.
Article12. Sevil E, Değer Kulaksiz B, Islamoglu A. Association between the inflammatory parameters and prognosis of Bell’s palsy. Northwestern Med J. 2021; 1:35–41.
Article13. Atan D, İkincioğulları A, Köseoğlu S, Özcan KM, Çetin MA, Ensari S, et al. New predictive parameters of Bell's palsy: neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio. Balkan Med J. 2015; 32:167–70.
Article14. Schimmel SJ, Acosta S, Lozano D. Neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury: a chronic response to an acute injury. Brain Circ. 2017; 3:135–42.
Article15. Kim SH, Ryu EW, Yang CW, Yeo SG, Park MS, Byun JY. The prognostic value of electroneurography of Bell's palsy at the orbicularis oculi versus nasolabial fold. Laryngoscope. 2016; 126:1644–8.
Article16. Weerapant E, Bunaprasert T, Chokrungvaranont P, Chentanez V. Anatomy of the facial nerve branching patterns, the marginal mandibular branch and its extraparotid ramification in relation to the lateral palpebral line. Asian Biomed. 2010; 4:603–8.
Article17. Myckatyn TM, Mackinnon SE. A review of facial nerve anatomy. Semin Plast Surg. 2004; 18:5–12.18. Martínez Pascual P, Maranillo E, Vázquez T, Simon de Blas C, Lasso JM, Sañudo JR. Extracranial course of the facial nerve revisited. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019; 302:599–608.
Article19. Redhead J, Mugliston T. Facial electroneuronography: action potential amplitude and latency studies in 50 normal subjects. J Laryngol Otol. 1985; 99:369–72.
Article20. Engström M, Jonsson L, Grindlund M, Stålberg E. Electroneurographic facial muscle pattern in Bell's palsy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 122:290–7.
Article21. Jeong J, Yoon SR, Lim H, Oh J, Choi HS. Risk factors for Bell's palsy based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service National Sample Cohort data. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:23387.
Article22. Lee JS, Kim YH. Epidemiological trends of Bell's palsy treated with steroids in Korea between 2008 and 2018. Muscle Nerve. 2021; 63:845–51.
Article23. Yoo MC, Park DC, Yeo SG. Association between initial severity of facial weakness and outcomes of Bell's palsy. J Clin Med. 2021; 10:3914.
Article24. Hultcrantz M. Rehabilitation of Bells' palsy from a multi-team perspective. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; 136:363–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bilateral Bell's Palsy with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus
- Two Cases of Central Facial Palsy due to Medullary Infarction
- Comparison of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Electroneuronography Between Bell's Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome in Their Acute Stages
- Bilateral Simultaneous Bell's Palsy-Two Case Studies
- Serious Neurological Disorders That Mimic Bell’s Palsy: A 10-Year Experience