J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Dec;38(49):e415. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e415.
Increased Estimated GFR Is Negatively Associated With the Risk of SARSCoV-2 Infection and Severe COVID-19 Within Normal to Mildly Decreased Levels: Nested Case-Control Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Informatics, CHA University School of Medicine, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Institute of Biomedical Informatics, CHA University School of Medicine, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2549178
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e415
Abstract
- Background
While accumulating evidence indicates chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the association between normal or mildly decreased kidney function and COVID-19 is unaddressed. Here, we have examined the association of an increase in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) with the incidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes among patients within normal to mildly decreased kidney function.
Methods
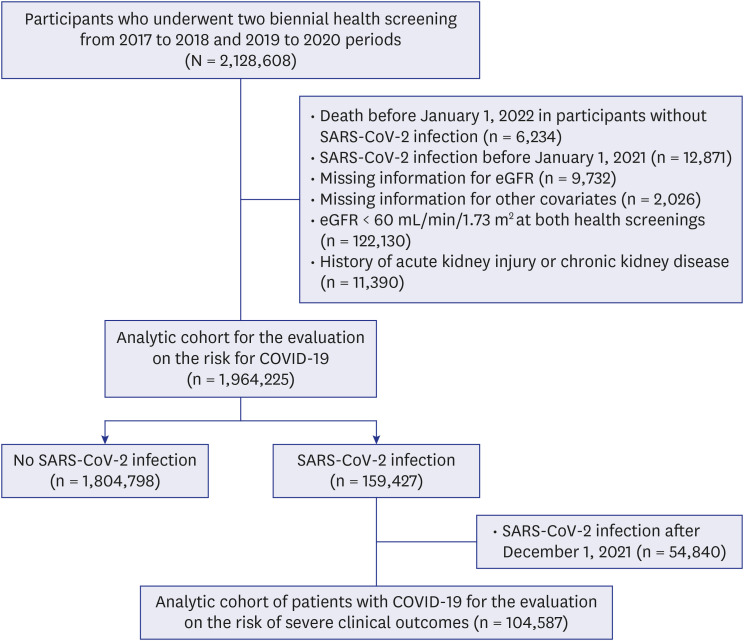
The patients who participated in both health screenings from period I (2017–2018) to II (2019–2020) were enrolled to our study. All participants were categorized into four groups according to the changes in eGFR stage from period I to II: 1) persistently stage G1, 2) from stage G2 to G1, 3) from stage G1 to G2, 4) persistently stage G2. In addition, the changes in eGFR value were defined by subtracting its value of period I from II. Patients were followed up for SARS-CoV-2 infection from January 1, 2021 to any diagnosis of COVID-19 or December 31, 2021, whichever happened first. In addition, those with SARS-CoV-2 infection were followed-up for one month after diagnosis to analyze severe COVID-19. Adjusted odds ratio (aOR) was calculated using multivariable-adjusted logistic regression.
Results
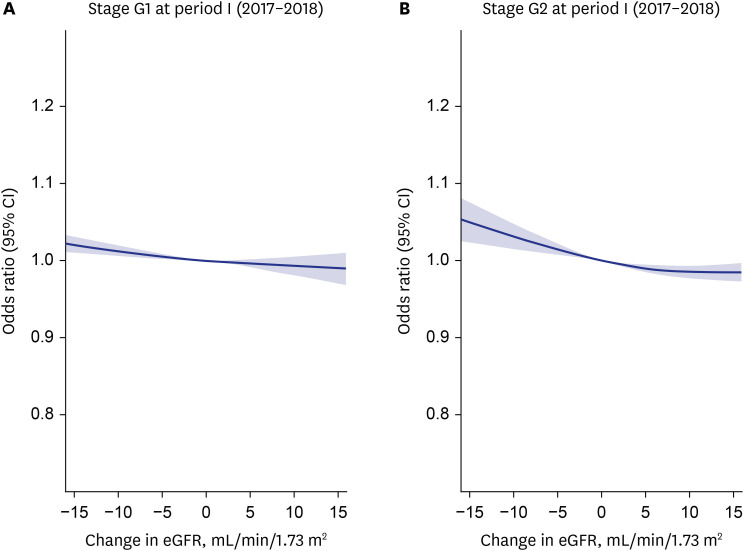
We identified 159,427 patients with and 1,804,798 patients without SARS-CoV-2 infection. The risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection decreased when eGFR stage changed from G2 to G1 (aOR, 0.957; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.938–0.977) and persistently maintained at G1 (aOR, 0.966; 95% CI, 0.943–0.990), compared with the persistently stage G2 group. In addition, the risk showed an inverse relationship with changes in eGFR value, which was depicted by restricted cubic spline curves. For the overall risk of severe COVID-19, the persistently stage G1 showed the lowest risk (aOR, 0.897; 95% CI, 0.827–0.972), followed by those from stage G1 to G2 (aOR, 0.900; 95% CI, 0.828–0.978) and those from stage G2 to G1 (aOR, 0.931; 95% CI, 0.871–0.995), compared with the persistently stage G2 group.
Conclusion
An increase in eGFR was negatively associated with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 among normal or mildly decreased kidney function. For severe COVID-19, maintaining higher baseline eGFR may act as a protective factor against its risk.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clark A, Jit M, Warren-Gash C, Guthrie B, Wang HHX, Mercer SW, et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe COVID-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2020; 8(8):e1003–e1017. PMID: 32553130.2. Pijls BG, Jolani S, Atherley A, Derckx RT, Dijkstra JI, Franssen GH, et al. Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: a meta-analysis of 59 studies. BMJ Open. 2021; 11(1):e044640.3. ERA-EDTA Council. ERACODA Working Group. Chronic kidney disease is a key risk factor for severe COVID-19: a call to action by the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020; 36(1):87–94.4. Gansevoort RT, Hilbrands LB. CKD is a key risk factor for COVID-19 mortality. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020; 16(12):705–706. PMID: 32848205.5. de Lusignan S, Dorward J, Correa A, Jones N, Akinyemi O, Amirthalingam G, et al. Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 among patients in the Oxford Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Centre primary care network: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20(9):1034–1042. PMID: 32422204.6. Syed-Ahmed M, Narayanan M. Immune dysfunction and risk of infection in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019; 26(1):8–15. PMID: 30876622.7. Cohen G, Haag-Weber M, Hörl WH. Immune dysfunction in uremia. Kidney Int Suppl. 1997; 62:S79–S82. PMID: 9350688.8. Carlson N, Nelveg-Kristensen KE, Freese Ballegaard E, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Hornum M, Kamper AL, et al. Increased vulnerability to COVID-19 in chronic kidney disease. J Intern Med. 2021; 290(1):166–178. PMID: 33452733.9. Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020; 584(7821):430–436. PMID: 32640463.10. Kim HK, Song SO, Noh J, Jeong IK, Lee BW. Data configuration and publication trends for the Korean National Health Insurance and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Database. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44(5):671–678. PMID: 33115211.11. Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, Khang YH, Kim HC, Park JH, et al. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open. 2017; 7(9):e016640.12. Levin A, Stevens PE. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. 2014; 85(1):49–61. PMID: 24284513.13. Quan H, Li B, Couris CM, Fushimi K, Graham P, Hider P, et al. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am J Epidemiol. 2011; 173(6):676–682. PMID: 21330339.14. Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd ed. New York, NY, USA: Routledge;2013.15. von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ. 2007; 335(7624):806–808. PMID: 17947786.16. Mirijello A, Piscitelli P, de Matthaeis A, Inglese M, D’Errico MM, Massa V, et al. Low eGFR Is a strong predictor of worse outcome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J Clin Med. 2021; 10(22):5224. PMID: 34830506.17. Tecklenborg J, Clayton D, Siebert S, Coley SM. The role of the immune system in kidney disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018; 192(2):142–150. PMID: 29453850.18. Chi M, Tian Z, Ma K, Li Y, Wang L, Nasser MI, et al. The diseased kidney: aging and senescent immunology. Immun Ageing. 2022; 19(1):58. PMID: 36384564.19. Mizuiri S, Ohashi Y. ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease. World J Nephrol. 2015; 4(1):74–82. PMID: 25664248.20. Nadarajah R, Milagres R, Dilauro M, Gutsol A, Xiao F, Zimpelmann J, et al. Podocyte-specific overexpression of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates diabetic nephropathy in mice. Kidney Int. 2012; 82(3):292–303. PMID: 22475818.21. Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003; 426(6965):450–454. PMID: 14647384.22. Pagliaro P, Penna C. ACE/ACE2 ratio: a key also in 2019 coronavirus disease (Covid-19)? Front Med (Lausanne). 2020; 7:335. PMID: 32626721.23. Dilauro M, Zimpelmann J, Robertson SJ, Genest D, Burns KD. Effect of ACE2 and angiotensin-(1-7) in a mouse model of early chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010; 298(6):F1523–F1532. PMID: 20357030.24. Wang G, Lai FM, Kwan BC, Lai KB, Chow KM, Li PK, et al. Expression of ACE and ACE2 in patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2011; 34(3):141–149. PMID: 21346373.25. Levey AS, Inker LA, Coresh J. GFR estimation: from physiology to public health. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 63(5):820–834. PMID: 24485147.26. Levey AS, Titan SM, Powe NR, Coresh J, Inker LA. Kidney disease, race, and GFR estimation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 15(8):1203–1212. PMID: 32393465.27. Park JI, Baek H, Jung HH. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2011-2013. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31(6):915–923. PMID: 27247501.28. Hu B, Gadegbeku C, Lipkowitz MS, Rostand S, Lewis J, Wright JT, et al. Kidney function can improve in patients with hypertensive CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012; 23(4):706–713. PMID: 22402803.29. Weis L, Metzger M, Haymann JP, Thervet E, Flamant M, Vrtovsnik F, et al. Renal function can improve at any stage of chronic kidney disease. PLoS One. 2013; 8(12):e81835. PMID: 24349134.30. Toyama K, Sugiyama S, Oka H, Sumida H, Ogawa H. Exercise therapy correlates with improving renal function through modifying lipid metabolism in patients with cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. J Cardiol. 2010; 56(2):142–146. PMID: 20696551.31. van Westing AC, Küpers LK, Geleijnse JM. Diet and kidney function: a literature review. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020; 22(2):14. PMID: 32016564.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- COVID-19 and Cancer: Questions to Be Answered
- The Role of COVID-19 Vaccination for Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in the Upcoming Endemic Era
- Risk of COVID-19 Transmission from Infected Outpatients to Healthcare Workers in an Outpatient Clinic
- Stroke in a Young Age COVID-19 Patient: Vasculitis Feature and Changes in Cerebral Vessel Stenosis
- Fear of COVID-19 and Its Impact on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention Among Egyptian Physicians