Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Dec;28(4):302-307. 10.6065/apem.2244016.008.
Metanephrine negative pheochromocytoma: a rare case report of dopamine-secreting tumor in an adolescent neurofibromatosis type 1 patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2549324
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2244016.008
Abstract
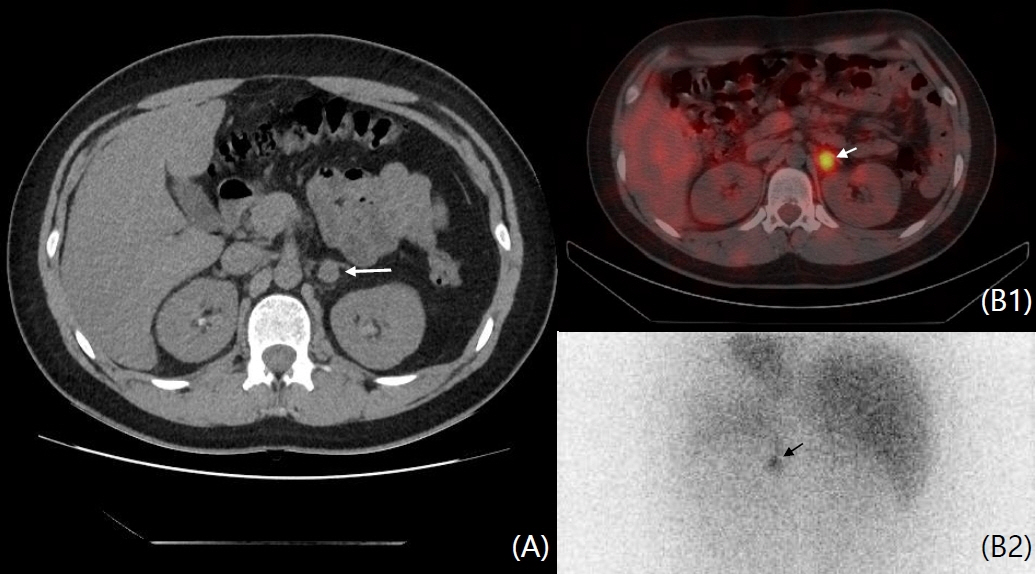
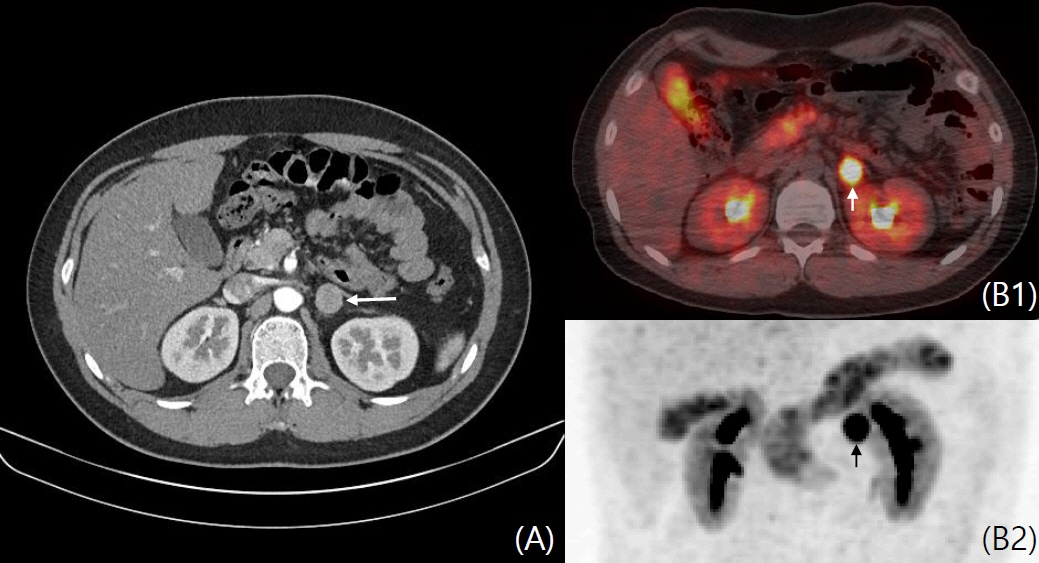
- Pheochromocytoma (PCC) occurs in 4% of pediatric neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) patients and is characterized by epinephrine and norepinephrine secretion. Herein, we report the first case of dopamine-secreting PCC in a 13-year-old patient with NF1. A left adrenal mass was incidentally found on abdominal computed tomography (CT ) during hypertension workup. Fractionated 24-hour urine metanephrine excretion was normal, but urine dopamine level was elevated. Focal 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine uptake was observed on single-photon emission tomography/CT (SPECT/CT). Surgery was delayed due to small tumor size, vague symptoms, and increased dopamine level. After 6 months, focal significant uptake of the lesion on 6‐[18F]fluoro‐L‐3,4‐dihydroxyphenylalanine (18F-FDOPA) PET/CT increased and tumor size increased on abdominal CT. Laparoscopic resection was performed, and the mass was histologically confirmed as PCC. Currently, the vital signs of the patient are stable, urine dopamine level is normal, and there is no abnormal uptake of 18F-FDOPA PET/CT. This study reports a rare case of dopamine-secreting PCC. A multidisciplinary approach and focused examination are needed in metanephrine-negative, high-risk PCC patients.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Overview of endocrine tumor syndromes manifesting as adrenal tumors
Ja Hye Kim
Ewha Med J. 2024;47(1):e4. doi: 10.12771/emj.2024.e4.
Reference
-
References
1. Havekes B, Romijn JA, Eisenhofer G, Adams K, Pacak K. Update on pediatric pheochromocytoma. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24:943–50.2. Neumann HP, Bausch B, McWhinney SR, Bender BU, Gimm O, Franke G, et al. Germ-line mutations in nonsyndromic pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1459–66.3. Londe S. Causes of hypertension in the young. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1978; 25:55–65.4. Ferner RE, Huson SM, Thomas N, Moss C, Willshaw H, Evans DG, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of individuals with neurofibromatosis 1. J Med Genet. 2007; 44:81–8.5. Gutmann DH. The neurofibromatoses: when less in more. Hum Mol Genet. 2001; 10:747–55.6. Zöller ME, Rembeck B, Odén A, Samuelsson M, Angervall L. Ma lig nant and b enig n tumors in p at ients w it h neurofibromatosis type 1 in a defined Swedish population. Cancer. 1997; 79:2125–31.7. Walther MM, Herring J, Enquist E, Keiser HR, Linehan WM. von Recklinghausen's disease and pheochromocytomas. J Urol. 1999; 162:1582–6.8. Bausch B, Wellner U, Bausch D, Schiavi F, Barontini M, Sanso G, et al. Long-term prognosis of patients with pediatric pheochromocytoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013; 21:17–25.9. Yasunari K, Kohno M, Minami M, Kano H, Ohhira M, Nakamura K, et al. A dopamine-secreting pheochromocytoma. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000; 36:S75–7.10. Foo SH, Chan SP, Ananda V, Rajasingam V. Dopamine-secreting phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas: clinical features and management. Singapore Med J. 2010; 51:e89–93.11. Proye C, Fossati P, Fontaine P, Lefebvre J, Decoulx M, Wemeau JL, et al. Dopamine-secreting pheochromocytoma: an unrecognized entity? Classification of pheochromo cytomas according to their type of secretion. Surgery. 1986; 100:1154–62.12. Park JK, Oh HK, Shon MH, Kim HH, Jeon EJ, Dal Jung E. A case of dopamine-secreting pheochromocytoma. Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 27:159–62.13. Dubois LA, Gray DK. Dopamine-secreting pheochromocytomas: in search of a syndrome. World J Surg. 2005; 29:909–13.14. Eisenhofer G, Goldstein DS, Sullivan P, Csako G, Brouwers FM, Lai EW, et al. Biochemical and clinical manifestations of dopamine-producing paragangliomas: utility of plasma methoxytyramine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:2068–75.15. Tam V, Ng KF, Fung LM, Wong YY, Chan MH, Lam CW, et al. The importance of the interpretation of urine catecholamines is essential for the diagnosis and management of patient with dopamine-secreting paraganglioma. Ann Clin Biochem. 2005; 42:73–7.16. Shotaro M, Yuichi Y, Yoshinori O, Mitsuhiro O, Koro G, Takayuki M, et al. Dopamine-sereting pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. J Endocr Soc. 2021; 5:brab163.17. Ito Y, Fuimoto Y, Obara T. The role of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dop amine in blo o d pressure disturbances in patients with pheochromocytoma. World J Surg. 1992; 16:759–63.18. Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Grebe SK, Murad MH, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. The J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:1915–42.19. Lee EJ, Lee KH. PET application in neuroendocrine tumors. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007; 22:397–406.20. Imani F, Agopian VG, Auerbach MS, Walter MA, Imani F, Benz MR, et al. 18F-FDOPA PET and PET/CT accurately localize pheochromocytomas. J Nucl Med. 2009; 50:513–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Dopamine-Secreting Pheochromocytoma
- A Case of Neurofibromatosis Type I with Pheochromocytoma
- Case Reports and Estimated Prevalence of Adrenal Pheochromocytoma in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type I in Korea
- A case of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in neurofibromatosis type 1 associated with pheochromocytoma
- Clinical Characteristics of Pheochromocytoma in Korean Children