J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Dec;38(47):e401. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e401.
A Report on a Nationwide Surveillance System for Pediatric Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Etiology in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Gangneung Asan Hospital, College of Medicine, Ulsan University, Gangneung, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Jeonbuk National University Medical School and Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 7Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Medical Center Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Children’s Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 9Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 10Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 11Department of Pediatrics, Eulji University Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 12Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 14Department of Pediatrics, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 15Department of Pediatrics, CHA University School of Medicine, Pocheon, Korea
- 16Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children’s Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 17Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children’s Hospital, Severance Pediatric Liver Research Group, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 18Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children’s Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2548803
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e401
Abstract
- Background
Several cases of pediatric acute hepatitis of unknown etiology related to adenoviral infections have been reported in Europe since January 2022. The aim of this study was to compare the incidence, severity, possible etiology, and prognosis of the disease with those in the past in Korea.
Methods
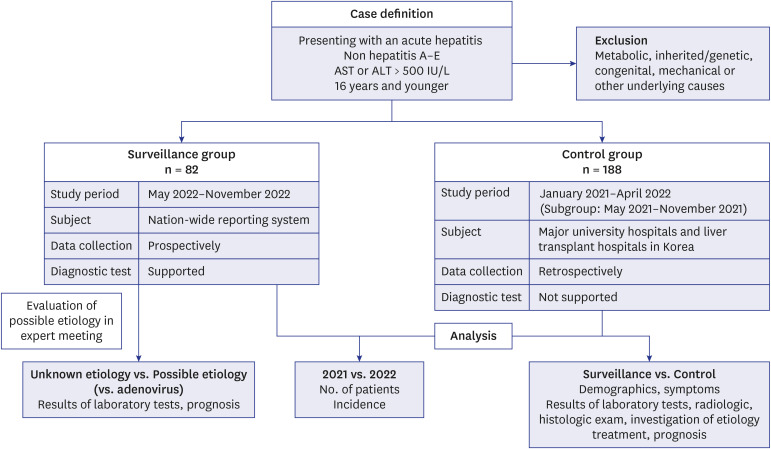
The surveillance group collected data between May and November 2022 using a surveillance system. Acute hepatitis of unknown etiology was defined in patients aged < 16 years with a serum transaminase level > 500 IU/L, not due to hepatitis A-E or other underlying causes. For comparison, data from 18 university hospitals were retrospectively collected as a control group between January 2021 and April 2022.
Results
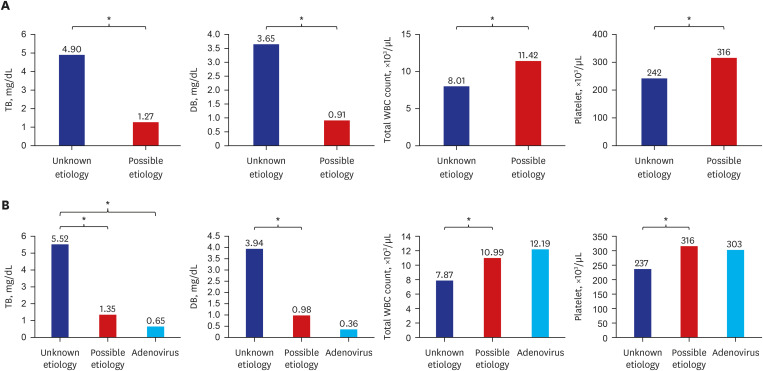
We enrolled 270 patients (mean age, 5 years). The most common symptom was fever. However, the incidence was similar between 2021 and 2022. Liver function test results, number of patients with acute liver failure (ALF), liver transplantation (LT), death, and adenovirus detection rates did not differ between the two groups. None of the adenoviruspositive patients in either group experienced ALF, LT, or death. In the surveillance group, adenovirus-associated virus-2 was detected in four patients, one of whom underwent LT. Patients with an unknown etiology showed significantly higher bilirubin levels, a lower platelet count, and a higher LT rate than patients with a possible etiology.
Conclusion
The incidence of pediatric acute hepatitis of unknown etiology and adenovirus detection rate have not increased in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jang M, Oh MS, Oh SC, Kang KS. Distribution of diseases causing liver function test abnormality in children and natural recovery time of the abnormal liver function. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31(11):1784–1789. PMID: 27709857.
Article2. Chan HL, Kwan AC, To KF, Lai ST, Chan PK, Leung WK, et al. Clinical significance of hepatic derangement in severe acute respiratory syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11(14):2148–2153. PMID: 15810082.
Article3. Eisenhut M, Thorburn K, Ahmed T. Transaminase levels in ventilated children with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30(5):931–934. PMID: 15024569.
Article4. Lee Y, Yi DY, Lee YM, Choi SY, Choi YJ, Lee KJ. A multicenter study of real-world practice for management of abnormal liver function tests in children with acute infectious diseases. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(47):e310. PMID: 34873882.
Article5. World Health Organization. Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Aetiology–the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2022.6. World Health Organization. Multi-Country – Acute, Severe Hepatitis of Unknown Origin in Children. Disease Outbreak News. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2022.7. UK Health Security Agency. Investigation into acute hepatitis of unknown aetiology in children in England, technical briefing 2. Updated 2022. Accessed May 7, 2022. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1073704/acute-hepatitis-technical-briefing-2.pdf .8. Baker JM, Buchfellner M, Britt W, Sanchez V, Potter JL, Ingram LA, et al. Acute hepatitis and adenovirus infection among children - Alabama, October 2021-February 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(18):638–640. PMID: 35511732.
Article9. Ho A, Orton R, Tayler R, Asamaphan P, Herder V, Davis C, et al. Adeno-associated virus 2 infection in children with non-A-E hepatitis. Nature. 2023; 617(7961):555–563. PMID: 36996873.
Article10. UK Health Security Agency. Investigation into acute hepatitis of unknown aetiology in children in England. Technical briefing 3. Updated 2022. Accessed May 19, 2022. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1077027/acute-hepatitis-technical-briefing_3.pdf .11. Schaberg KB, Kambham N, Sibley RK, Higgins JP. Adenovirus hepatitis: clinicopathologic analysis of 12 consecutive cases from a single institution. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017; 41(6):810–819. PMID: 28296681.12. Squires RH Jr, Shneider BL, Bucuvalas J, Alonso E, Sokol RJ, Narkewicz MR, et al. Acute liver failure in children: the first 348 patients in the pediatric acute liver failure study group. J Pediatr. 2006; 148(5):652–658. PMID: 16737880.
Article13. World Health Organization. Laboratory Testing for Severe Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Aetiology in Children: Interim Guidance. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2022.14. Cates J, Baker JM, Almendares O, Kambhampati AK, Burke RM, Balachandran N, et al. Interim analysis of acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children aged <10 years - United States, October 2021–June 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(26):852–858. PMID: 35771734.15. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Increase in Severe Acute Hepatitis Cases of Unknown Aetiology in Children. Solna, Sweden: ECDC;2022.16. Kambhampati AK, Burke RM, Dietz S, Sheppard M, Almendares O, Baker JM, et al. Trends in acute hepatitis of unspecified etiology and adenovirus stool testing results in children - United States, 2017–2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(24):797–802. PMID: 35709071.17. Kim KR, Won J, Kim H, Kim BI, Kim MJ, Kim JY, et al. The changes in respiratory and enteric adenovirus epidemiology in Korea from 2017 to June 2022. J Korean Med Sci. 2023; 38(9):e71. PMID: 36880111.
Article18. UK Health Security Agency. Investigation into acute hepatitis of unknown aetiology in children in England, technical briefing 4. Updated 2022. Accessed July 26, 2022. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1094573/acute-hepatitis-technical-briefing-4.pdf .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Changes in Respiratory and Enteric Adenovirus Epidemiology in Korea From 2017 to June 2022
- Evaluation of the acute hepatitis B surveillance system in the Republic of Korea following the transition to mandatory surveillance
- Erythrovirus B19 Infection in Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Etiology
- Perspective of Nationwide Surveillance System for Surgical Site Infections
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination