Korean J Transplant.
2023 Sep;37(3):179-188. 10.4285/kjt.23.0030.
Characteristics of living liver donors in a national referral hospital in Indonesia: a 13-year experience with living donor liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Digestive Surgery, Department of Surgery, Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
- KMID: 2546476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.23.0030
Abstract
- Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma and biliary atresia lead to end-stage liver disease, which requires liver transplantation and is linked to increased mortality. Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital is the national referral center in Indonesia and is the only center that routinely performs living donor liver transplantation (LDLT). This study presents the characteristics of living liver donors (LLDs) in Indonesia.
Methods
Using the LDLT registry, we conducted a retrospective analysis of all approved donors from 2010 to 2022. The variables included clinical characteristics of the donors, graft types, and intraoperative and postoperative characteristics.
Results
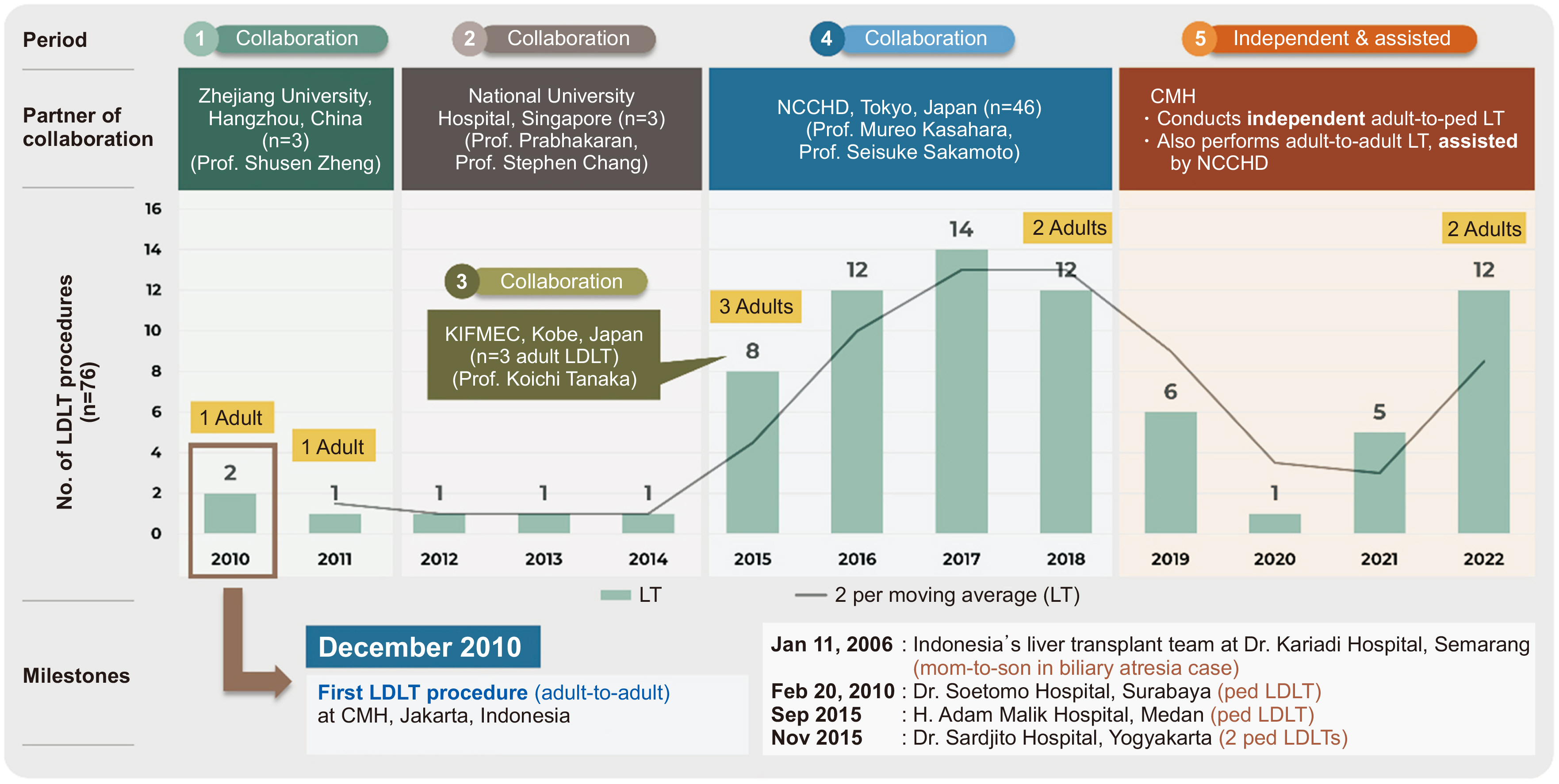
The LDLT rate has increased from 5.8 to 8.8 procedures/year in the last 8 years. The average age of the 76 LLDs was 31.8 years. They were predominantly female (59%) and lived within a family relationship (90%). Pediatric LDLT was more frequent than adult LDLT (88% vs. 12%, respectively). Most grafts (86%) were obtained by left lateral sectionectomy, with a median ratio of remnant liver volume to total liver volume of 79.5% (range, 47.7%–85.8%) and a mean graft-to-recipient weight ratio of 2.65%±1.21%. The median intensive care unit length of stay (LOS) was 2 days (range, 1–5 days) and the total hospital LOS was 7 days (range, 4–28 days). The complication rate was 23%. No donor mortality was reported.
Conclusions
LDLT in Indonesia has increased over the years. The shortage of donors for adult-to-adult liver transplantation is due to cultural differences and challenges in finding eligible donors. This study aims to explain the eligibility criteria of LLDs and contribute to creating a national policy.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Seizing tumor factors for mortality and survival outcomes following liver resection in Indonesia’s hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Lam Sihardo, Arnetta Naomi Louise Lalisang, Ridho Ardhi Syaiful, Afid Brilliana Putra, Yarman Mazni, Agi Satria Putranto, Toar Jean Maurice Lalisang
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2025;29(1):11-20. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.24-179.
Reference
-
1. Lianti H, Kurnia N, Rinaldhy K, Aji AS, Ismet MF, Amaliah R. 2020; Analysis of knowledge regarding biliary atresia among healthcare providers and laypersons in East Jakarta after educational intervention. ASEAN J Community Engagem. 4:278–301. DOI: 10.7454/ajce.v4i1.1053.2. Jasirwan CO, Hasan I, Sulaiman AS, Lesmana CR, Kurniawan J, Kalista KF, et al. 2020; Risk factors of mortality in the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter study in Indonesia. Curr Probl Cancer. 44:100480. DOI: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2019.05.003. PMID: 31130257.3. Oswari H, Rahayatri TH, Soedibyo S. 2020; Pediatric living donor liver transplant in Indonesia's national referral hospital. Transplantation. 104:1305–7. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003154. PMID: 32568998.4. Cuschieri S. 2019; The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J Anaesth. 13(Suppl 1):S31–4. DOI: 10.4103/sja.SJA_543_18. PMID: 30930717. PMCID: PMC6398292.5. Cotter TG, Minhem M, Wang J, Peeraphatdit T, Ayoub F, Pillai A, et al. 2021; Living donor liver transplantation in the United States: evolution of frequency, outcomes, center volumes, and factors associated with outcomes. Liver Transpl. 27:1019–31. DOI: 10.1002/lt.26029. PMID: 33619854. PMCID: PMC9257956.6. Durand F, Levitsky J, Cauchy F, Gilgenkrantz H, Soubrane O, Francoz C. 2019; Age and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 70:745–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.009. PMID: 30576701.7. Rinella ME, Alonso E, Rao S, Whitington P, Fryer J, Abecassis M, et al. 2001; Body mass index as a predictor of hepatic steatosis in living liver donors. Liver Transpl. 7:409–14. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2001.23787. PMID: 11349260.8. Trotter JF, Wisniewski KA, Terrault NA, Everhart JE, Kinkhabwala M, Weinrieb RM, et al. 2007; Outcomes of donor evaluation in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. Hepatology. 46:1476–84. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21845. PMID: 17668879. PMCID: PMC3732162.9. Goldaracena N, Barbas AS. 2019; Living donor liver transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 24:131–7. DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000610. PMID: 30694993.10. Knaak M, Goldaracena N, Doyle A, Cattral MS, Greig PD, Lilly L, et al. 2017; Donor BMI >30 is not a contraindication for live liver donation. Am J Transplant. 17:754–60. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14019. PMID: 27545327.11. Fan R, Wang J, Du J. 2018; Association between body mass index and fatty liver risk: a dose-response analysis. Sci Rep. 8:15273. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33419-6. PMID: 30323178. PMCID: PMC6189125.12. Shukla A, Vadeyar H, Rela M, Shah S. 2013; Liver transplantation: East versus West. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 3:243–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.08.004. PMID: 25755506. PMCID: PMC3940244.13. Ozcelik U, Eren E, Tutpınar Y, Urut DU, Tokac M, Dinckan A. 2021; A comparison of actual graft weight and estimated graft volume calculated with new software used for anatomical and volumetric analysis of the liver with computed tomography in living liver donors. Experimed. 11:96–101. DOI: 10.26650/experimed.2021.942836.14. Taema MI, Fawz MM, Ali AM, Al-Fawal MM. 2022; Assessment of role of computed tomography volumetry in preoperative evaluation of liver volume in living donor liver transplantation. Egypt J Hosp Med. 88:2400–5. DOI: 10.21608/ejhm.2022.236120.15. Mohapatra N, Bharathy KG, Sinha PK, Sasturkar SV, Patidar Y, Pamecha V. 2020; Three-dimensional volumetric assessment of graft volume in living donor liver transplantation: does it minimise errors of estimation? J Clin Exp Hepatol. 10:1–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2019.03.006. PMID: 32025161. PMCID: PMC6995882.16. Baskiran A, Kahraman AS, Cicek IB, Sahin T, Isik B, Yilmaz S. 2017; Preoperative evaluation of liver volume in living donor liver transplantation. North Clin Istanb. 5:1–5. DOI: 10.14744/nci.2017.14227. PMID: 29607424. PMCID: PMC5864700.17. Mokry T, Bellemann N, Muller D, Bermejo JL, Klaus M, Stampfl U, et al. 2014; Accuracy of estimation of graft size for living-related liver transplantation: first results of a semi-automated interactive software for CT-volumetry. PLoS One. 9:e110201. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110201. PMID: 25330198. PMCID: PMC4201494.18. Yoh T, Cauchy F, Soubrane O. 2019; Techniques for laparoscopic liver parenchymal transection. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 8:572–81. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.04.16. PMID: 31929984. PMCID: PMC6943017.19. Ishiko T, Inomata Y, Beppu T, Asonuma K, Okajima H, Takeiti T, et al. 2012; An improved technique for liver transection using a new device for soft coagulation in living donor hepatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1907–10.20. Gad EH, Alsebaey A, Lotfy M, Eltabbakh M, Sherif AA. 2015; Complications and mortality after adult to adult living donor liver transplantation: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 4:162–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2015.04.021. PMID: 26005570. PMCID: PMC4434206.21. Lalisang AN, Nugroho A, Tendean M, Irwan , Situmorang I, Uwuratuw JA, et al. 2023; Hemostasis in liver surgery: Indonesian Society of Digestive Surgeons (IKABDI) consensus statements. Bali Med J. 12:782–7.22. Hibi T, Chieh AK, Chan AC, Bhangui P. 2020; Current status of liver transplantation in Asia. Int J Surg. 83(Suppl):4–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.05.071. PMID: 32535264.23. Alqahtani SA, Stepanova M, Kabbara KW, Younossi I, Mishra A, Younossi Z. 2022; Liver transplant center size and the impact on clinical outcomes and resource utilization. Transplantation. 106:988–96. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003915. PMID: 34366386.24. Yeow M, Bonney GK, Kow WC, Wee P, Madhavan K, Iyer SG. 2022; Liver transplantation in Singapore: challenges and strategies of low- to mid-volume centers. Transplantation. 106:895–7. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003925. PMID: 35470351.25. Lapisatepun W, Chotirosniramit A, Udomsin K, Lapisatepun W, Chanthima P, Boonsri S, et al. 2022; Around the world: adult living donor liver transplantation in Thailand. Transplantation. 106:421–4. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003813. PMID: 35192579.26. Khan JF, Shah DM, Sivapakiam S, Mokhtar S, Subramaniam M, Raman K, et al. 2021; Liver transplantation in Malaysia: needs, obstacles, and opportunities. Transplantation. 105:2507–12. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003591. PMID: 34818304.27. Latt NL, Niazi M, Pyrsopoulos NT. 2022; Liver transplant allocation policies and outcomes in United States: a comprehensive review. World J Methodol. 12:32–42. DOI: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i1.32. PMID: 35117980. PMCID: PMC8790309.28. Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia (FKUI). 2020. Tingkat keberhasilan transplantasi hati anak di Indonesia setara dengan Jepang [Internet]. FKUI;Available from: https://fk.ui.ac.id/infosehat/tingkat-keberhasilan-transplantasi-hati-anak-di-indonesia-setara-dengan-jepang/. cited 2023 Jun 1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Liver retransplantation for adult recipients
- Endoscopic management of anastomotic stricture after living-donor liver transplantation
- Decreasing the operation time of living donor liver transplantation in the era of laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy
- Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- A Single Center Experience for a Feasibility of Totally Laparoscopic Living Donor Right Hepatectomy