J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Oct;38(42):e362. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e362.
Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization Versus Radiofrequency Ablation as an Initial Treatment of Single Small (≤ 3 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2547563
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e362
Abstract
- Background
In this study, we aimed to compare the long-term therapeutic outcomes of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) with those of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for the initial treatment of a single small (≤ 3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
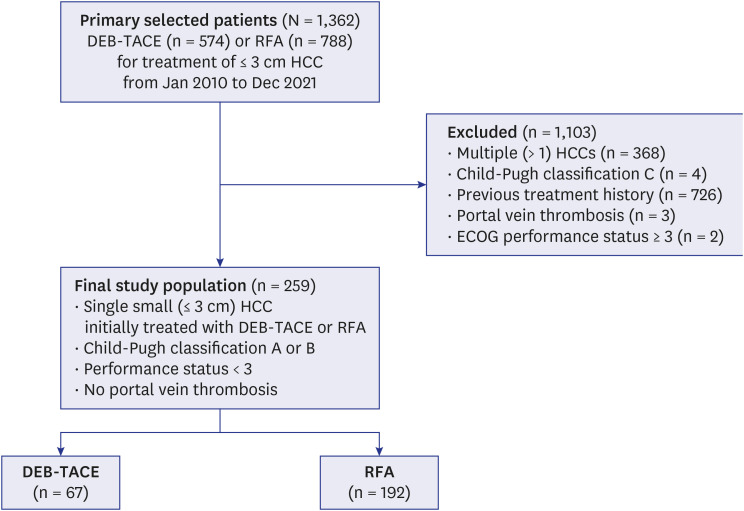
From January 2010 to December 2021, 259 consecutive patients who underwent DEB-TACE (67 patients) or RFA (192 patients) as a first-line treatment for a single small HCC were enrolled in this retrospective study. The therapeutic outcomes, including cumulative intrahepatic local tumor progression (LTP), progression-free survival (PFS), and longterm overall survival (OS) rates, were compared between the two groups before and after propensity score (PS) matching. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard models were used to evaluate the prognostic factors and differences in OS and PFS between the two groups for all 92 patients after PS matching.
Results
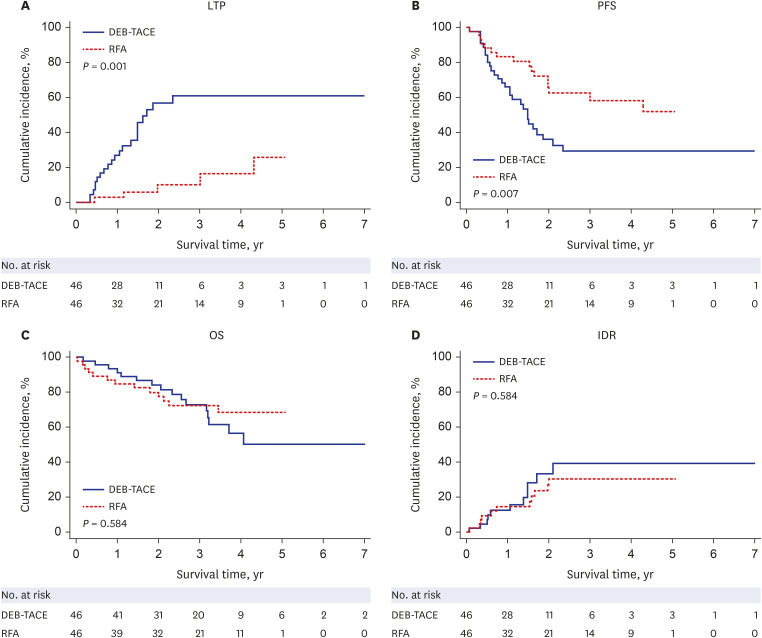
After PS matching, the 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year LTP rates were lower in the RFA group than those in the DEB-TACE group (P < 0.001), and the 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year PFS rates in the RFA group were higher than those in the DEB-TACE group (P = 0.007). However, the 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were not significantly different between the RFA and DEB-TACE groups (P = 0.584). Moreover, the OS was not significantly different between the RFA and DEB-TACE groups in the univariate and multivariate analyses, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.81. The PFS was significantly higher in the RFA group than that in the DEB-TACE group in the univariate analyses, with a HR of 0.44 (P = 0.009). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that albumin (P = 0.019) was an independent prognostic factor for OS. Additionally, the major complication rates were not significantly different between the DEB-TACE and RFA groups (P = 1.000).
Conclusion
The LTP and PFS rates of RFA were superior to those of DEB-TACE in the initial treatment of single small HCC after PS matching. However, the OS rates were not significantly different between RFA and DEB-TACE. Therefore, DEB-TACE may be considered an efficient substitute for RFA in some patients with a single small HCC who are ineligible for RFA.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. European Association for the Study of the Liver. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56(4):908–943. PMID: 22424438.2. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: the 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022; 76(3):681–693. PMID: 34801630.3. Lencioni R. Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 52(2):762–773. PMID: 20564355.4. Lee MW, Kim YJ, Park HS, Yu NC, Jung SI, Ko SY, et al. Targeted sonography for small hepatocellular carcinoma discovered by CT or MRI: factors affecting sonographic detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194(5):W396–W400. PMID: 20410384.5. Kim YS, Rhim H, Cho OK, Koh BH, Kim Y. Intrahepatic recurrence after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the pattern and risk factors. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 59(3):432–441. PMID: 16690240.6. Zhang Y, Zhang MW, Fan XX, Mao DF, Ding QH, Zhuang LH, et al. Drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization sequentially combined with radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of untreated and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2020; 12(8):355–368. PMID: 32903981.7. Hong K, Khwaja A, Liapi E, Torbenson MS, Georgiades CS, Geschwind JF. New intra-arterial drug delivery system for the treatment of liver cancer: preclinical assessment in a rabbit model of liver cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12(8):2563–2567. PMID: 16638866.8. Lee KH, Liapi EA, Cornell C, Reb P, Buijs M, Vossen JA, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded QuadraSphere microspheres: plasma pharmacokinetics and intratumoral drug concentration in an animal model of liver cancer. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33(3):576–582. PMID: 20087738.9. Lee KH, Joo SM, Yum TJ, Jung SH. Conventional versus drug-eluting beads trans-arterial chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma at very early and early stages. J Liver Cancer. 2017; 17(2):144–152.10. Kim JW, Kim JH, Sung KB, Ko HK, Shin JH, Kim PN, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization vs. radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma 2 cm or smaller. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109(8):1234–1240. PMID: 24935276.11. Suh YJ, Jin YJ, Jeong Y, Shin WY, Lee JM, Cho S, et al. Resection or ablation versus transarterial therapy for Child-Pugh A patients with a single small hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021; 100(43):e27470. PMID: 34713824.12. Hsu CY, Huang YH, Chiou YY, Su CW, Lin HC, Lee RC, et al. Comparison of radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a propensity score analysis. Liver Transpl. 2011; 17(5):556–566. PMID: 21506244.13. Kim TH, Kim NH, Kim JD, Kim YN, Kim YJ, Kim EJ, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting bead compared with radiofrequency ablation for treatment of single small hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot non-randomized trial. J Liver Cancer. 2021; 21(2):146–154. PMID: 37383084.14. Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG). National Cancer Center, Korea (NCC). 2014 Korean Liver Cancer Study Group-National Cancer Center Korea practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16(3):465–522. PMID: 25995680.15. Gaba RC, Lewandowski RJ, Hickey R, Baerlocher MO, Cohen EI, Dariushnia SR, et al. Transcatheter therapy for hepatic malignancy: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016; 27(4):457–473. PMID: 26851158.16. Goldberg SN, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, Gervais DA, Gillams AR, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: proposal for standardization of terms and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2003; 228(2):335–345. PMID: 12893895.17. Punt CJ, Buyse M, Köhne CH, Hohenberger P, Labianca R, Schmoll HJ, et al. Endpoints in adjuvant treatment trials: a systematic review of the literature in colon cancer and proposed definitions for future trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007; 99(13):998–1003. PMID: 17596575.18. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2005; 235(3):728–739. PMID: 15845798.19. Lam VW, Ng KK, Chok KS, Cheung TT, Yuen J, Tung H, et al. Incomplete ablation after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of risk factors and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15(3):782–790. PMID: 18095030.20. Kang TW, Lim HK, Lee MW, Kim YS, Choi D, Rhim H. Perivascular versus nonperivascular small HCC treated with percutaneous RF ablation: retrospective comparison of long-term therapeutic outcomes. Radiology. 2014; 270(3):888–899. PMID: 24475820.21. Peng ZW, Lin XJ, Zhang YJ, Liang HH, Guo RP, Shi M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas 2 cm or smaller: a retrospective comparative study. Radiology. 2012; 262(3):1022–1033. PMID: 22357902.22. Nakazawa T, Kokubu S, Shibuya A, Ono K, Watanabe M, Hidaka H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between local tumor progression after ablation and ablative margin. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188(2):480–488. PMID: 17242258.23. Lee M, Chung JW, Lee KH, Won JY, Chun HJ, Lee HC, et al. Korean multicenter registry of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting embolic agents for nodular hepatocellular carcinomas: six-month outcome analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28(4):502–512. PMID: 27856136.24. Idée JM, Guiu B. Use of Lipiodol as a drug-delivery system for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013; 88(3):530–549. PMID: 23921081.25. Lee DH, Lee JM, Lee JY, Kim SH, Yoon JH, Kim YJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in 162 patients with cirrhosis. Radiology. 2014; 270(3):900–909. PMID: 24475823.26. Woo HY, Heo J. Transarterial chemoembolization using drug eluting beads for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: now and future. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015; 21(4):344–348. PMID: 26770921.27. Facciorusso A, Mariani L, Sposito C, Spreafico C, Bongini M, Morosi C, et al. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 31(3):645–653. PMID: 26331807.28. Malagari K, Pomoni M, Kelekis A, Pomoni A, Dourakis S, Spyridopoulos T, et al. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with BeadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33(3):541–551. PMID: 19937027.29. Razi M, Safiullah S, Gu J, He X, Razi M, Kong J. Comparison of tumor response following conventional versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in early- and very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Interv Med. 2021; 5(1):10–14. PMID: 35586278.30. Zou JH, Zhang L, Ren ZG, Ye SL. Efficacy and safety of cTACE versus DEB-TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Dig Dis. 2016; 17(8):510–517. PMID: 27384075.31. D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006; 44(1):217–231. PMID: 16298014.32. Fleck A, Raines G, Hawker F, Trotter J, Wallace PI, Ledingham IM, et al. Increased vascular permeability: a major cause of hypoalbuminaemia in disease and injury. Lancet. 1985; 325(8432):781–784.33. Wang H, Cao C, Wei X, Shen K, Shu Y, Wan X, et al. A comparison between drug-eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials. J Cancer Res Ther. 2020; 16(2):243–249. PMID: 32474508.34. Fonseca AZ, Santin S, Gomes LG, Waisberg J, Ribeiro MA Jr. Complications of radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: frequency and risk factors. World J Hepatol. 2014; 6(3):107–113. PMID: 24672640.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting bead compared with radiofrequency ablation for treatment of single small hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot non-randomized trial
- Complications Related to Transarterial Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
- Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?