Korean J Transplant.
2023 Sep;37(3):210-215. 10.4285/kjt.23.0021.
Robot-assisted kidney transplantation in a morbidly obese patient with incisional hernia reconstruction and abdominoplasty: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546500
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.23.0021
Abstract
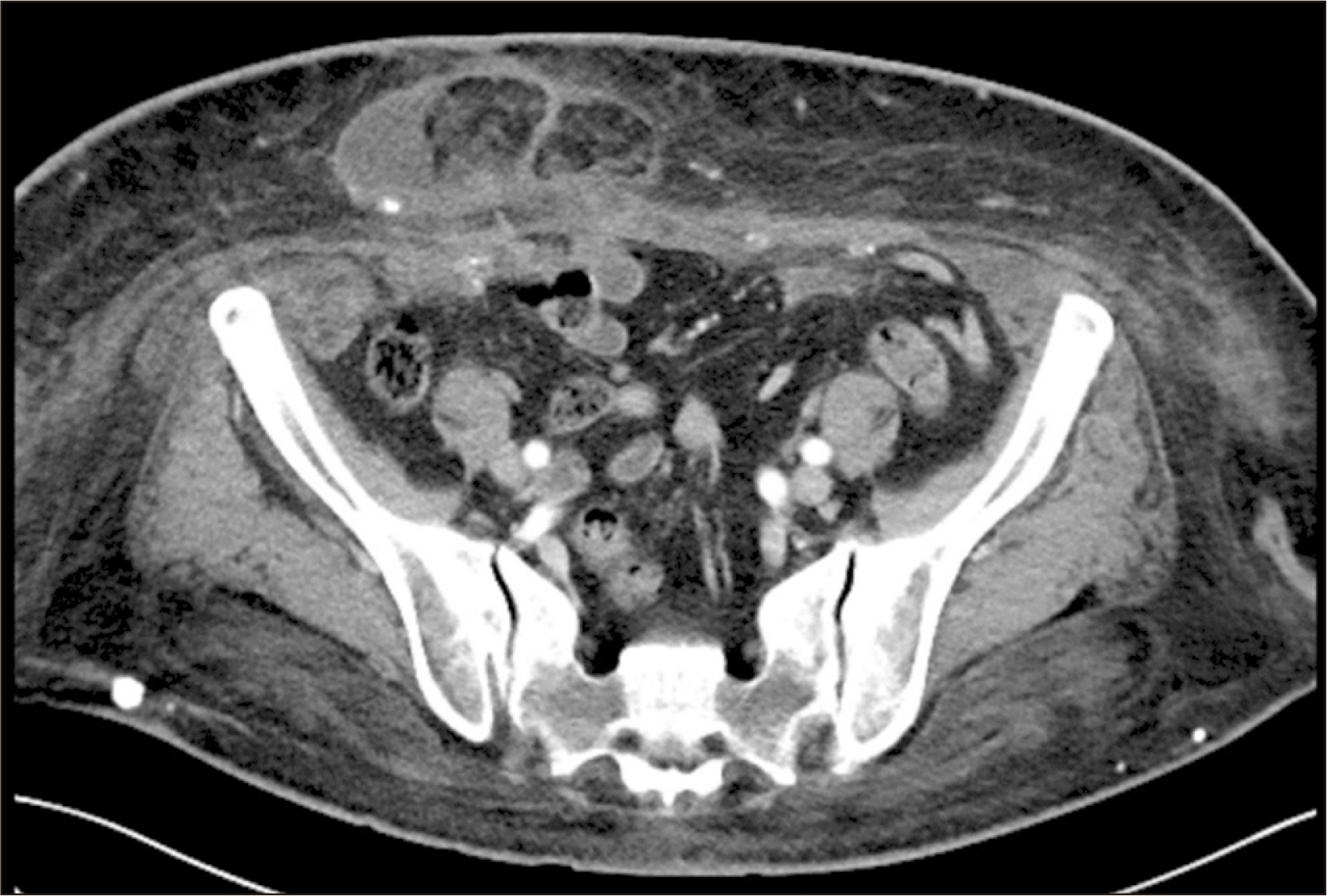
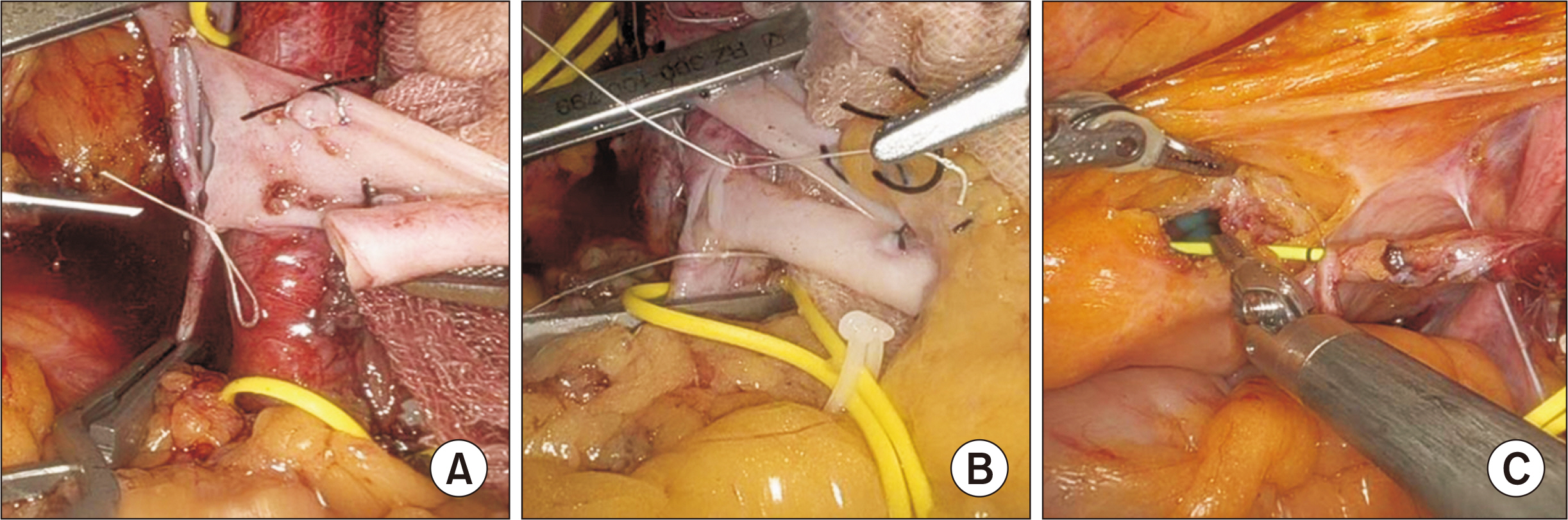
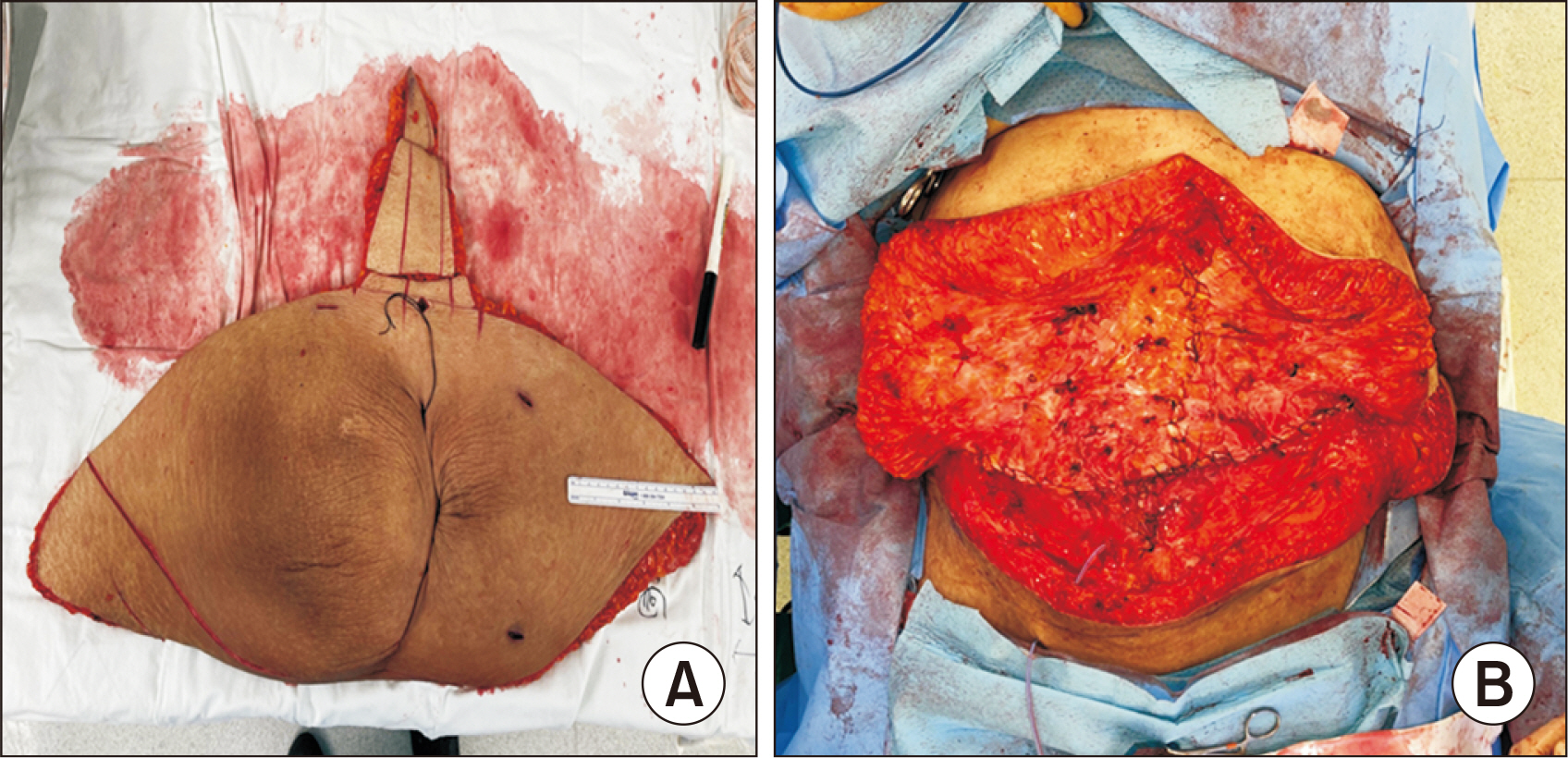
- Performing kidney transplantations in patients with morbid obesity presents unique challenges using the conventional retroperitoneal approach. Robot-assisted kidney transplantation (RAKT) offers several advantages, such as better access to hard-to-reach areas. A 56-year-old morbidly obese woman presented with end-stage renal disease due to diabetic nephropathy. The patient had a history of obesity for over 20 years, with a peak body mass index (BMI) of 46.9 kg/m2. Before transplantation, she successfully reduced her BMI to 28.9 kg/m2, but was left with excessive skin folds. The surgery began with the removal of the sac from the incisional hernia and umbilical hernia, which was then used as the site for the GelPOINT port. The da Vinci X robot system was utilized to perform RAKT. After completing RAKT, the plastic surgery team initiated abdominal reconstruction involving panniculectomy, followed by hernial reconstruction and abdominoplasty. The patient’s postoperative course was uneventful, and she was discharged on postoperative day 7. Her creatinine level was 0.69 mg/dL, and she did not experience any episodes of rejection during the 16 months following RAKT. This case report describes the successful combination of RAKT with incisional hernia reconstruction and abdominoplasty in a patient with morbid obesity.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, et al. GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. 2017; Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 377:13–27. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362. PMID: 28604169. PMCID: PMC5477817.2. Ladhani M, Craig JC, Irving M, Clayton PA, Wong G. 2017; Obesity and the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 32:439–49. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfw075. PMID: 27190330.3. Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. 2017; Obesity and kidney disease: from population to basic science and the search for new therapeutic targets. Kidney Int. 92:313–23. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.12.034. PMID: 28341271.4. Lambert DM, Marceau S, Forse RA. 2005; Intra-abdominal pressure in the morbidly obese. Obes Surg. 15:1225–32. DOI: 10.1381/096089205774512546. PMID: 16259876.5. Giulianotti P, Gorodner V, Sbrana F, Tzvetanov I, Jeon H, Bianco F, et al. 2010; Robotic transabdominal kidney transplantation in a morbidly obese patient. Am J Transplant. 10:1478–82. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03116.x. PMID: 20486912.6. Modlin CS, Flechner SM, Goormastic M, Goldfarb DA, Papajcik D, Mastroianni B, et al. 1997; Should obese patients lose weight before receiving a kidney transplant? Transplantation. 64:599–604. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199708270-00009. PMID: 9293872.7. Orofino L, Pascual J, Quereda C, Burgos J, Marcen R, Ortuño J. 1997; Influence of overweight on survival of kidney transplant. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 12:855. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/12.4.855. PMID: 9141040.8. Beddhu S, Pappas LM, Ramkumar N, Samore M. 2003; Effects of body size and body composition on survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:2366–72. DOI: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000083905.72794.E6. PMID: 12937315.9. Holley JL, Shapiro R, Lopatin WB, Tzakis AG, Hakala TR, Starzl TE. 1990; Obesity as a risk factor following cadaveric renal transplantation. Transplantation. 49:387–9. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199002000-00032. PMID: 2305469. PMCID: PMC2965531.10. Richens G, Piepkorn MW, Krueger GG. 1982; Calcifying panniculitis associated with renal failure: a case of Selye's calciphylaxis in man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 6(4 Pt 1):537–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0190-9622(82)70046-5. PMID: 7076908.11. Lugo-Somolinos A, Sánchez JL, Méndez-Coll J, Joglar F. 1990; Calcifying panniculitis associated with polycystic kidney disease and chronic renal failure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 22(5 Pt 1):743–7. DOI: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70101-M. PMID: 2347961.12. Ngaage LM, Elegbede A, Tadisina KK, Gebran SG, Masters BM, Rada EM, et al. 2019; Panniculectomy at the time of living donor renal transplantation: an 8-year experience. Am J Transplant. 19:2284–93. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15285. PMID: 30720924.13. Zemlyak AY, Colavita PD, El Djouzi S, Walters AL, Hammond L, Hammond B, et al. 2012; Comparative study of wound complications: isolated panniculectomy versus panniculectomy combined with ventral hernia repair. J Surg Res. 177:387–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.06.029. PMID: 22795269.14. Berry MF, Paisley S, Low DW, Rosato EF. 2007; Repair of large complex recurrent incisional hernias with retromuscular mesh and panniculectomy. Am J Surg. 194:199–204. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.10.031. PMID: 17618804.15. Lafranca JA, IJermans JN, Betjes MG, Dor FJ. 2015; Body mass index and outcome in renal transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 13:111. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-015-0340-5. PMID: 25963131. PMCID: PMC4427990.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trocar Site Hernia after Use of an 8-mm Bladeless Trocar in Robotic Colorectal Surgery
- Spare parts neoumbilicoplasty
- Risk of incisional hernia after laparoscopic colorectal surgery: surgeon’s worries and challenges
- Utility of a modified components separation for abdominal wall reconstruction in the liver and kidney transplant population
- Components separation technique for large abdominal wall defect