Korean J Sports Med.
2023 Dec;41(4):250-255. 10.5763/kjsm.2023.41.4.250.
Novel Therapeutic Approach for Extensor Digiti Minimi Tendon Traction in Chronic Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain Diagnosed as Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Borntouch Orthopaedic Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Sarang Clinic, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2549000
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2023.41.4.250
Abstract
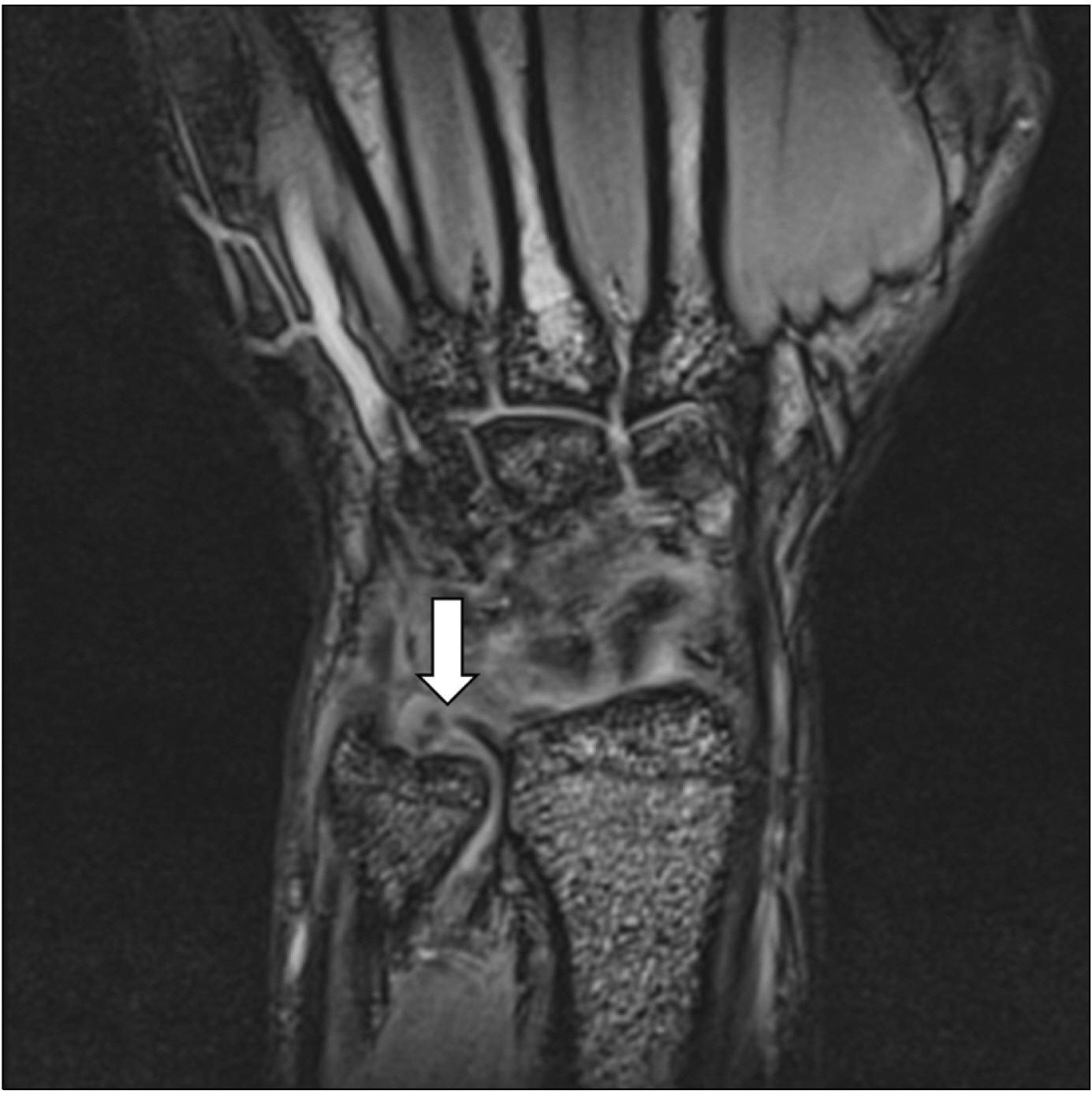
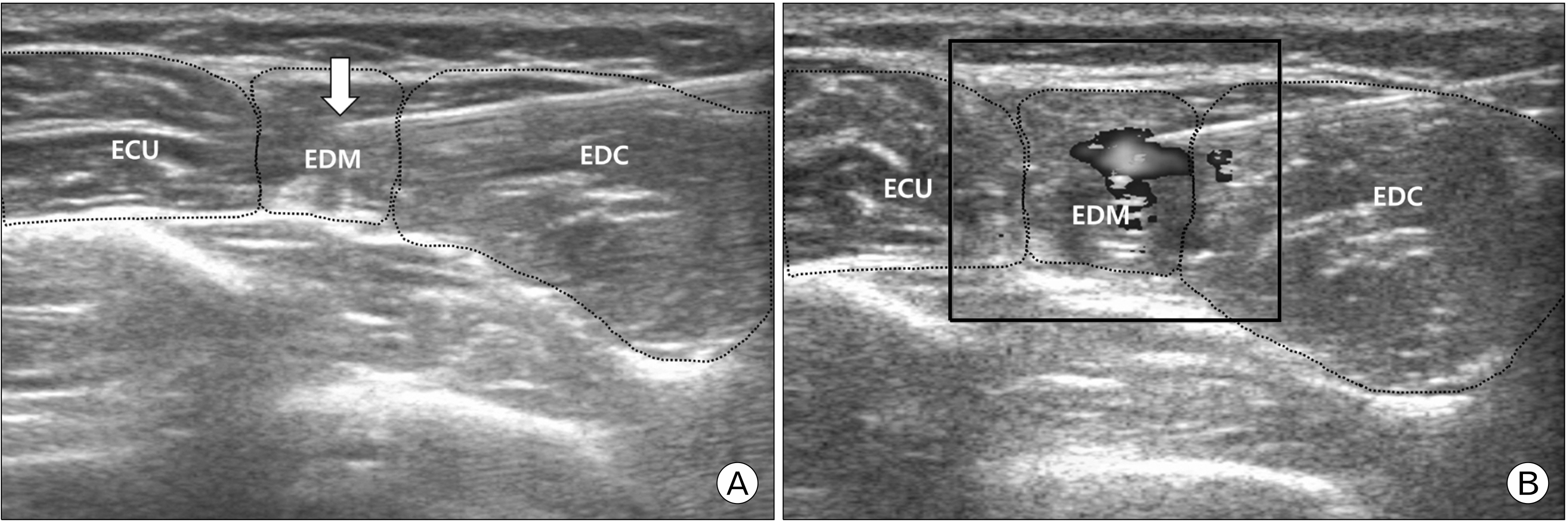
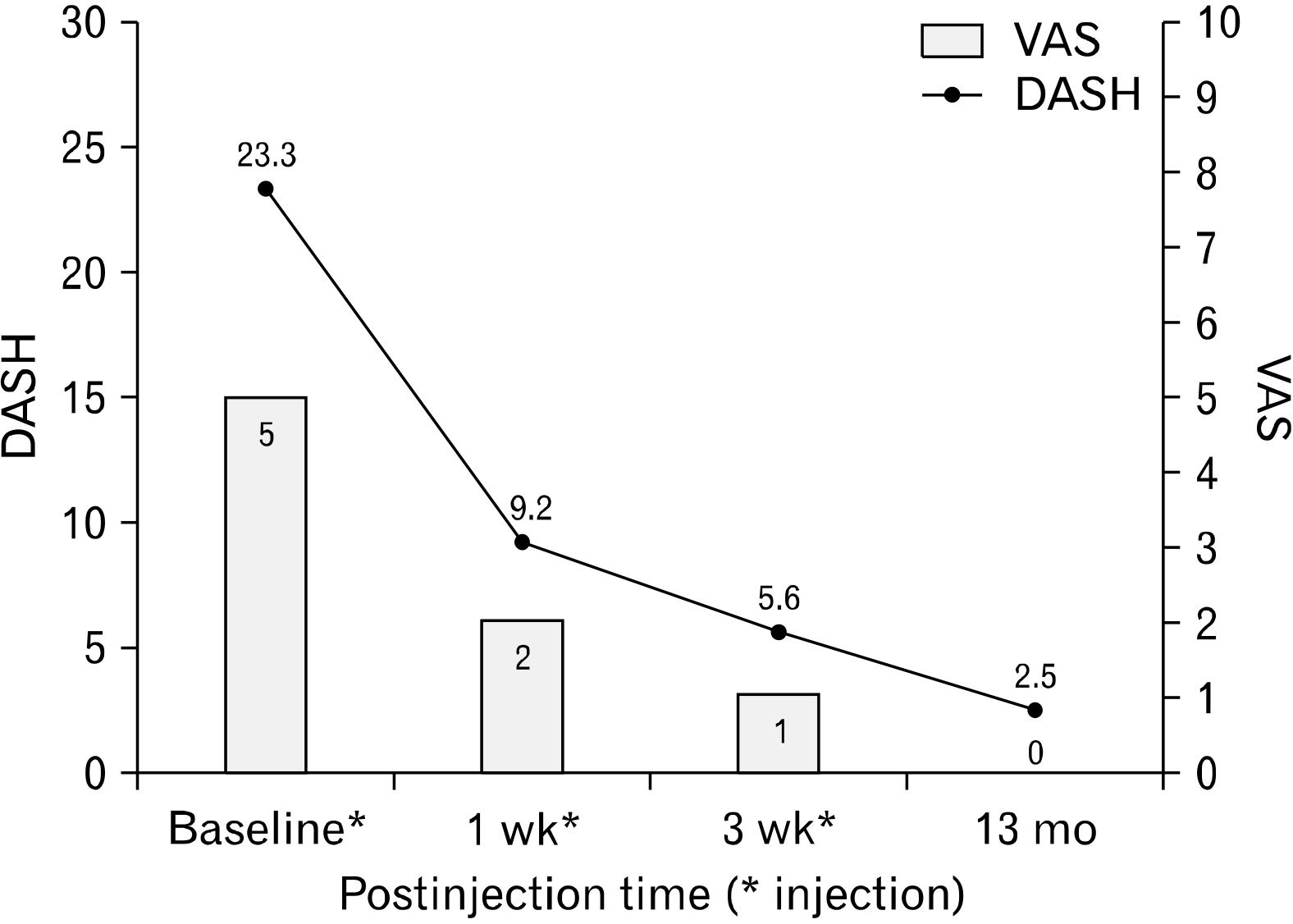
- Ulnar-sided wrist pain is common in sports medicine and orthopedics, typically diagnosed as a triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injury. We present a case study involving a 22-year-old male who has been experiencing chronic left wrist pain for the past 9 months. He was diagnosed with a TFCC injury and received conservative treatment. Surgery was recommended if the pain persisted after 9 months. He exhibited tenderness in the dorsal radioulnar joint region and the proximal one-third portion of the extensor digiti minimi (EDM) muscle. At a tendon traction point (TTP) over the EDM muscle, 4 mL of isotonic saline was injected at presentation, 1 and 3 weeks later. The pain significantly improved, and he did not experience any adverse effects or worsening of his symptoms during the 13-month follow-up. The injection therapy at the TTP of the EDM can be considered in chronic unhealed ulnar-sided wrist pain, including TFCC injury, to release the tightly contracted EDM muscle.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rios-Russo JL, Lozada-Bado LS, de Mel S, Frontera W, Micheo W. 2021; Ulnar-sided wrist pain in the athlete: sport-specific demands, clinical presentation, and management options. Curr Sports Med Rep. 20:312–8. DOI: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000853. PMID: 34099609.
Article2. Seong JW, Kwon DR. 2020; A proposal for a new headache classification system for general practitioners. Med Hypotheses. 143:110103. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110103. PMID: 32721801.
Article3. Seong JW. Principle and insights into pain. Vol. 1:Koonja Press;2015.4. Cole DW, Elsaidi GA, Kuzma KR, Kuzma GR, Smith BP, Ruch DS. 2006; Distal radioulnar joint instability in distal radius fractures: the role of sigmoid notch and triangular fibrocartilage complex revisited. Injury. 37:252–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2005.08.019. PMID: 16324702.
Article5. Tsai PC, Paksima N. 2009; The distal radioulnar joint. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 67:90–6.6. Watanabe A, Souza F, Vezeridis PS, Blazar P, Yoshioka H. 2010; Ulnar-sided wrist pain. II. Clinical imaging and treatment. Skeletal Radiol. 39:837–57. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-009-0842-3. PMID: 20012039. PMCID: PMC2904904.
Article7. Schmauss D, Pöhlmann S, Lohmeyer JA, Germann G, Bickert B, Megerle K. 2016; Clinical tests and magnetic resonance imaging have limited diagnostic value for triangular fibrocartilaginous complex lesions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 136:873–80. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-016-2441-9. PMID: 26969464.
Article8. Andrade-Silva FB, Rocha JP, Carvalho A, Kojima KE, Silva JS. 2019; Influence of postoperative immobilization on pain control of patients with distal radius fracture treated with volar locked plating: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Injury. 50:386–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.12.001. PMID: 30558805.
Article9. Park JH, Kim D, Park JW. 2018; Arthroscopic one-tunnel transo-sseous foveal repair for triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) peripheral tear. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 138:131–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-017-2835-3. PMID: 29124362.
Article10. Staud R, Weyl EE, Bartley E, Price DD, Robinson ME. 2014; Analgesic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of muscle injections with lidocaine or saline in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Eur J Pain. 18:803–12. DOI: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00422.x. PMID: 24193993. PMCID: PMC4010579.
Article11. Yelland MJ, Glasziou PP, Bogduk N, Schluter PJ, McKernon M. 2004; Prolotherapy injections, saline injections, and exercises for chronic low-back pain: a randomized trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:9–16. DOI: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000105529.07222.5B. PMID: 14699269.
Article12. Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B, Yaşar E, Yazicioğlu K. 2013; Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 41:2609–16. DOI: 10.1177/0363546513496542. PMID: 23893418.
Article13. Wolf JM, Ozer K, Scott F, Gordon MJ, Williams AE. 2011; Comparison of autologous blood, corticosteroid, and saline injection in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter study. J Hand Surg Am. 36:1269–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.05.014. PMID: 21705157.
Article14. Ay S, Evcik D, Tur BS. 2010; Comparison of injection methods in myofascial pain syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rheumatol. 29:19–23. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-009-1307-8. PMID: 19838864.
Article15. Frost FA, Jessen B, Siggaard-Andersen J. 1980; A control, double-blind comparison of mepivacaine injection versus saline injection for myofascial pain. Lancet. 1:499–500. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(80)92761-0. PMID: 6102230.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ganglion of the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: A Case Report
- Treatment of Extensor Digiti Minimi Triggering: Two Cases Report
- Extensor Digiti Minimi Triggering Caused by an Anatomical Variation: A Case Report
- Guyon’s Canal Syndrome Caused by an Accessory Abductor Digiti Minimi Muscle
- Surgical Technique for Repairing Foveal Tear of the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Arthroscopic Knotless Repair