J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Nov;38(43):e339. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e339.
Etiology and Clinical Characteristics of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Korean Children During the PreCOVID-19 Period, 2015-2020
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e339
Abstract
- Background
There have been many epidemiologic studies on community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) among children, most of which had substantial limitations. This study investigated the etiologic distribution and clinical characteristics of CAP in Korean children for 5 years before the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of children hospitalized for CAP at 4 referral hospitals during 2015-2020 was performed. Cases in which bronchiolitis was suspected or pulmonary infiltration was not evident on chest radiography (CXR) were excluded. Viruses and atypical bacteria were defined as detected when positive in the polymerase chain reaction test performed for respiratory specimens. Serologic testing result for Mycoplasma pneumoniae was incorporated with strict interpretation. Pyogenic bacteria were included only when cultured in blood, pleural fluid, or bronchoalveolar lavage, but those cultured in endotracheal aspirate or sputum when the case was clinically evident bacterial pneumonia were also included.
Results
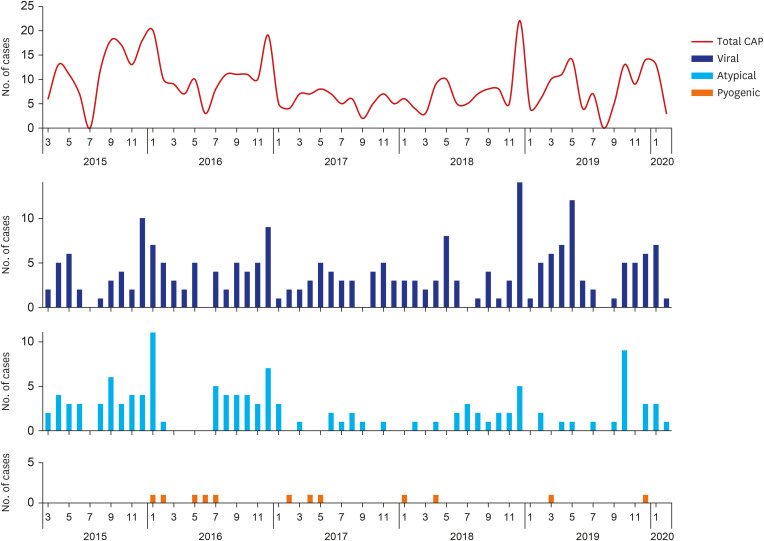
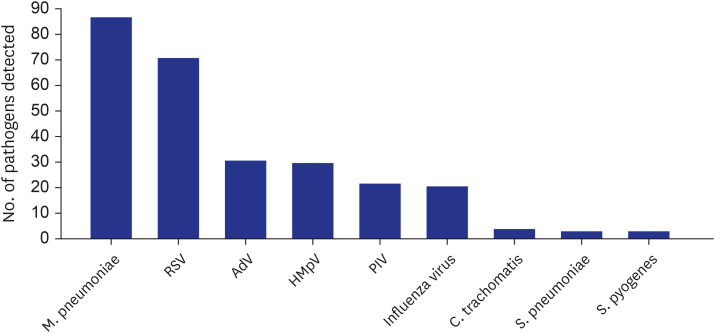
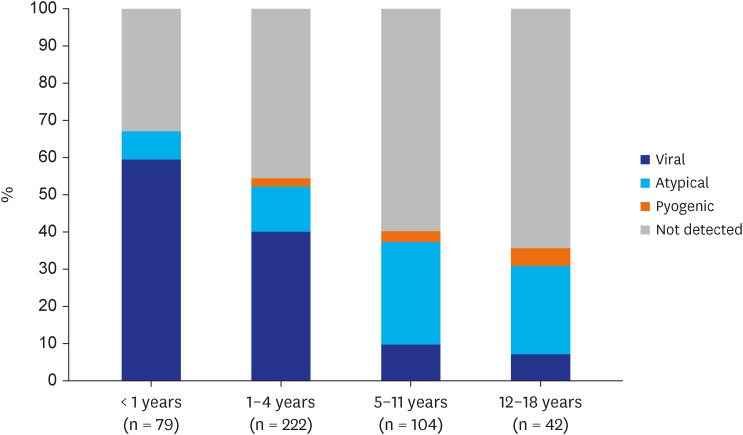
A total of 2,864 cases of suspected pneumonia were selected by diagnosis code and CXR findings. Medical chart and CXR review excluded nosocomial pneumonia and cases without evident infiltration, resulting in 517 (18.1%) CAP cases among 489 children. Regarding clinical symptoms, high fever was present in 59.4% and dyspnea in 19.9% of cases. Respiratory support was required for 29.2% of patients, including mechanical ventilation for 3.9%. Pathogens were detected in 49.9% of cases, with viruses in 32.3%, atypical bacteria in 17.8%, and pyogenic bacteria in 2.3% of cases. As single pathogens, M. pneumoniae (16.8%) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV, 13.7%) were the most common. Parenteral β-lactam and macrolide antibiotics were administered in 81.6% and 50.7% of cases, respectively. A total of 12 (2.3%) cases resulted in poor outcomes, including 3 deaths.
Conclusion
M. pneumoniae and RSV were the most commonly detected pathogens of pediatric CAP, which was selected by strict clinical and radiologic criteria. It is necessary to carefully decide whether to use parenteral antibiotics based on the epidemiology and clinical features of CAP in children.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fact sheet - pneumonia. Updated 2021. Accessed August 9, 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia .2. Jain S, Williams DJ, Arnold SR, Ampofo K, Bramley AM, Reed C, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(9):835–845. PMID: 25714161.
Article3. Witt WP, Weiss AJ, Elixhauser A. Overview of hospital stays for children in the United States, 2012. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Rockville, MD, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality;2006.4. Shin EJ, Kim Y, Jeong JY, Jung YM, Lee MH, Chung EH. The changes of prevalence and etiology of pediatric pneumonia from National Emergency Department Information System in Korea, between 2007 and 2014. Korean J Pediatr. 2018; 61(9):291–300. PMID: 30274507.
Article5. Lee E, Kim CH, Lee YJ, Kim HB, Kim BS, Kim HY, et al. Annual and seasonal patterns in etiologies of pediatric community-acquired pneumonia due to respiratory viruses and Mycoplasma pneumoniae requiring hospitalization in South Korea. BMC Infect Dis. 2020; 20(1):132. PMID: 32050912.6. Roh EJ, Lee MH, Lee JY, Kim HB, Ahn YM, Kim JK, et al. Analysis of national surveillance of respiratory pathogens for community-acquired pneumonia in children and adolescents. BMC Infect Dis. 2022; 22(1):330. PMID: 35379181.
Article7. Turner GD, Bunthi C, Wonodi CB, Morpeth SC, Molyneux CS, Zaki SR, et al. The role of postmortem studies in pneumonia etiology research. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:Suppl 2. (Suppl 2):S165–S171. PMID: 22403232.
Article8. Zhang Y, Huang Y, Ai T, Luo J, Liu H. Effect of COVID-19 on childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Chengdu, China. BMC Pediatr. 2021; 21(1):202. PMID: 33910509.9. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, et al. The management of community-acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 53(7):e25–e76. PMID: 21880587.
Article10. Kim NH, Lee JA, Eun BW, Shin SH, Chung EH, Park KW, et al. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and the indirect particle agglutination antibody test for the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children during two outbreaks. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007; 26(10):897–903. PMID: 17901794.
Article11. Self WH, Williams DJ, Zhu Y, Ampofo K, Pavia AT, Chappell JD, et al. Respiratory viral detection in children and adults: comparing asymptomatic controls and patients with community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 2016; 213(4):584–591. PMID: 26180044.
Article12. Martin ET, Fairchok MP, Kuypers J, Magaret A, Zerr DM, Wald A, et al. Frequent and prolonged shedding of bocavirus in young children attending daycare. J Infect Dis. 2010; 201(11):1625–1632. PMID: 20415535.
Article13. Heimdal I, Moe N, Krokstad S, Christensen A, Skanke LH, Nordbø SA, et al. Human coronavirus in hospitalized children with respiratory tract infections: a 9-year population-based study from Norway. J Infect Dis. 2019; 219(8):1198–1206. PMID: 30418633.
Article14. Yun KW, Wallihan R, Desai A, Alter S, Ambroggio L, Cohen DM, et al. Clinical characteristics and etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in US Children, 2015-2018. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2022; 41(5):381–387. PMID: 35143427.
Article15. Yun KW, Wallihan R, Juergensen A, Mejias A, Ramilo O. Community-acquired pneumonia in children: myths and facts. Am J Perinatol. 2019; 36(S 02):S54–S57. PMID: 31238360.
Article16. Driscoll AJ, Deloria Knoll M, Hammitt LL, Baggett HC, Brooks WA, Feikin DR, et al. The effect of antibiotic exposure and specimen volume on the detection of bacterial pathogens in children with pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2017; 64(suppl_3):S368–S377. PMID: 28575366.
Article17. Spuesens EB, Fraaij PL, Visser EG, Hoogenboezem T, Hop WC, van Adrichem LN, et al. Carriage of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in the upper respiratory tract of symptomatic and asymptomatic children: an observational study. PLoS Med. 2013; 10(5):e1001444. PMID: 23690754.18. Lee WJ, Huang EY, Tsai CM, Kuo KC, Huang YC, Hsieh KS, et al. Role of serum Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgA, IgM, and IgG in the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-related pneumonia in school-age children and adolescents. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017; 24(1):e00471-16. PMID: 27760779.
Article19. Chiang WC, Teoh OH, Chong CY, Goh A, Tang JP, Chay OM. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and antimicrobial resistance patterns of community-acquired pneumonia in 1702 hospitalized children in Singapore. Respirology. 2007; 12(2):254–261. PMID: 17298459.
Article20. Chi H, Huang YC, Liu CC, Chang KY, Huang YC, Lin HC, et al. Characteristics and etiology of hospitalized pediatric community-acquired pneumonia in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020; 119(10):1490–1499. PMID: 32682702.
Article21. Yun KW, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Molecular epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus for 28 consecutive seasons (1990-2018) and genetic variability of the duplication region in the G gene of genotypes ON1 and BA in South Korea. Arch Virol. 2020; 165(5):1069–1077. PMID: 32144544.
Article22. Kim YK, Song SH, Ahn B, Lee JK, Choi JH, Choi SH, et al. Shift in clinical epidemiology of human parainfluenza virus type 3 and respiratory syncytial virus B infections in Korean children before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multicenter retrospective study. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(28):e215. PMID: 35851860.
Article