Korean Circ J.
2023 Oct;53(10):677-689. 10.4070/kcj.2023.0012.
Machine Learning Prediction for the Recurrence After Electrical Cardioversion of Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Intelligence and Information, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2023.0012
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
There is limited evidence regarding machine-learning prediction for the recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) after electrical cardioversion (ECV). This study aimed to predict the recurrence of AF after ECV using machine learning of clinical features and electrocardiograms (ECGs) in persistent AF patients.
Methods
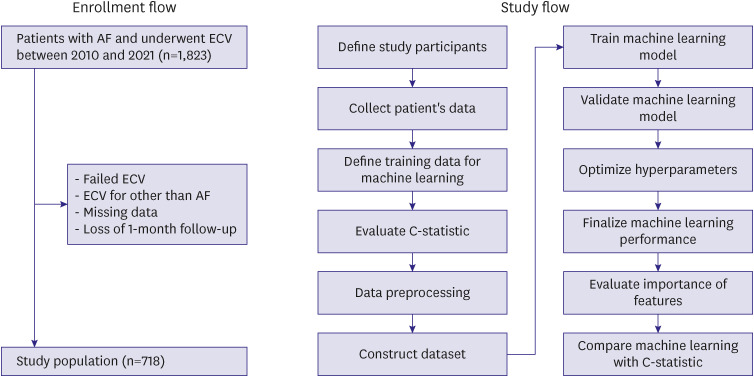
We analyzed patients who underwent successful ECV for persistent AF. Machine learning was designed to predict patients with 1-month recurrence. Individual 12-lead ECGs were collected before and after ECV. Various clinical features were collected and trained the extreme gradient boost (XGBoost)-based model. Ten-fold cross-validation was used to evaluate the performance of the model. The performance was compared to the C-statistics of the selected clinical features.
Results
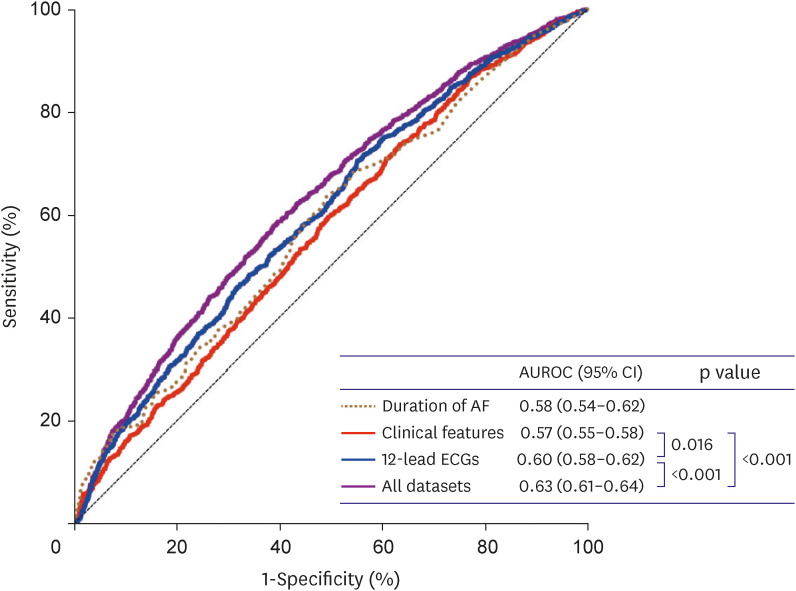
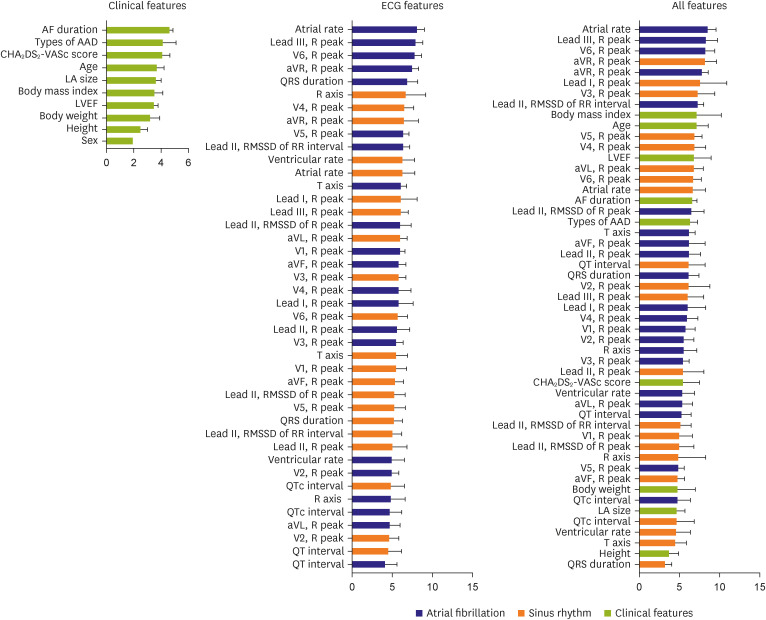
Among 718 patients (mean age 63.5±9.3 years, men 78.8%), AF recurred in 435 (60.6%) patients after 1 month. With the XGBoost-based model, the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) were 0.57, 0.60, and 0.63 if the model was trained by clinical features, ECGs, and both (the final model), respectively. For the final model, the sensitivity, specificity, and F1-score were 84.7%, 28.2%, and 0.73, respectively. Although the AF duration showed the best predictive performance (AUROC, 0.58) among the clinical features, it was significantly lower than that of the final machine-learning model (p<0.001). Additional training of extended monitoring data of 15-minute single-lead ECG and photoplethysmography in available patients (n=261) did not significantly improve the model’s performance.
Conclusions
Machine learning showed modest performance in predicting AF recurrence after ECV in persistent AF patients, warranting further validation studies.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Machine Learning for Predicting Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Cardioversion: A Modest Leap Forward
Junbeom Park
Korean Circ J. 2023;53(10):690-692. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2023.0196.
Reference
-
1. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace. 2016; 18:1609–1678. PMID: 27567465.
Article2. Juul-Möller S, Edvardsson N, Rehnqvist-Ahlberg N. Sotalol versus quinidine for the maintenance of sinus rhythm after direct current conversion of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1990; 82:1932–1939. PMID: 2242519.
Article3. Van Gelder IC, Crijns HJ, Van Gilst WH, Van Wijk LM, Hamer HP, Lie KI. Efficacy and safety of flecainide acetate in the maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1989; 64:1317–1321. PMID: 2511744.
Article4. Van Gelder IC, Crijns HJ. Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and subsequent maintenance of sinus rhythm. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1997; 20:2675–2683. PMID: 9358514.
Article5. Inoue K, Kurotobi T, Kimura R, et al. Trigger-based mechanism of the persistence of atrial fibrillation and its impact on the efficacy of catheter ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012; 5:295–301. PMID: 22042883.
Article6. Brandes A, Crijns HJ, Rienstra M, et al. Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter revisited: current evidence and practical guidance for a common procedure. Europace. 2020; 22:1149–1161. PMID: 32337542.
Article7. Ehrlich JR, Schadow K, Steul K, Zhang GQ, Israel CW, Hohnloser SH. Prediction of early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after external cardioversion by means of P wave signal-averaged electrocardiogram. Z Kardiol. 2003; 92:540–546. PMID: 12883838.
Article8. Wałek P, Sielski J, Starzyk K, Gorczyca I, Roskal-Wałek J, Wożakowska-Kapłon B. Echocardiographic assessment of left atrial morphology and function to predict maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion in patients with non-valvular persistent atrial fibrillation and normal function or mild dysfunction of left ventricle. Cardiol J. 2020; 27:246–253. PMID: 31313277.
Article9. Andersson J, Rosenqvist M, Tornvall P, Boman K. NT-proBNP predicts maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion. Thromb Res. 2015; 135:289–291. PMID: 25481046.
Article10. Liu T, Li G, Li L, Korantzopoulos P. Association between C-reactive protein and recurrence of atrial fibrillation after successful electrical cardioversion: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49:1642–1648. PMID: 17433956.
Article11. Vizzardi E, Curnis A, Latini MG, et al. Risk factors for atrial fibrillation recurrence: a literature review. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2014; 15:235–253. PMID: 23114271.12. Al’Aref SJ, Anchouche K, Singh G, et al. Clinical applications of machine learning in cardiovascular disease and its relevance to cardiac imaging. Eur Heart J. 2019; 40:1975–1986. PMID: 30060039.
Article13. Feeny AK, Chung MK, Madabhushi A, et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in arrhythmias and cardiac electrophysiology. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2020; 13:e007952. PMID: 32628863.
Article14. Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001; 45:5–32.15. Kwon S, Hong J, Choi EK, et al. Detection of atrial fibrillation using a ring-type wearable device (CardioTracker) and deep learning analysis of photoplethysmography signals: prospective observational proof-of-concept study. J Med Internet Res. 2020; 22:e16443. PMID: 32348254.
Article16. Hansen ML, Jepsen RM, Olesen JB, et al. Thromboembolic risk in 16 274 atrial fibrillation patients undergoing direct current cardioversion with and without oral anticoagulant therapy. Europace. 2015; 17:18–23. PMID: 25231909.
Article17. Apostolakis S, Haeusler KG, Oeff M, et al. Low stroke risk after elective cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: an analysis of the Flec-SL trial. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 168:3977–3981. PMID: 23871349.
Article18. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021; 42:373–498. PMID: 32860505.19. Vinter N, Frederiksen AS, Albertsen AE, et al. Role for machine learning in sex-specific prediction of successful electrical cardioversion in atrial fibrillation? Open Heart. 2020; 7:e001297. PMID: 32565431.
Article20. Nuñez-Garcia JC, Sánchez-Puente A, Sampedro-Gómez J, et al. Outcome analysis in elective electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation patients: development and validation of a machine learning prognostic model. J Clin Med. 2022; 11:2636. PMID: 35566761.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Influence of Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation on Left Atrial Appendage Function: A Transesophageal Echocardiography Study
- Electrical Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation after Successful Percutaneous Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty
- A Case of Successful Ablation of Right-Sided Accessory Pathway during Atrial Fibrillation
- Newly Developed Persistent Atrial Fibrillation during Central Venous Catheterization Treated with Electric Cardioversion: A case report
- Machine Learning for Predicting Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Cardioversion: A Modest Leap Forward