J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Dec;38(48):e416. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e416.
Case 17: A 62-Year-Old Man With Dyspnea and Chest Discomfort for 1 Month
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2549170
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e416
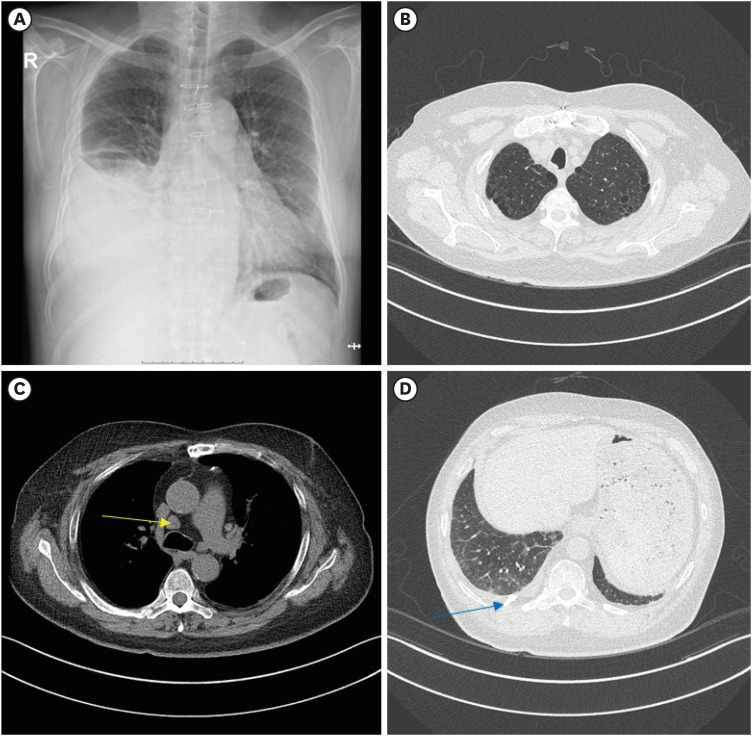
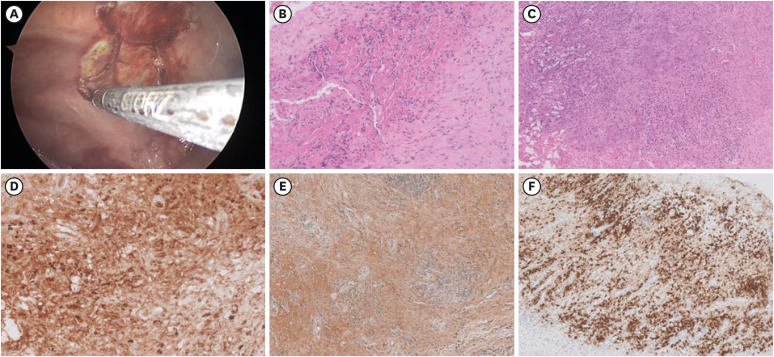
Figure
Reference
-
1. Porcel JM, Light RW. Diagnostic approach to pleural effusion in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2006; 73(7):1211–1220. PMID: 16623208.2. Perugino CA, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020; 16(12):702–714. PMID: 32939060.
Article3. Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, Choi HK, Della-Torre E, Dicaire JF, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79(1):77–87. PMID: 31796497.
Article4. Kim HW, Kim KH, Shin AY, Choi JY, Ahn JH, Kim JS, et al. Investigating the appropriate adenosine deaminase cutoff value for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion in a country with decreasing TB burden. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):7586. PMID: 35534515.
Article5. Jeon D. Tuberculous pleurisy: an update. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2014; 76(4):153–159. PMID: 24851127.
Article6. Doita S, Tamura T, Baba T, Oomori H, Nishii K, Nakanishi M, et al. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related disease with pleural effusion, requiring exclusion of tuberculous pleurisy. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022; 37:101654. PMID: 35540692.
Article7. Bagcchi S. WHO’s global tuberculosis report 2022. Lancet Microbe. 2023; 4(1):e20. PMID: 36521512.
Article