Korean J Health Promot.
2023 Dec;23(4):217-225. 10.15384/kjhp.2023.23.4.217.
Comparison of Heat Treatments by Floor Heating and Fan Heating for Bed Bug Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Environment and Energy Research Laboratory, Research Institute of Industrial Science and Technology, Gwangyang, Korea
- 2Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2549692
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15384/kjhp.2023.23.4.217
Abstract
- Background
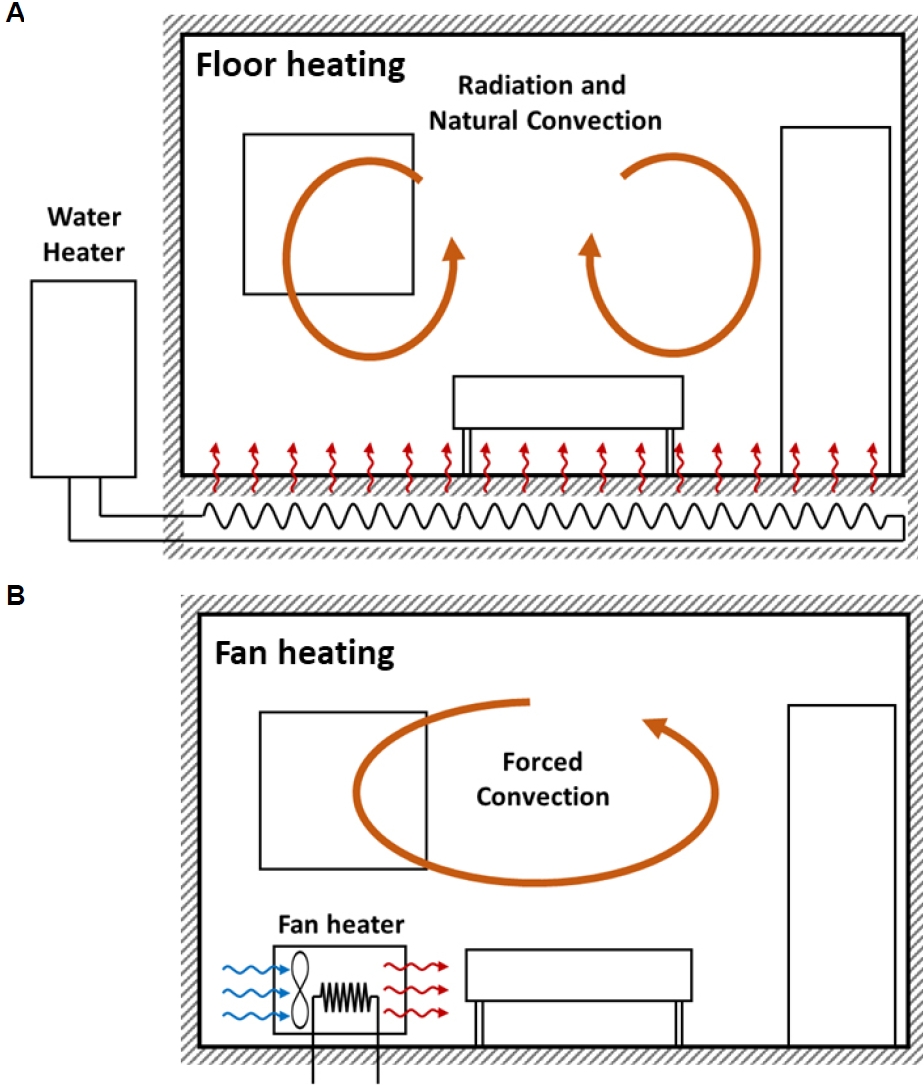
Non-chemical methods are as important as pesticides to control bed bugs. The most effective method is heat treatment. Underfloor heating is widely used in residential buildings in Korea, and the benefits of floor heating can be utilized in heat treatment for bed bug control.
Methods
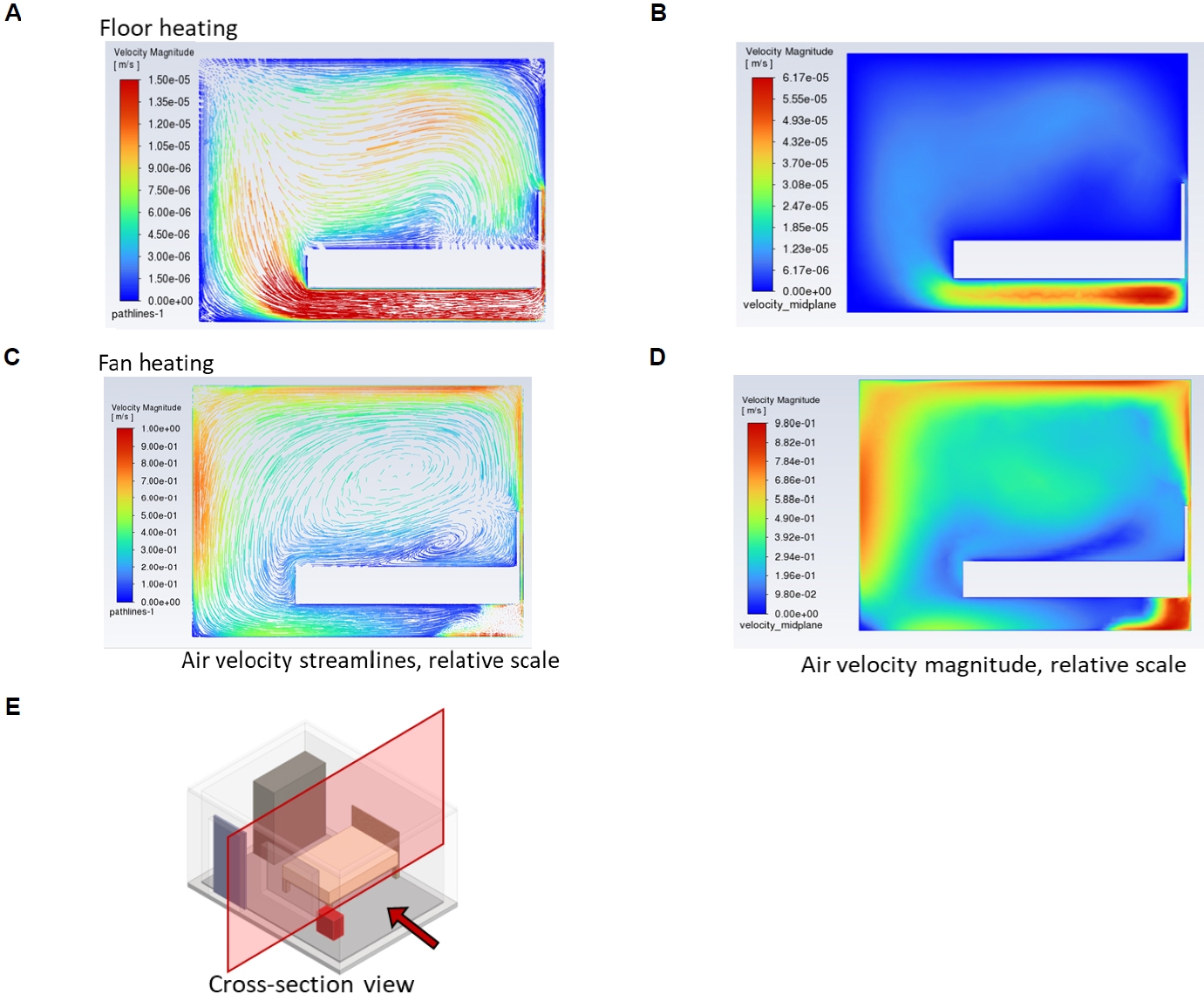
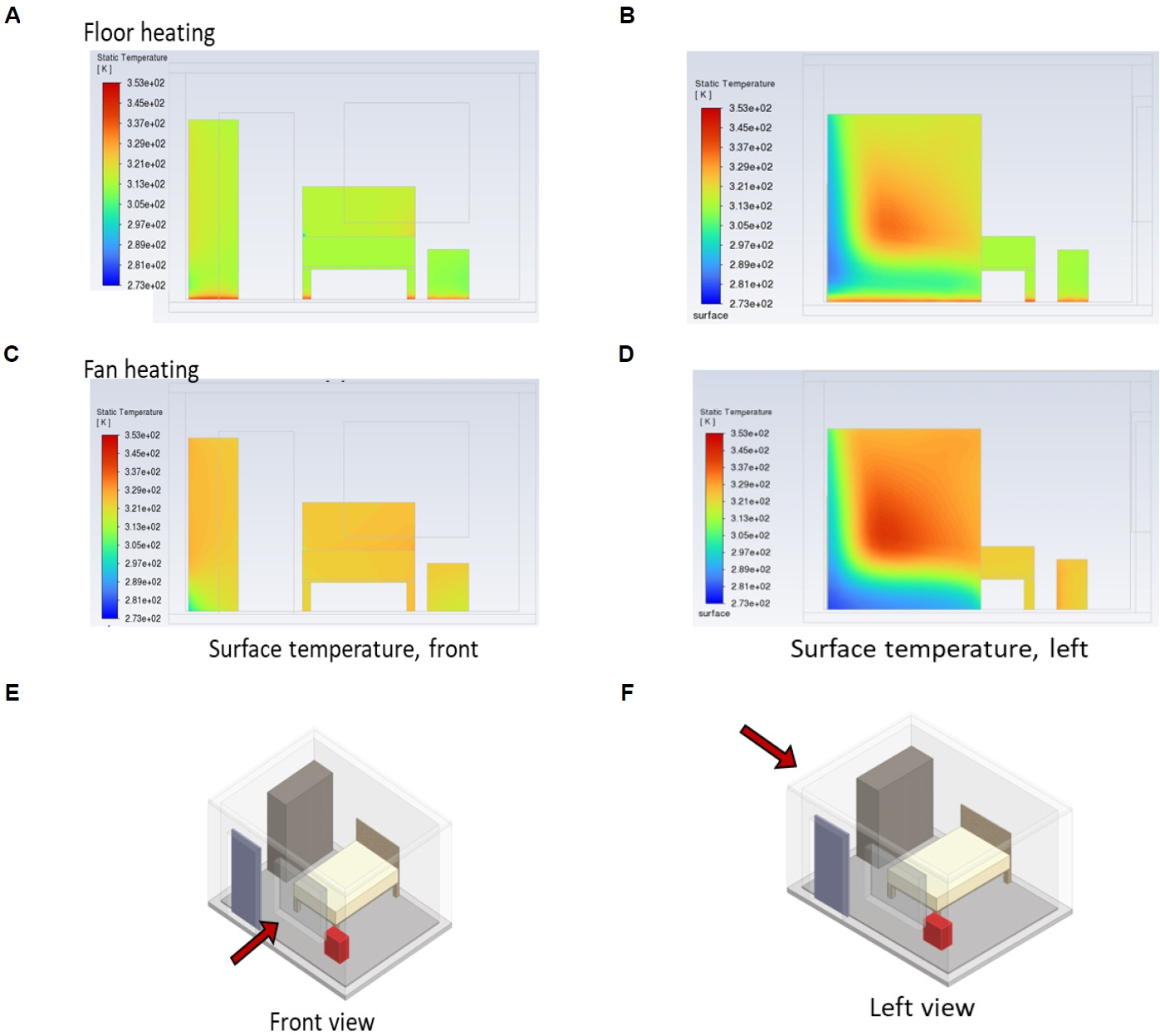
Simulations of indoor air flow and heat transfer were performed to compare and analyze the temperature distributions with different heating methods for bed bug control using floor heating and fan heater methods.
Results
Even though the average indoor temperature of floor heating was lower, it was more uniform with floor heating than that of fan heating under the assumed conditions. Local cold spots disappeared with the floor heating method.
Conclusions
It was confirmed that floor heating has advantages over fan heating to achive uniform high temperatures during heat treatment for exterminating bed bugs.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agency KDCaP. Bed bug information book. 2ed ed. Cheongju: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;2023. p. 5–6.2. Parola P, Izri A. Bedbugs. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(23):2230–7.
Article3. Doggett SL, Dwyer DE, Peñas PF, Russell RC. Bed bugs: clinical relevance and control options. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25(1):164–92.
Article4. Byun Y, Yang YS, Kim JH, Cho BK, Lee IY, Kim H, et al. Bedbug bite. Korean J Dermatology. 2015; 53(2):157–9.5. Lee IY, Ree HI, An SJ, Linton JA, Yong TS. Reemergence of the bedbug cimex lectularius in Seoul, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2008; 46(4):269–71.
Article6. Goddard J, deShazo R. Bed bugs (cimex lectularius) and clinical consequences of their bites. JAMA. 2009; 301(13):1358–66.
Article7. Pritchard MJ, Hwang SW. Cases: severe anemia from bedbugs. CMAJ. 2009; 181(5):287–8.8. Pietri JE. Case not closed: arguments for new studies of the interactions between bed bugs and human pathogens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020; 103(2):619–24.
Article9. Koganemaru R, Miller DM. The bed bug problem: past, present, and future control methods. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2013; 106(3):177–89.
Article10. Haynes KF, Potter MF. Recent progress in bed bug management. In: Ishaaya I, Palli SR, Horowitz AR, eds. Advanced technologies for managing insect pests. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; 2013. p.269-78.11. Lee JY, Chae WR, Huh DA, Moon KW. Environmental exposure to mercury, cadmium, and pyrethroid pesticide and its association with delayed puberty in children: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS). J Environ Health Sci. 2021; 47(3):245–58.12. Lim TG. Fear of re-emergence of bed bugs... How to search and remove ‘hiding places’ in the bedroom [Internet]. Seoul: The Farmers Newspaper; 2023 [cited Nov 21, 2023]. Available from: https://www.nongmin.com/article/20231016500353.13. Korea Boiler Engineering Association. 'Ondol is science'. KBEA. 2007; 160(5):140–9.14. Kells SA, Goblirsch MJ. Temperature and time requirements for controlling bed bugs (cimex lectularius) under commercial heat treatment conditions. Insects. 2011; 2(3):412–22.
Article15. Catron KA, Wilson MS, Miller DM. Efficacy of thermal remediation for bed bug (hemiptera: cimicidae) control in apartments of different clutter levels. 9th ed. Birmingham: International Conference on Urban Pests;2017. p. 61–5.16. Cha CH, Ham KS, Yoon JJ, Hwang JH, Lee KW, Koo SH. Insecticide resistance in bedbugs (cimex lectularius) in Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi. 1970; 8(1):5–7.17. Singh N, Wang C, Zha C, Cooper R, Robson M. Testing a threshold-based bed bug management approach in apartment buildings. Insects. 2017; 8(3):76.
Article18. Sanford MR, Torres M, Ross J. Unexpected human fatality associated with bed bug (hemiptera: cimicidae) heat treatment. J Forensic Sci. 2019; 64(2):622–4.
Article