J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2023 Nov;40(Suppl):S87-S92. 10.12701/jyms.2023.00108.
Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the vulva: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Pathology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2548347
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00108
Abstract
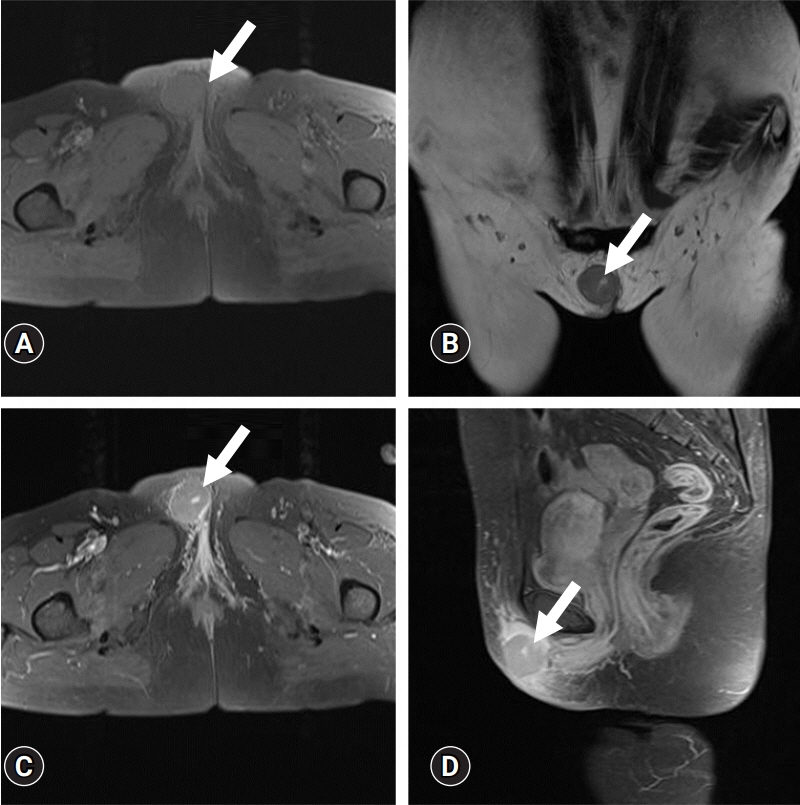
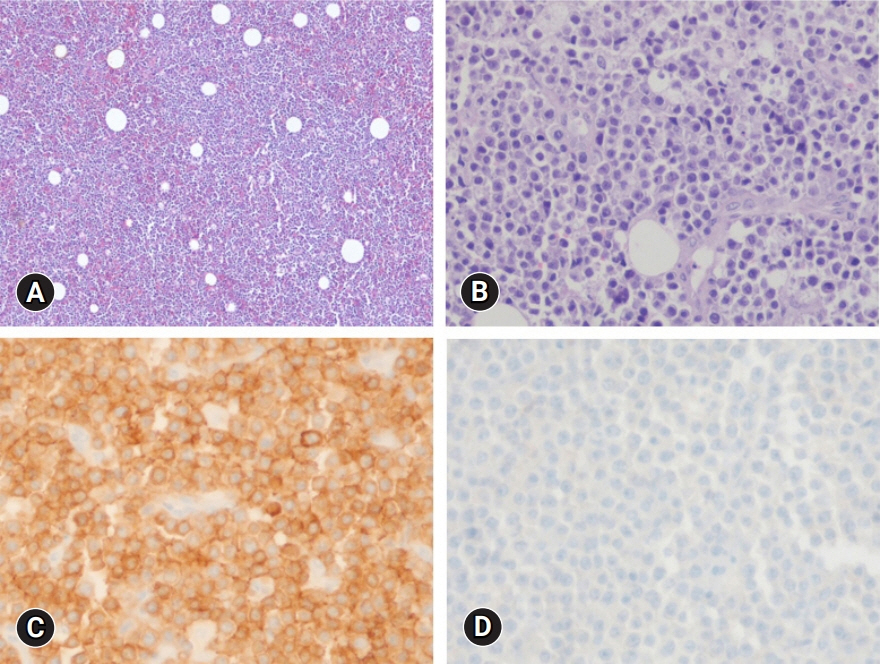
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and is estimated to account for approximately 30% of all NHL cases. NHL can also occur in the female genital tract and accounts for approximately 1.5% of all NHL cases. Many doctors have difficulty diagnosing or treating vulvar DLBCL because of its very low prevalence. A 55-year-old woman presented with a solid mass on the right side of the vulva. No significantly enlarged lymph nodes were observed in the inguinal region. She underwent excisional biopsy at our institution. DLBCL was diagnosed based on histological examination. According to the Hans algorithm, the lesion was diagnosed as a non-germinal center B-cell-like subtype. The patient was referred to a hematologic oncologist. The disease stage was classified as IE according to the Ann Arbor staging classification. The patient received four cycles of chemotherapy with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone and localized radiation therapy with 36 Gy in 20 fractions. She showed complete remission and maintained this status on the latest computed tomography scan. Gynecologists should rule out lymphoma in patients presenting with a vulvar mass.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. García Zueco JC, Delgado P. Epidemiology of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Sangre (Barc). 1994; 39:267–75.2. Sehn LH, Salles G. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:842–58.
Article3. Signorelli M, Maneo A, Cammarota S, Isimbaldi G, Garcia Parra R, Perego P, et al. Conservative management in primary genital lymphomas: the role of chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. 2007; 104:416–21.
Article4. Ye AL, Willis MS, Link BK, Naridze RL, Syrbu SI, Liu V. Primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the vulva: two new cases of a rare entity and review of the literature. JAAD Case Rep. 2018; 4:962–7.5. Clemente N, Alessandrini L, Rupolo M, Bulian P, Lucia E, Canzonieri V, et al. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the vulva: a case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3041.6. Sehn LH, Donaldson J, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Klasa R, et al. Introduction of combined CHOP plus rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5027–33.
Article7. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004; 103:275–82.
Article8. El Kacemi H, Lalya I, Kebdani T, Benjaafar N. Primary non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the vulva in an immunocompetent patient. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015; 11:657.
Article9. Plaza JA, Kacerovska D, Stockman DL, Buonaccorsi JN, Baillargeon P, Suster S, et al. The histomorphologic spectrum of primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study of 79 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011; 33:649–55.
Article10. Tjalma WA, Van de Velde AL, Schroyens WA. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Bartholin’s gland. Gynecol Oncol. 2002; 87:308–9.
Article11. Vang R, Medeiros LJ, Fuller GN, Sarris AH, Deavers M. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma involving the gynecologic tract: a review of 88 cases. Adv Anat Pathol. 2001; 8:200–17.
Article12. Iczkowski KA, Han AC, Edelson MI, Rosenblum NG. Primary, localized vulvar B-cell lymphoma expressing CD44 variant 6 but not cadherins: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2000; 45:853–6.13. Kaplan EJ, Chadburn A, Caputo TA. HIV-related primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the vulva. Gynecol Oncol. 1996; 61:131–8.
Article14. Nam JH, Park MC, Lee KH, Yoon C, Park HR, Chun BK. Primary non-Hodgkin’s malignant lymphoma of the vulva: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 1992; 7:271–5.
Article15. Shetty AS, Menias CO. MR imaging of vulvar and vaginal cancer. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2017; 25:481–502.16. Onyiuke I, Kirby AB, McCarthy S. Primary gynecologic lymphoma: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:W648–55.
Article17. Jenkins N, Husband J, Sellars N, Gore M. MRI in primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the vagina associated with a uterine congenital anomaly. Br J Radiol. 1997; 70:219–22.
Article18. Thyagarajan MS, Dobson MJ, Biswas A. Case report: appearance of uterine cervical lymphoma on MRI: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Radiol. 2004; 77:512–5.19. Griffin N, Grant LA, Sala E. Magnetic resonance imaging of vaginal and vulval pathology. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:1269–80.
Article20. McNicholas MM, Fennelly JJ, MacErlaine DP. Imaging of primary vaginal lymphoma. Clin Radiol. 1994; 49:130–2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- Primary Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Developing at the Ileocolonic Anastomosis Site after Right Hemicolectomy for Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Primary Rectal Diffuse Large B Cell LymphomaPresented as Multiple Polypoid Lesions