Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Oct;55(4):1198-1209. 10.4143/crt.2022.1543.
Efficacy of Limited Dose Modifications for Palbociclib-Related Grade 3 Neutropenia in Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Biostatistics and Computing, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.1543
Abstract
- Purpose
Frequent neutropenia hinders uninterrupted palbociclib treatment in patients with hormone receptor (HR)–positive breast cancer. We compared the efficacy outcomes in multicenter cohorts of patients with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) receiving palbociclib following conventional dose modification or limited modified schemes for afebrile grade 3 neutropenia.
Materials and Methods
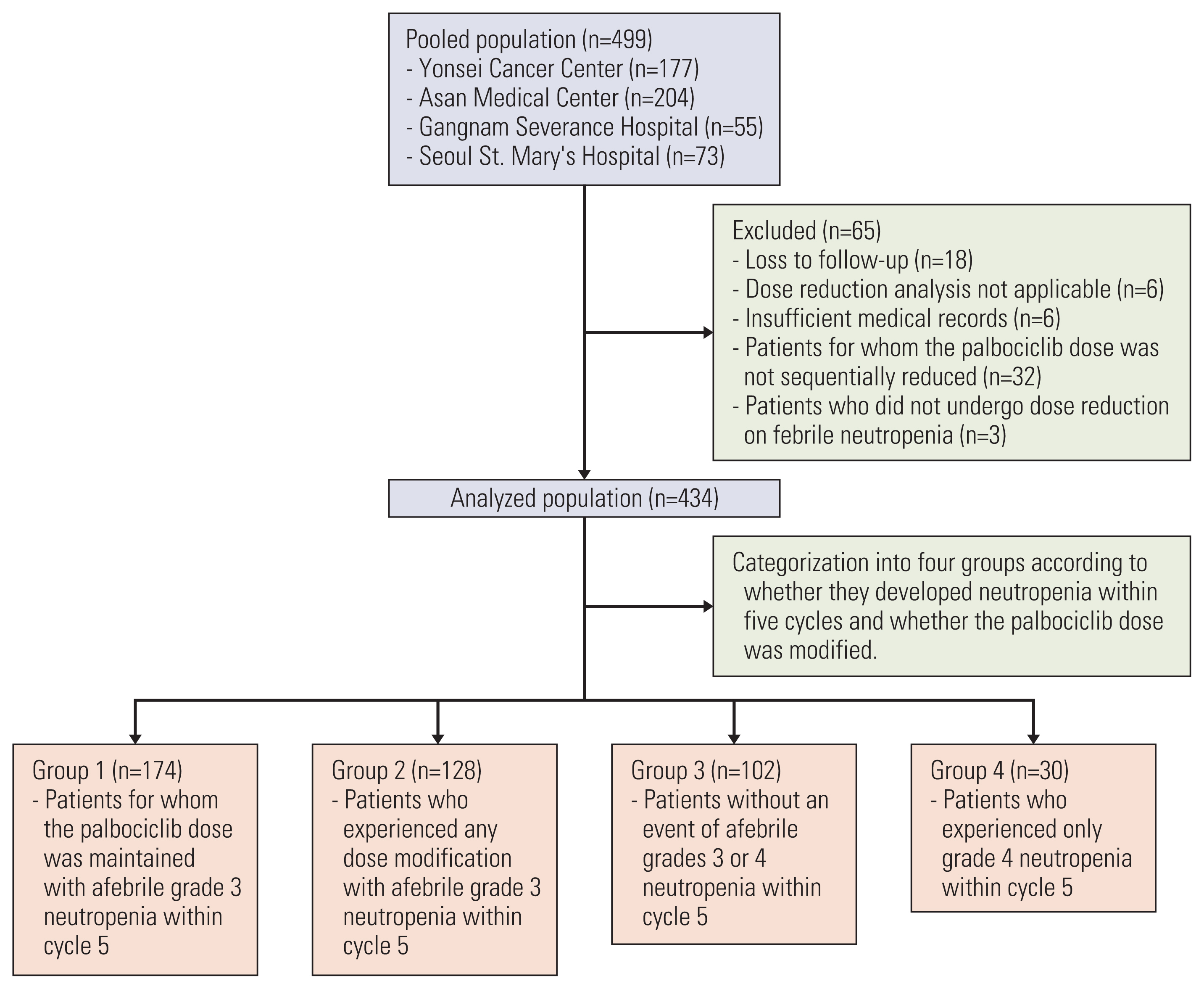
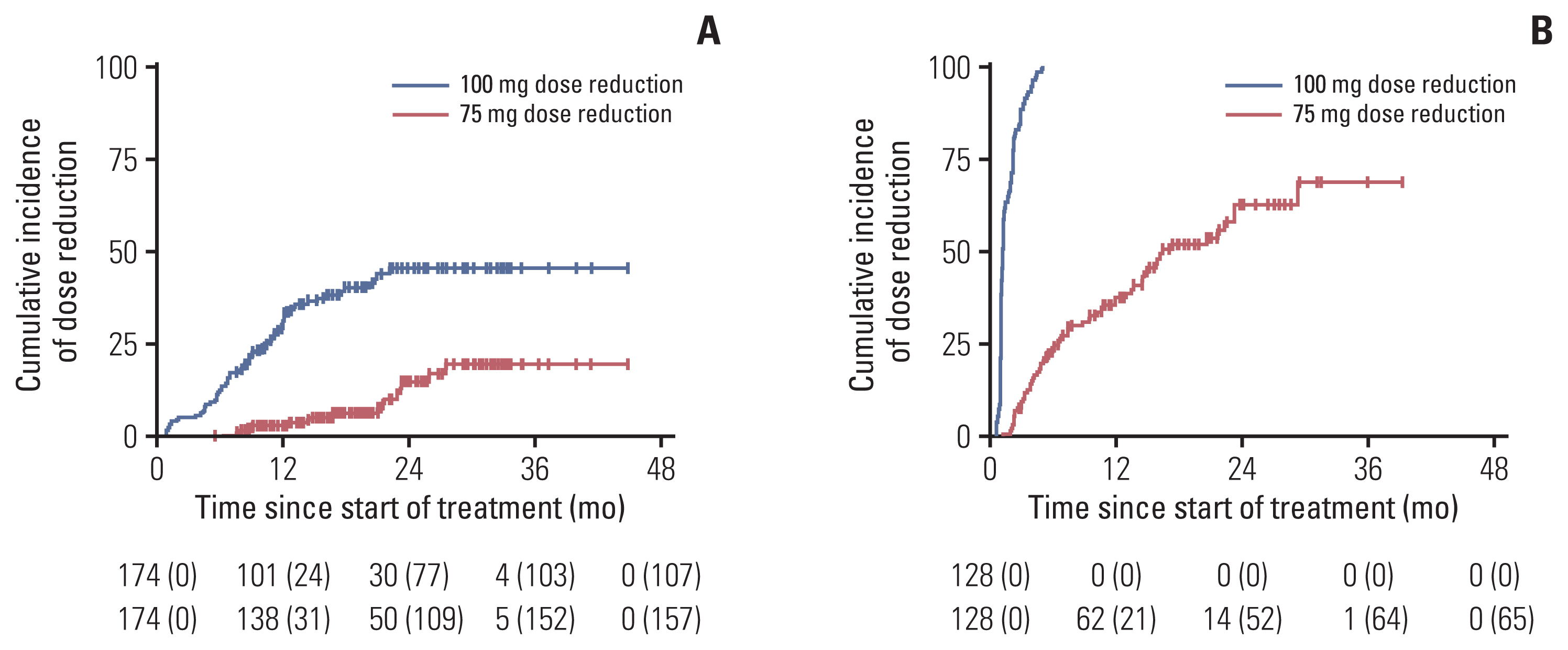
Patients with HR-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative mBC (n=434) receiving palbociclib with letrozole as first-line therapy were analyzed and classified based on neutropenia grade and afebrile grade 3 neutropenia management as follows: group 1 (maintained palbociclib dose, limited scheme), group 2 (dose delay or reduction, conventional scheme), group 3 (no afebrile grade 3 neutropenia event), and group 4 (grade 4 neutropenia event). The primary and secondary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) between groups 1 and 2 and PFS, overall survival, and safety profiles among all groups.
Results
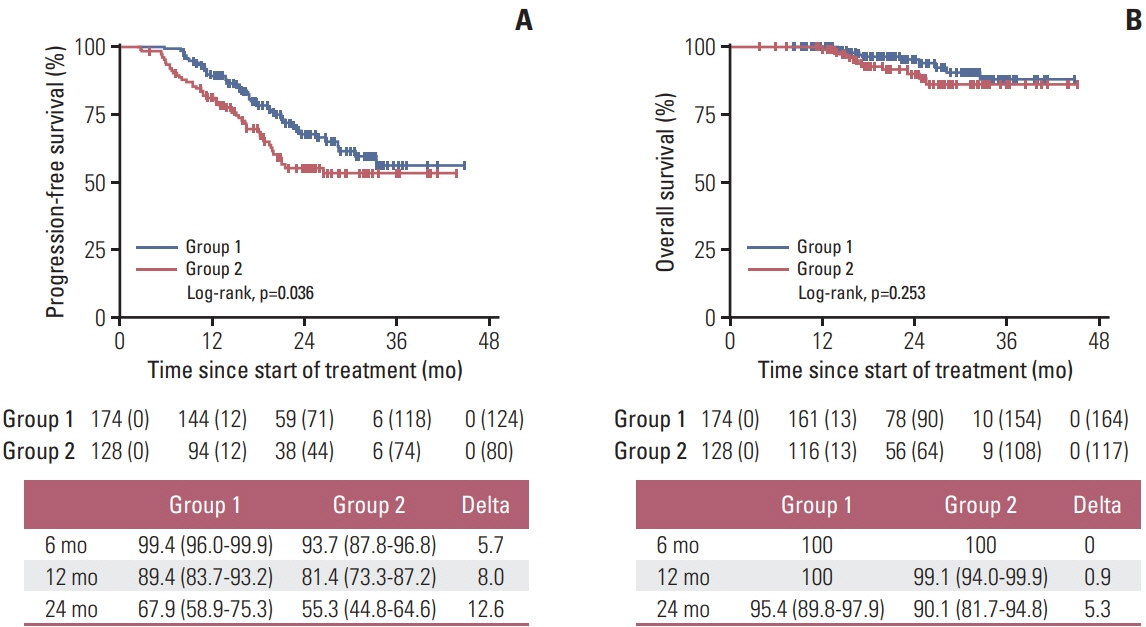
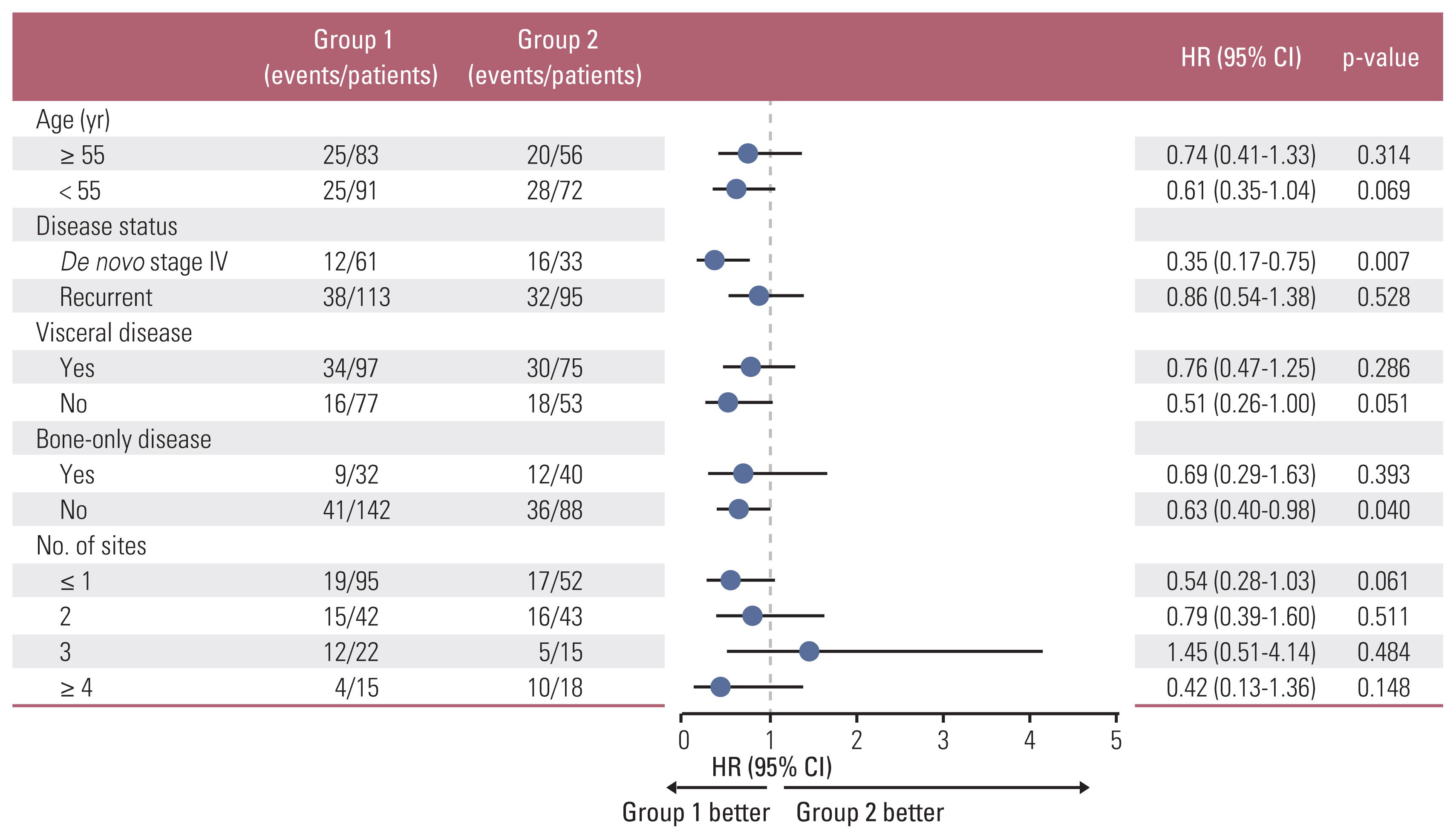
During follow-up (median 23.7 months), group 1 (2-year PFS, 67.9%) showed significantly longer PFS than did group 2 (2-year PFS, 55.3%; p=0.036), maintained across all subgroups, and upon adjustment of the factors. Febrile neutropenia occurred in one and two patients of group 1 and group 2, respectively, without mortality.
Conclusion
Limited dose modification for palbociclib-related grade 3 neutropenia may lead to longer PFS, without increasing toxicity, than the conventional dose scheme.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im SA, Gelmon K, et al. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1925–36.2. Cristofanilli M, Rugo HS, Im SA, Slamon DJ, Harbeck N, Bondarenko I, et al. Overall survival (OS) with palbociclib (PAL) + fulvestrant (FUL) in women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2−) advanced breast cancer (ABC): updated analyses from PALOMA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39(15 Suppl):1000.3. Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1738–48.4. Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, et al. Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:2465–72.5. Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, et al. The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020; 6:116–24.6. Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J, Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, et al. MONARCH 3: abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:3638–46.7. Im SA, Lu YS, Bardia A, Harbeck N, Colleoni M, Franke F, et al. Overall survival with ribociclib plus endocrine therapy in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:307–16.8. Mayer EL, Dueck AC, Martin M, Rubovszky G, Burstein HJ, Bellet-Ezquerra M, et al. Palbociclib with adjuvant endocrine therapy in early breast cancer (PALLAS): interim analysis of a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021; 22:212–22.9. Johnston SR, Harbeck N, Hegg R, Toi M, Martin M, Shao ZM, et al. Abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy for the adjuvant treatment of HR+, HER2-, node-positive, high-risk, early breast cancer (monarchE). J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:3987–98.10. Cunningham NC, Turner NC. Understanding divergent trial results of adjuvant CDK4/6 inhibitors for early stage breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2021; 39:307–9.11. O’Leary B, Finn RS, Turner NC. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016; 13:417–30.12. Hu W, Sung T, Jessen BA, Thibault S, Finkelstein MB, Khan NK, et al. Mechanistic investigation of bone marrow suppression associated with palbociclib and its differentiation from cytotoxic chemotherapies. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:2000–8.13. Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, Kalous O, Cohen DJ, Desai AJ, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009; 11:R77.14. Ham A, Kim MH, Kim GM, Kim JH, Kim JY, Park HS, et al. Palbociclib use with grade 3 neutropenia in hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020; 183:107–16.15. IBRANCE (palbociclib). Summary of product characteristics. Sandwich: Pfizer Ltd.;2018.16. Berek JS, Matulonis UA, Peen U, Ghatage P, Mahner S, Redondo A, et al. Safety and dose modification for patients receiving niraparib. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:1784–92.17. Sun W, O’Dwyer PJ, Finn RS, Ruiz-Garcia A, Shapiro GI, Schwartz GK, et al. Characterization of neutropenia in advan-ced cancer patients following palbociclib treatment using a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation approach. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017; 57:1159–73.18. Budman DR, Berry DA, Cirrincione CT, Henderson IC, Wood WC, Weiss RB, et al. Dose and dose intensity as determinants of outcome in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. The Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90:1205–11.19. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Increasing the dose intensity of chemotherapy by more frequent administration or sequential scheduling: a patient-level meta-analysis of 37 298 women with early breast cancer in 26 randomised trials. Lancet. 2019; 393:1440–52.20. Veitch Z, Khan OF, Tilley D, Tang PA, Ribnikar D, Stewart DA, et al. Impact of cumulative chemotherapy dose on survival with adjuvant FEC-D chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019; 17:957–67.21. Shirotake S, Yasumizu Y, Ito K, Masunaga A, Ito Y, Miyazaki Y, et al. Impact of second-line targeted therapy dose intensity on patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2016; 14:e575–83.22. Di Leo A, Jerusalem G, Petruzelka L, Torres R, Bondarenko IN, Khasanov R, et al. Results of the CONFIRM phase III trial comparing fulvestrant 250 mg with fulvestrant 500 mg in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:4594–600.23. Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N, et al. Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:1926–36.24. Im SA, Mukai H, Park IH, Masuda N, Shimizu C, Kim SB, et al. Palbociclib plus letrozole as first-line therapy in postmenopausal Asian women with metastatic breast cancer: results from the phase III, randomized PALOMA-2 study. J Glob Oncol. 2019; 5:1–19.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hormone Treatment for Breast Cancer
- Comparison of the Efficacy between First-Line Treatment Regimens for Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive and HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Palbociclib Plus Fulvestrant in Korean Patients from PALOMA-3 With Hormone Receptor-Positive/Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer
- The Therapeutic Effect of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor on Relapsed Ectopic Male Breast Cancer
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Patient Treated with Letrozole and Palbociclib