Pediatr Emerg Med J.
2023 Oct;10(4):142-148. 10.22470/pemj.2023.00724.
Coronavirus disease 2019-associated acute necrotizing encephalopathy in a 9-year-old boy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children’s Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Division of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children’s Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2546288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.22470/pemj.2023.00724
Abstract
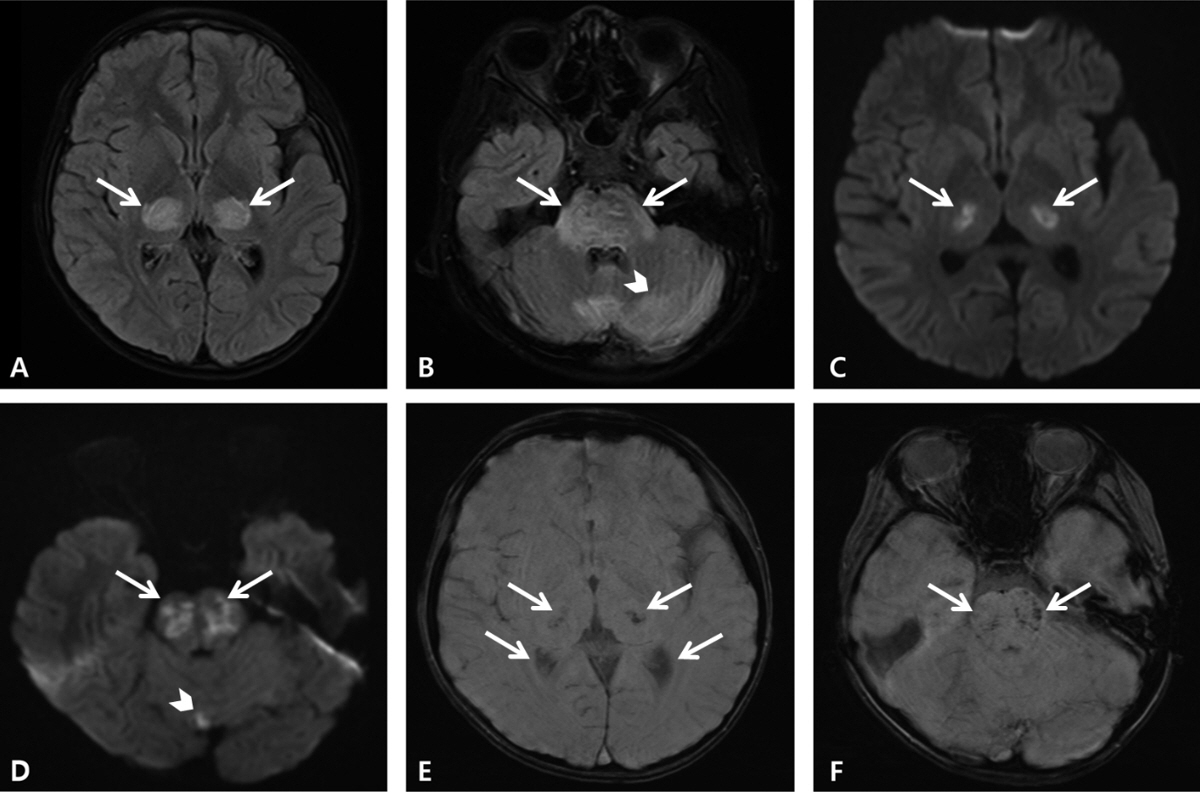
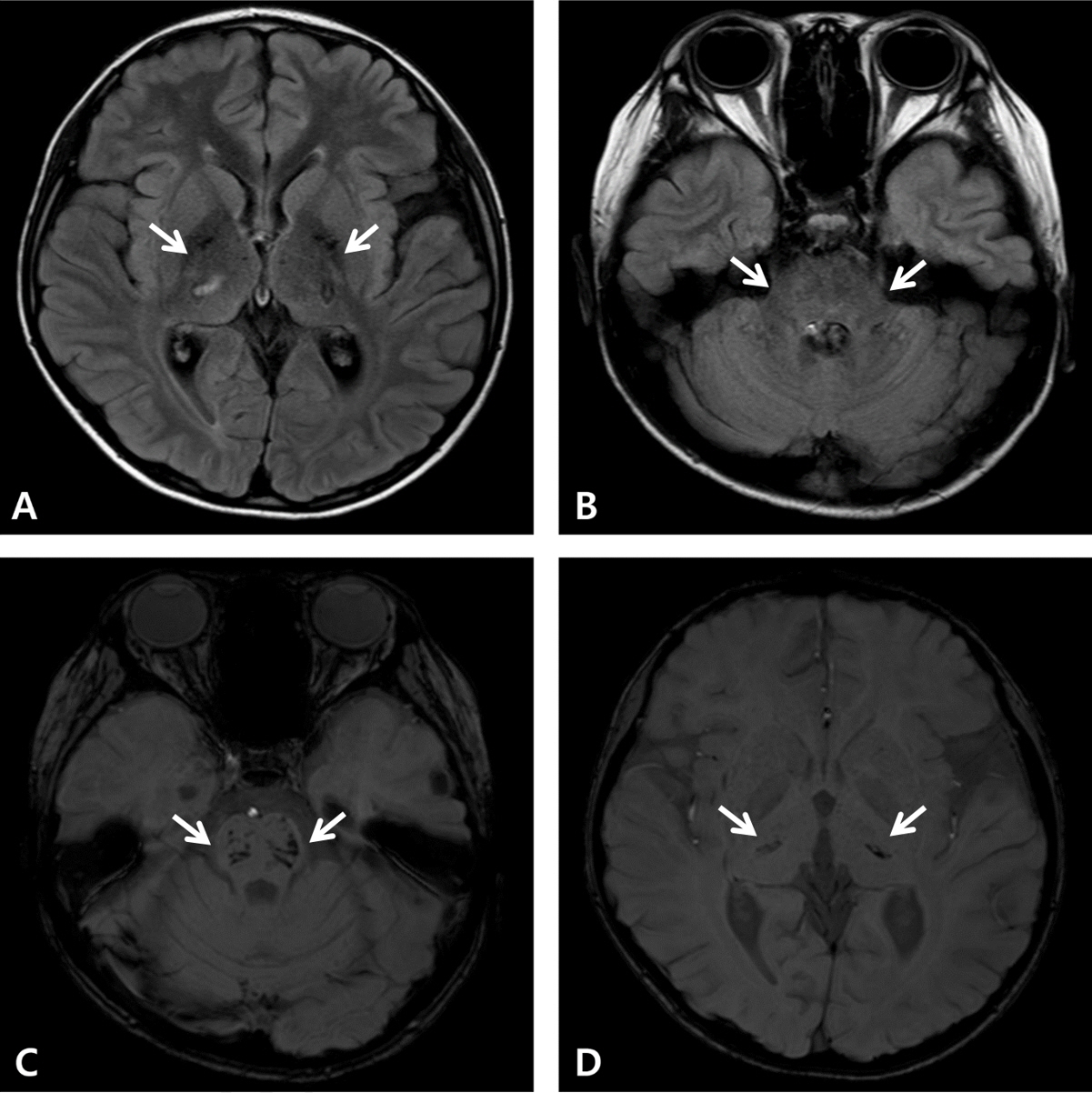
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is associated with a variety of neurologic manifestations. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) is a rare, life-threatening complication characterized by rapid deterioration of neurologic status following viral infection, such as influenza or human herpesvirus 6. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, a rise in ANE cases associated with the infectious disease has been reported in adult patients. We present a case of COVID-19-associated ANE in a 9-year-old boy. The patient experienced 3 days of fever and mild respiratory symptoms, followed by lethargy. Magnetic resonance imaging on day 4 showed hyperintensity in the bilateral thalami, midbrain, pons, hypothalamus, and cerebellum, along with some areas of hemorrhage. From the imaging findings, ANE was strongly suspected, leading to the initiation treatment involving a 5-day course of remdesivir and multiple immunomodulator therapies, including high-dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, tocilizumab, and 10 cycles of therapeutic plasma exchange. Subsequently, the patient gradually improved, experiencing only minor neurological sequelae and showing favorable radiologic improvement. In COVID-19-infected patients presenting neurologic symptoms, it is crucial to promptly suspect and investigate unexplained encephalopathy using neuroimaging. Early administration of immunomodulator therapy is vital for the diagnosis and optimizing clinical outcomes.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77:683–90.2. LaRovere KL, Riggs BJ, Poussaint TY, Young CC, Newhams MM, Maamari M, et al. Neurologic involvement in children and adolescents hospitalized in the United States for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2021; 78:536–47.3. Vanjare HA, Selvi BT, Karuppusami R, Manesh A, Gunasekaran K, Prabhakar AT, et al. Clinical and radiologic findings of acute necrotizing encephalopathy in young adults. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020; 41:2250–4.4. Mizuguchi M. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood: a novel form of acute encephalopathy prevalent in Japan and Taiwan. Brain Dev. 1997; 19:81–92.5. Poyiadji N, Shahin G, Noujaim D, Stone M, Patel S, Griffith B. COVID-19-associated acute hemorrhagic necrotizing encephalopathy: imaging features. Radiology. 2020; 296:E119–20.6. Lazarte-Rantes C, Guevara-Castañón J, Romero L, Guillén-Pinto D. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with SARS-CoV-2 exposure in a pediatric patient. Cureus. 2021; 13:e15018.7. Avery RA, Shah SS, Licht DJ, Seiden JA, Huh JW, Boswinkel J, et al. Reference range for cerebrospinal fluid opening pressure in children. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:891–3.8. Mizuguchi M, Ichiyama T, Imataka G, Okumura A, Goto T, Sakuma H, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute encephalopathy in childhood. Brain Dev. 2021; 43:2–31.9. Shukla P, Mandalla A, Elrick MJ, Venkatesan A. Clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of acute necrotizing encephalopathy: the interface between systemic infection and neurologic injury. Front Neurol. 2022; 12:628811.10. Wu X, Wu W, Pan W, Wu L, Liu K, Zhang HL. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy: an underrecognized clinicoradiologic disorder. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:792578.11. Wong AM, Simon EM, Zimmerman RA, Wang HS, Toh CH, Ng SH. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood: correlation of MR findings and clinical outcome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1919–23.12. Chow CK, Ma CKL. Presentation and outcome of acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood: a 10-year single-center retrospective study from Hong Kong. J Child Neurol. 2020; 35:674–80.13. Levine JM, Ahsan N, Ho E, Santoro JD. Genetic acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with RANBP2: clinical and therapeutic implications in pediatrics. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020; 43:102194.14. Lou JJ, Movassaghi M, Gordy D, Olson MG, Zhang T, Khurana MS, et al. Neuropathology of COVID-19 (neuro-COVID): clinicopathological update. Free Neuropathol. 2021; 2:2.15. DosSantos MF, Devalle S, Aran V, Capra D, Roque NR, Coelho-Aguiar JM, et al. Neuromechanisms of SARS-CoV-2: a review. Front Neuroanat. 2020; 14:37.16. Virhammar J, Kumlien E, Fällmar D, Frithiof R, Jackmann S, Sköld MK, et al. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy with SARS-CoV-2 RNA confirmed in cerebrospinal fluid. Neurology. 2020; 95:445–9.17. Rettenmaier LA, Abdel-Wahed L, Abdelmotilib H, Conway KS, Narayanan N, Groth CL. COVID-19-associated necrotizing encephalopathy presenting without active respiratory symptoms: a case report with histopathology. J Neurovirol. 2022; 28:172–6.18. Neilson DE, Adams MD, Orr CM, Schelling DK, Eiben RM, Kerr DS, et al. Infection-triggered familial or recurrent cases of acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by mutations in a component of the nuclear pore, RANBP2. Am J Hum Genet. 2009; 84:44–51.19. Okumura A, Mizuguchi M, Kidokoro H, Tanaka M, Abe S, Hosoya M, et al. Outcome of acute necrotizing encephalopathy in relation to treatment with corticosteroids and gammaglobulin. Brain Dev. 2009; 31:221–7.20. Koh JC, Murugasu A, Krishnappa J, Thomas T. Favorable outcomes with early interleukin 6 receptor blockade in severe acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood. Pediatr Neurol. 2019; 98:80–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy
- MRI Findings of COVID-19 Associated Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy in Two Pediatric Patients: Case Report and Literature Review
- Hypertensive Encephalopathy in a 10-year-old Boy with Ureteral Stone
- Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis and Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19)
- MR Imaging of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy:A Report of Two Cases