J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Oct;38(42):e330. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e330.
Community-Acquired Pneumococcal Pneumonia in Highly Vaccinated Population: Analysis by Serotypes, Vaccination Status, and Underlying Medical Conditions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Asia Pacific Influenza Institute, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Vaccine Innovation Center-KU Medicine (VIC-K), Seoul, Korea
- 4Vaccine Innovation Center-KU Medicine (VIC-K), Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 6Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea
- 7Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e330
Abstract
- Background
Targeted risk population has been highly vaccinated against pneumococcal diseases in South Korea. Despite this, the pneumococcal serotype distribution is evolving, which impedes efficient roll-out of vaccines.
Methods
This prospective cohort study included patients aged ≥ 19 years with communityacquired pneumonia (CAP) from five university hospitals in South Korea between September 2018 and July 2021. The outcomes of interest were the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with CAP, pneumococcal serotype distribution, and risk factors of 30-day mortality in patients with pneumococcal CAP (pCAP). Considering the high seroprevalence, we analyzed the clinical characteristics of serotype 3 pCAP.
Results
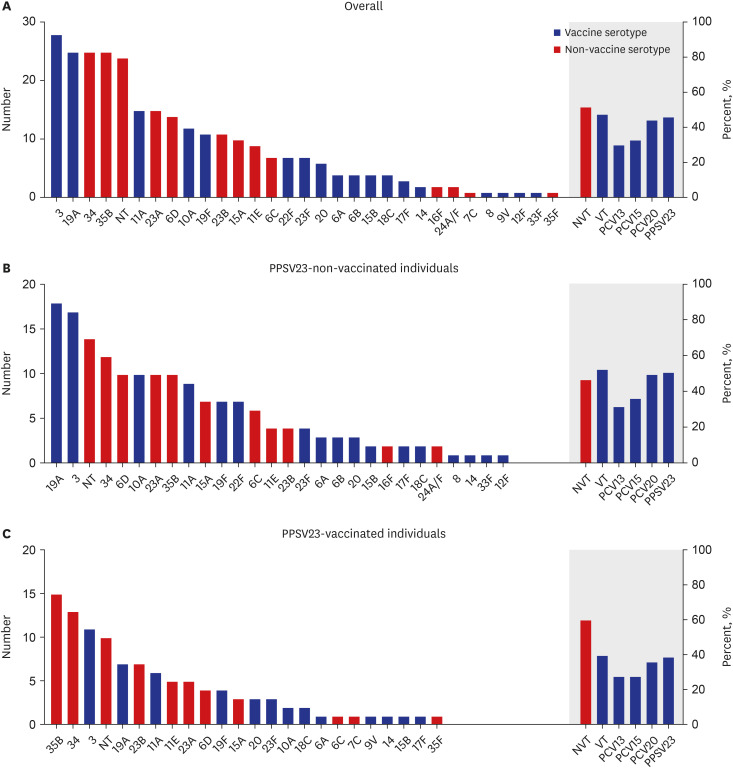
A total of 5,009 patients hospitalized with CAP was included (mean age ± standard deviation, 70.3 ± 16.0 years; 3,159 [63.1%] men). Streptococcus pneumoniae was the leading causative agent of CAP (11.8% overall, 17.7% in individuals aged < 65 years with chronic medical conditions). Among the 280 serotyped Streptococcus pneumococcus, serotype 3 was the most common (10.0%), followed by serotypes 19A (8.9%), 34 (8.9%), and 35B (8.9%). Non-vaccine serotypes (serotype 35B [13.9%] and 34 [12.0%]) were the most prevalent in 108 individuals vaccinated with 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). Serotype 3 was prevalent, irrespective of PPSV23 vaccination status, and more common in individuals with chronic lung disease (P = 0.008). Advanced age (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.040; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.011–1.071), long-term care facility residence (aOR, 2.161; 95% CI, 1.071–4.357), and bacteremia (aOR, 4.193; 95% CI, 1.604–10.962) were independent risk factors for 30-day mortality in patients with pCAP. PPSV23 vaccination reduced the risk of mortality (aOR, 0.507; 95% CI, 0.267–0.961).
Conclusion
Serotype 3 and 19A were still the most common serotypes of pCAP in South Korea despite the national immunization program of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugated vaccine in children and PPSV23 in old adults. PPSV23 vaccination might reduce the risk of mortality in patients with pCAP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Global health estimates: life expectancy and leading causes of death and disability. Updated 2020. Accessed March 8, 2023. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates .2. Said MA, Johnson HL, Nonyane BA, Deloria-Knoll M, O’Brien KL, Andreo F, et al. Estimating the burden of pneumococcal pneumonia among adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic techniques. PLoS One. 2013; 8(4):e60273. PMID: 23565216.3. Hausdorff WP, Feikin DR, Klugman KP. Epidemiological differences among pneumococcal serotypes. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005; 5(2):83–93. PMID: 15680778.4. Song JY, Nahm MH, Moseley MA. Clinical implications of pneumococcal serotypes: invasive disease potential, clinical presentations, and antibiotic resistance. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28(1):4–15. PMID: 23341706.5. Ganaie F, Saad JS, McGee L, van Tonder AJ, Bentley SD, Lo SW, et al. A new pneumococcal capsule type, 10D, is the 100th serotype and has a large cps fragment from an oral streptococcus. MBio. 2020; 11(3):e00937-20. PMID: 32430472.6. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Seniors 65 Years of Age or Older Should Get the Pneumococcal Vaccine [Press Release]. Sejong, Korea: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2014.7. World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory (GHO) data. Pneumococcal conjugate 3rd dose (PCV) immunization coverage. Updated 2023. Accessed March 8, 2023. https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.PCV3n?lang=en .8. Loo JD, Conklin L, Fleming-Dutra KE, Knoll MD, Park DE, Kirk J, et al. Systematic review of the indirect effect of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine dosing schedules on pneumococcal disease and colonization. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014; 33 Suppl 2:S161–S171. PMID: 24336058.9. Shiri T, Datta S, Madan J, Tsertsvadze A, Royle P, Keeling MJ, et al. Indirect effects of childhood pneumococcal conjugate vaccination on invasive pneumococcal disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017; 5(1):e51–e59. PMID: 27955789.10. Hanquet G, Krizova P, Dalby T, Ladhani SN, Nuorti JP, Danis K, et al. Serotype replacement after introduction of 10-valent and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in 10 countries, Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022; 28(1):137–138. PMID: 34932457.11. Weinberger DM, Malley R, Lipsitch M. Serotype replacement in disease after pneumococcal vaccination. Lancet. 2011; 378(9807):1962–1973. PMID: 21492929.12. Pilishvili T, Lexau C, Farley MM, Hadler J, Harrison LH, Bennett NM, et al. Sustained reductions in invasive pneumococcal disease in the era of conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2010; 201(1):32–41. PMID: 19947881.13. Balsells E, Guillot L, Nair H, Kyaw MH. Serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae causing invasive disease in children in the post-PCV era: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12(5):e0177113. PMID: 28486544.14. Ladhani SN, Collins S, Djennad A, Sheppard CL, Borrow R, Fry NK, et al. Rapid increase in non-vaccine serotypes causing invasive pneumococcal disease in England and Wales, 2000–17: a prospective national observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018; 18(4):441–451. PMID: 29395999.15. Ben-Shimol S, Regev-Yochay G, Givon-Lavi N, van der Beek BA, Brosh-Nissimov T, Peretz A, et al. Dynamics of invasive pneumococcal disease in Israel in children and adults in the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) era: a nationwide prospective surveillance. Clin Infect Dis. 2022; 74(9):1639–1649. PMID: 34293091.16. Torres A, Menéndez R, España PP, Fernández-Villar JA, Marimón JM, Cilloniz C, et al. The evolution and distribution of pneumococcal serotypes in adults hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia in Spain using a serotype-specific urinary antigen detection test: the CAPA study, 2011–2018. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 73(6):1075–1085. PMID: 33851220.17. Pick H, Daniel P, Rodrigo C, Bewick T, Ashton D, Lawrence H, et al. Pneumococcal serotype trends, surveillance and risk factors in UK adult pneumonia, 2013–18. Thorax. 2020; 75(1):38–49. PMID: 31594801.18. Bahrs C, Kesselmeier M, Kolditz M, Ewig S, Rohde G, Barten-Neiner G, et al. A longitudinal analysis of pneumococcal vaccine serotypes in pneumonia patients in Germany. Eur Respir J. 2022; 59(2):2102432. PMID: 34824055.19. Isturiz R, Grant L, Gray S, Alexander-Parrish R, Jiang Q, Jodar L, et al. Expanded analysis of 20 pneumococcal serotypes associated with radiographically confirmed community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized US adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 73(7):1216–1222. PMID: 33982098.20. LeBlanc JJ, ElSherif M, Ye L, MacKinnon-Cameron D, Ambrose A, Hatchette TF, et al. Recalibrated estimates of non-bacteremic and bacteremic pneumococcal community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized Canadian adults from 2010 to 2017 with addition of an extended spectrum serotype-specific urine antigen detection assay. Vaccine. 2022; 40(18):2635–2646. PMID: 35315326.21. Syrogiannopoulos GA, Katopodis GD, Grivea IN, Beratis NG. Antimicrobial use and serotype distribution of nasopharyngeal Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates recovered from Greek children younger than 2 years old. Clin Infect Dis. 2002; 35(10):1174–1182. PMID: 12410477.22. Orsi A, Domnich A, Mosca S, Ogliastro M, Sticchi L, Prato R, et al. Prevalence of pneumococcal serotypes in community-acquired pneumonia among older adults in Italy: a multicenter cohort study. Microorganisms. 2022; 11(1):70. PMID: 36677362.23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccination coverage among adults in the United States, National Health Interview Survey, 2019–2020. Updated 2022. Accessed March 12, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/imz-managers/coverage/adultvaxview/pubs-resources/vaccination-coverage-adults-2019-2020.html .24. Jung YH, Choe YJ, Lee CY, Jung SO, Lee DH, Yoo JI. Impact of national pneumococcal vaccination program on invasive pneumococcal diseases in South Korea. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):15833. PMID: 36138123.25. Vestrheim DF, Høiby EA, Aaberge IS, Caugant DA. Impact of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccination program on carriage among children in Norway. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010; 17(3):325–334. PMID: 20107006.26. Heo JY, Seo YB, Choi WS, Lee J, Yoon JG, Lee SN, et al. Incidence and case fatality rates of community-acquired pneumonia and pneumococcal diseases among Korean adults: catchment population-based analysis. PLoS One. 2018; 13(3):e0194598. PMID: 29596444.27. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance and reporting of pneumococcal disease. Updated 2020. Accessed March 12, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/surveillance.html .28. Heo JY, Seo YB, Jeong HW, Choi MJ, Min KH, Choi WS, et al. Epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia in the era of extended serotype-covering multivalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Vaccine. 2020; 38(49):7747–7755. PMID: 33164798.29. Kim JH, Baik SH, Chun BC, Song JY, Bae IG, Kim HY, et al. Adult invasive pneumococcal disease in the Republic of Korea: Risk medical conditions and mortality stratified by age group. Int J Infect Dis. 2018; 74:136–144. PMID: 30055332.30. Song JY, Nahm MH, Cheong HJ, Kim WJ. Impact of preceding flu-like illness on the serotype distribution of pneumococcal pneumonia. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4):e93477. PMID: 24691515.31. Andrews NJ, Waight PA, Burbidge P, Pearce E, Roalfe L, Zancolli M, et al. Serotype-specific effectiveness and correlates of protection for the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a postlicensure indirect cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14(9):839–846. PMID: 25042756.32. Jackson LA, Gurtman A, Rice K, Pauksens K, Greenberg RN, Jones TR, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in adults 70 years of age and older previously vaccinated with 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Vaccine. 2013; 31(35):3585–3593. PMID: 23688527.33. Poolman J, Kriz P, Feron C, Di-Paolo E, Henckaerts I, Miseur A, et al. Pneumococcal serotype 3 otitis media, limited effect of polysaccharide conjugate immunisation and strain characteristics. Vaccine. 2009; 27(24):3213–3222. PMID: 19446194.34. Choi EH, Zhang F, Lu YJ, Malley R. Capsular polysaccharide (CPS) release by serotype 3 pneumococcal strains reduces the protective effect of anti-type 3 CPS antibodies. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015; 23(2):162–167. PMID: 26677201.35. Platt HL, Greenberg D, Tapiero B, Clifford RA, Klein NP, Hurley DC, et al. A phase II trial of safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of V114, a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, compared with 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in healthy infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020; 39(8):763–770. PMID: 32639460.36. Simon JK, Staerke NB, Hemming-Harlo M, Layle S, Dagan R, Shekar T, et al. Lot-to-lot consistency, safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of V114, a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, in healthy adults aged ≥50 years: a randomized phase 3 trial (PNEU-TRUE). Vaccine. 2022; 40(9):1342–1351. PMID: 35039194.37. Varon E, Cohen R, Béchet S, Doit C, Levy C. Invasive disease potential of pneumococci before and after the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine implementation in children. Vaccine. 2015; 33(46):6178–6185. PMID: 26476365.38. Cohen R, Levy C, Ouldali N, Goldrey M, Béchet S, Bonacorsi S, et al. Invasive disease potential of pneumococcal serotypes in children after PCV13 implementation. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(8):1453–1456. PMID: 32804200.39. Welte T. Risk factors and severity scores in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia: prediction of severity and mortality. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31(1):33–47. PMID: 21533875.40. Nakashima K, Suzuki K, Aoshima M, Murabata M, Kondo K, Ohfuji S, et al. Effectiveness of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine against community-acquired pneumonia in older individuals after the introduction of childhood 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a multicenter hospital-based case-control study in Japan. Vaccine. 2022; 40(46):6589–6598. PMID: 36184405.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Disease Burden and Etiologic Distribution of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults: Evolving Epidemiology in the Era of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines
- An Update on Pneumococcal Vaccination
- Pneumococcal vaccine
- Community-acquired pneumonia in elderly patients
- A Case on Streptococcal Pneumonia Associated with Leptomeningitis, Osteomyelitis and Epidural Abscess in a Patient with AIDS