Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Oct;82(4):180-189. 10.4166/kjg.2023.032.
Diagnosis and Treatment of GastroEsophageal Reflux Disease at the Primary Health Care Clinics in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1SOK Hepato-Gastroenterology Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- 2Best Internal Medicine Clinic, Hwaseong, Korea
- 3Kim Jong Woong Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.032
Abstract
- Background/Aims
The prevalence of GERD and treatment costs are continuously rising in Korea, and the importance of primary health care clinics where the most treatment of actual patients is conducted is increasing. In this study, the diagnosis of GERD, selection of therapeutic drugs, and treatment methods in primary health care clininics were investigated through a large-scale multi-dimensional surveys.
Methods
From January 2015 to December 2018, the study data of 18,010 patients with GERD were retrospectively investigated based on eletronic medical record at 542 primary health care clinics in Korea.
Results
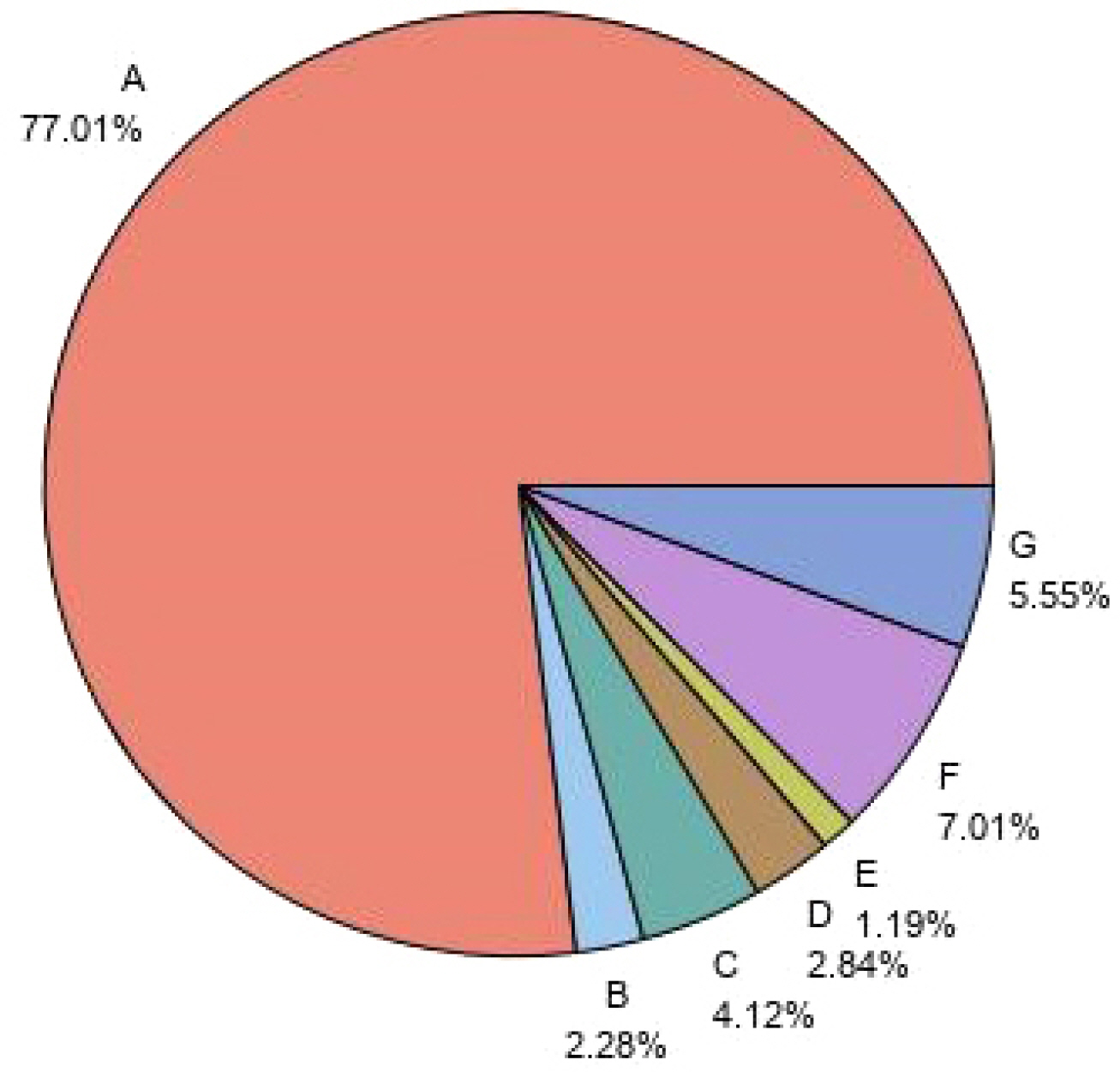
Among all GERD patients, endoscopy was used for diagnosis in 16.11% of cases, and the most frequently performed in gastroenterology department (28.85%). The average BMI and the proportion of patients in stages 1 to 3 of obesity were highest in the ERD group, and the majority of the severity of ERD group was mild. Symptoms of the patients with GERD were mainly heartburn, gastric acid reflux, and chest pain. Drug treatment was performed in most of the patients with GERD, and PPI was the main drug, and Esomeprazol was prescribed the most among the main ingredients, and the ratio of PPI alone was high. The rate of symptom improvement after GERD treatment was slightly higher in the ERD group (75.91%) and the NERD group (74.36%) than in the GERD diagnosed without endoscopy group (63.89%).
Conclusions
In domestic primary health care clinics, the majority were diagnosed with GERD without endoscopy on the basis of symptoms. The most preferred treatment for GERD was PPI, which was prescribed alone in the majority.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Healthcare Bigdata Hub. [Internet]. Wonju: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;cited 2022 Aug 4. Available from: https://opendata.hira.or.kr/op/opc/olap3thDsInfo.do.2. Hwang JK, Kim J, Hong SG, et al. 2009; [A prospective multicenter study on the prevalence and symptoms of erosive reflux esophagitis in secondary and tertiary hospitals in Korea]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 53:283–291. Korean. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2009.53.5.283. PMID: 19458464.
Article3. Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. Global Consensus Group. 2006; The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:1900–1920. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x. PMID: 16928254.
Article4. Fock KM, Talley NJ, Fass R, et al. 2008; Asia-Pacific consensus on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: update. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:8–22. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05249.x. PMID: 18171339.
Article5. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. 1999; Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 45:172–180. DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.2.172. PMID: 10403727. PMCID: PMC1727604.
Article6. Diagnosis and evaluation of obesity. [Internet]. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obesity;cited 2022 Aug 4. Available from: http://general.kosso.or.kr/html/?pmode=obesityDiagnosis.7. Kim N, Lee SW, Cho SI, et al. 2008; The prevalence of and risk factors for erosive oesophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease: a nationwide multicentre prospective study in Korea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 27:173–185. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03561.x. PMID: 17973646.
Article8. Kim BC, Yoon YH, Jyung HS, et al. 2006; [Clinical characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux diseases and association with Helicobacter pylori infection]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 47:363–369. Korean.9. Jeon SG, Rhee PL, Shin MH, et al. 1998; The prevalence and risk factors of reflux esophagitis in routine check-up subjects. Korean J Gastroenterol. 32:701–708.10. El-Serag H. 2008; The association between obesity and GERD: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Dig Dis Sci. 53:2307–2312. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-008-0413-9. PMID: 18651221. PMCID: PMC2827866.
Article11. Singh M, Lee J, Gupta N, et al. 2013; Weight loss can lead to resolution of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: a prospective intervention trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 21:284–290. DOI: 10.1002/oby.20279. PMID: 23532991. PMCID: PMC3853378.
Article12. Tack J, Pandolfino JE. 2018; Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 154:277–288. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.09.047. PMID: 29037470.
Article13. Friedenberg FK, Xanthopoulos M, Foster GD, Richter JE. 2008; The association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and obesity. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:2111–2122. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01946.x. PMID: 18796104.
Article14. Jacobson BC, Somers SC, Fuchs CS, Kelly CP, Camargo CA Jr. 2006; Body-mass index and symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux in women. N Engl J Med. 354:2340–2348. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa054391. PMID: 16738270. PMCID: PMC2782772.
Article15. El-Serag HB, Graham DY, Satia JA, Rabeneck L. 2005; Obesity is an independent risk factor for GERD symptoms and erosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 100:1243–1250. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41703.x. PMID: 15929752.
Article16. Nocon M, Labenz J, Willich SN. 2006; Lifestyle factors and symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux -- a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:169–174. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02727.x. PMID: 16393294.
Article17. Eusebi LH, Ratnakumaran R, Yuan Y, Solaymani-Dodaran M, Bazzoli F, Ford AC. 2018; Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: a meta-analysis. Gut. 67:430–440. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313589. PMID: 28232473.
Article18. Lagergren J, Bergström R, Nyrén O. 2000; No relation between body mass and gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms in a Swedish population based study. Gut. 47:26–29. DOI: 10.1136/gut.47.1.26. PMID: 10861260. PMCID: PMC1727954.
Article19. Lundell L, Ruth M, Sandberg N, Bove-Nielsen M. 1995; Does massive obesity promote abnormal gastroesophageal reflux? Dig Dis Sci. 40:1632–1635. DOI: 10.1007/BF02212682. PMID: 7648961.
Article20. Castell DO, Murray JA, Tutuian R, Orlando RC, Arnold R. 2004; Review article: the pathophysiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease-oesophageal manifestations. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 20 Suppl 9:14–25. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02238.x. PMID: 15527461.
Article21. Pan J, Cen L, Chen W, Yu C, Li Y, Shen Z. 2019; Alcohol consumption and the risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Alcohol Alcohol. 54:62–69. DOI: 10.1093/alcalc/agy063. PMID: 30184159.
Article22. Nilsson M, Johnsen R, Ye W, Hveem K, Lagergren J. 2004; Lifestyle related risk factors in the aetiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut. 53:1730–1735. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.043265. PMID: 15542505. PMCID: PMC1774312.
Article23. Kim HY, Kim NY, Kim SM, et al. 2006; Clinical spectrum and risk factors of erosive and non-erosive GERD in health check-up subjects. Korean J Med. 71:491–500.24. Yoo SS, Lee WH, Ha J, et al. 2007; [The prevalence of esophageal disorders in the subjects examined for health screening]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 50:306–312. Korean.25. Shim KN, Hong SJ, Sung JK, et al. 2009; Clinical spectrum of reflux esophagitis among 25,536 Koreans who underwent a health check-up: a nationwide multicenter prospective, endoscopy-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 43:632–638. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181855055. PMID: 19169148.
Article26. Jung HK, Tae CH, Song KH, et al. 2021; 2020 Seoul Consensus on the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 27:453–481. DOI: 10.5056/jnm21077. PMID: 34642267. PMCID: PMC8521465.
Article27. Min YW, Lim SW, Lee JH, et al. 2014; Prevalence of extraesophageal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A multicenter questionnaire-based study in Korea. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20:87–93. DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2014.20.1.87. PMID: 24466449. PMCID: PMC3895614.
Article28. Dent J, Yeomans ND, Mackinnon M, et al. 1994; Omeprazole v ranitidine for prevention of relapse in reflux oesophagitis. A controlled double blind trial of their efficacy and safety. Gut. 35:590–598. DOI: 10.1136/gut.35.5.590. PMID: 8200548. PMCID: PMC1374738.
Article29. Harris RA, Kuppermann M, Richter JE. 1997; Proton pump inhibitors or histamine-2 receptor antagonists for the prevention of recurrences of erosive reflux esophagitis: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 92:2179–2187.30. Harris RA, Kuppermann M, Richter JE. 1997; Prevention of recurrences of erosive reflux esophagitis: a cost-effectiveness analysis of maintenance proton pump inhibition. Am J Med. 102:78–88. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9343(96)00301-4. PMID: 9209204.
Article31. Birbara C, Breiter J, Perdomo C, Hahne W. 2000; Rabeprazole for the prevention of recurrent erosive or ulcerative gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Rabeprazole Study Group. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:889–897. DOI: 10.1097/00042737-200012080-00008. PMID: 10958216.
Article32. Yun HR, Jung HY, Park HJ, Bae SC. 2002; Cost-effectiveness analysis of proton pump inhibitors and ranitidine in the treatment of gastroesophageal disease. Korean J Med. 62:504–512.33. Korean Medical Association. Guideline for using gastrointestinal drugs. Seoul: Korean Medical Association;2003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Achalasia Coincident or Not?
- Health-Related Quality of Life Issues in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Usefulness of the Korean Version of the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Questionnaire for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Using Validation Study
- Radiologic studies on gastroesophageal reflux