J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2023 Sep;27(3):99-102. 10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.3.99.
Chronic Longitudinal Rupture of the Tibialis Anterior Tendon: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2545988
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.3.99
Abstract
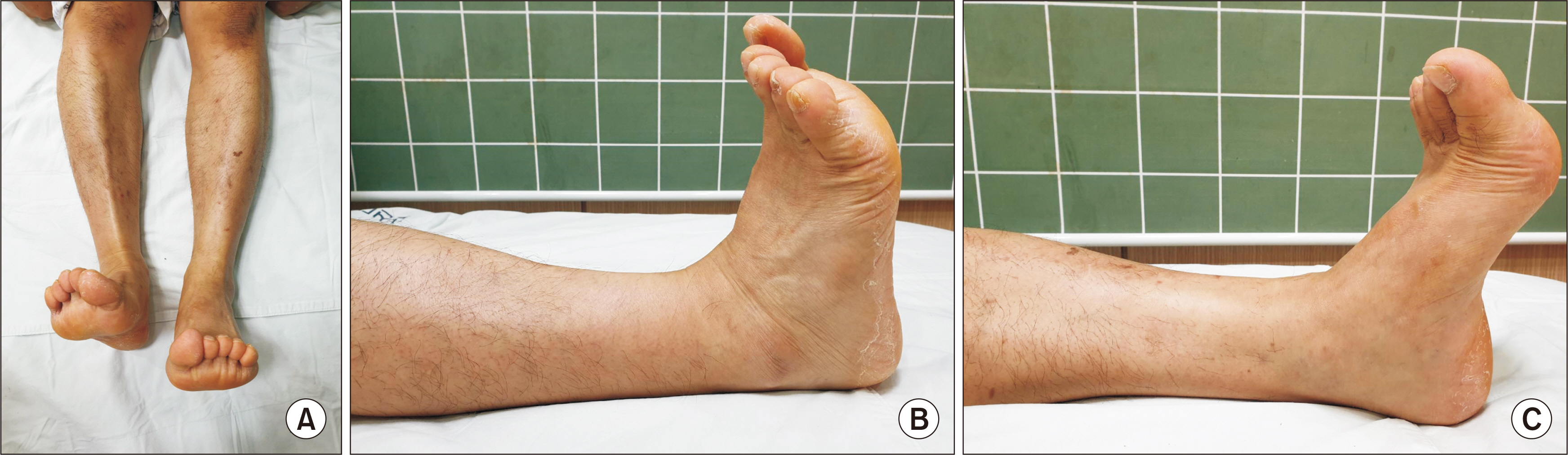
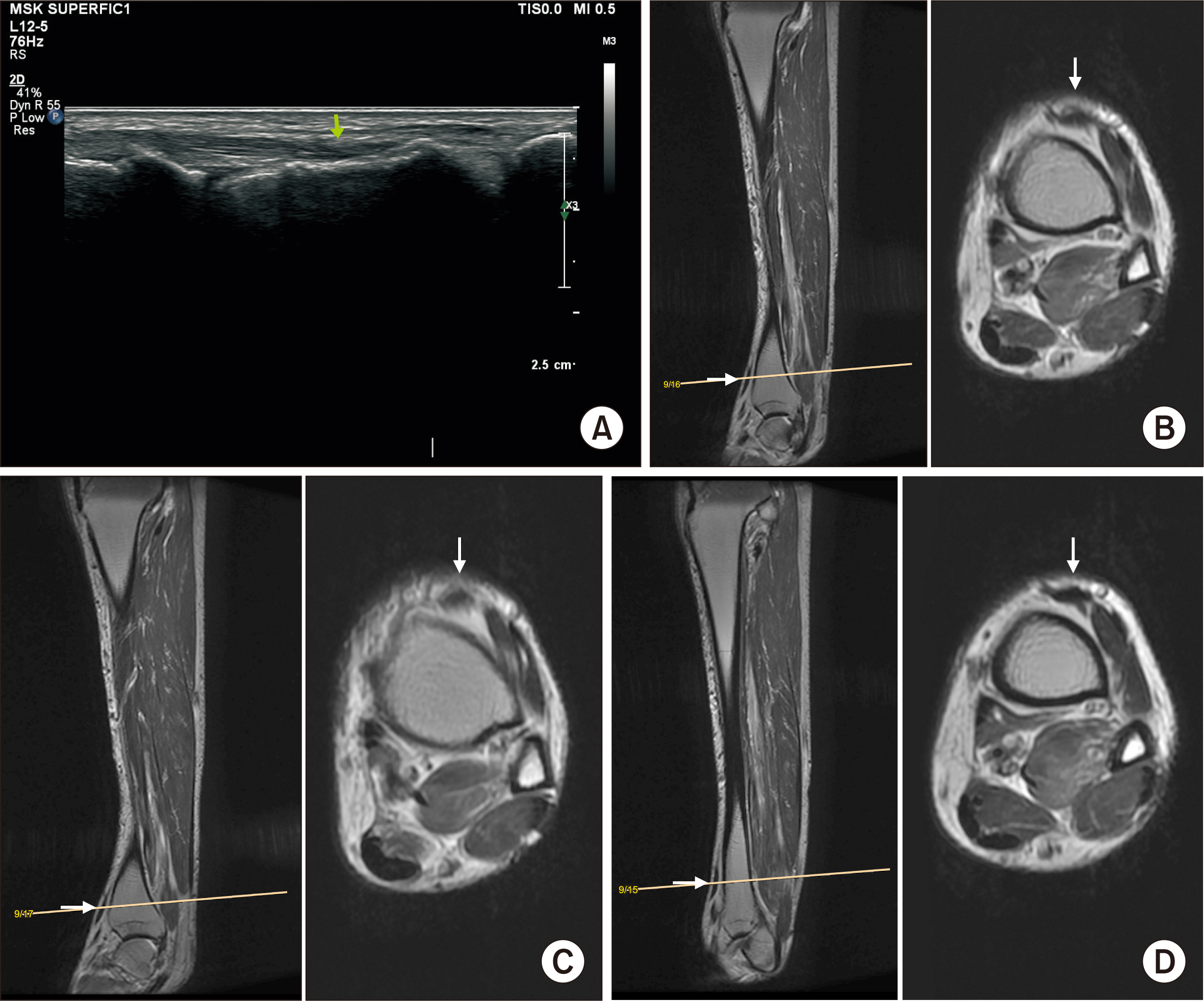
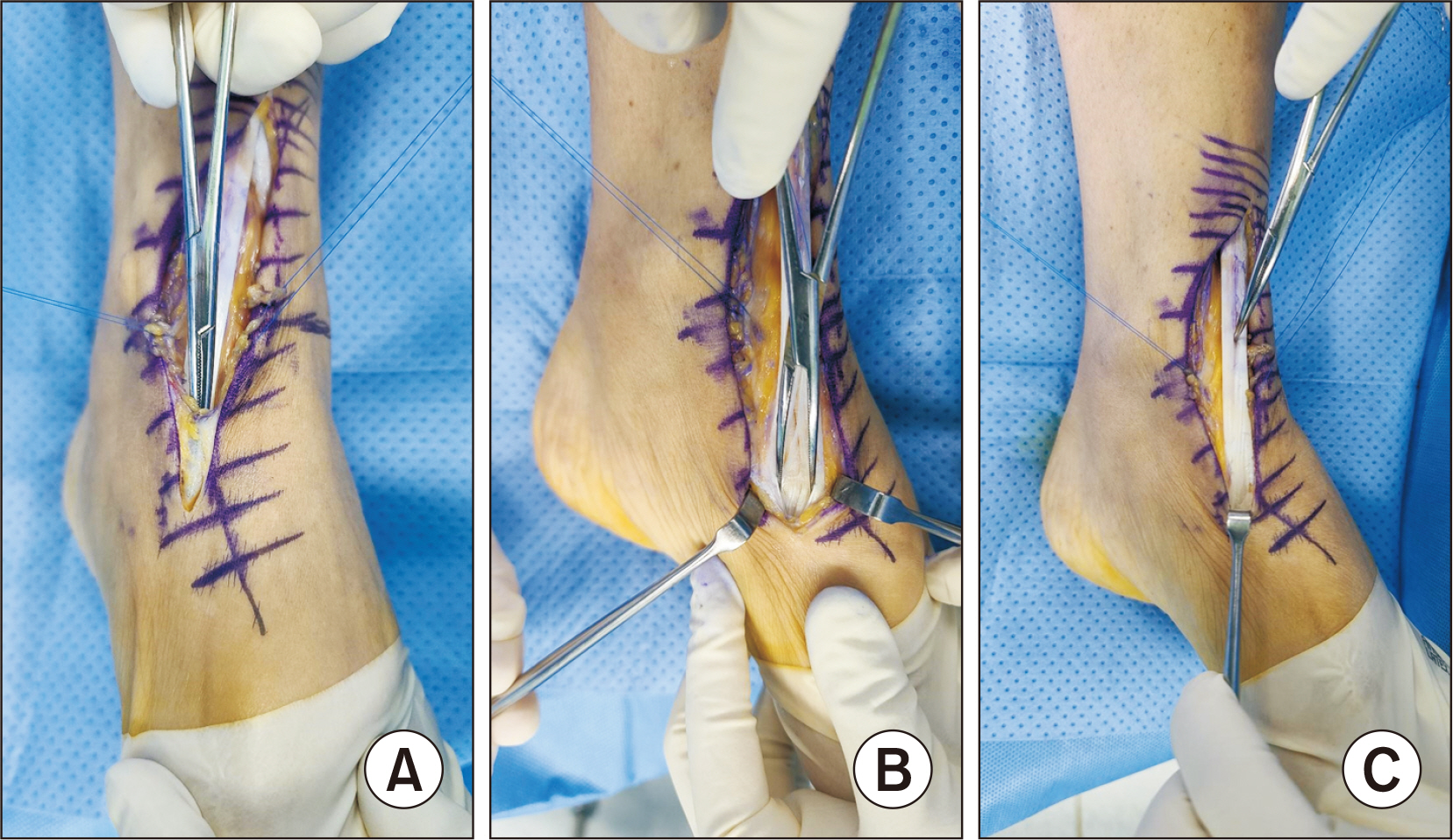
- Acute rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon is rare, but the diagnosis is often delayed when it occurs. Acute rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon is often caused by minor trauma or it occurs spontaneously. Therefore, the diagnosis is more likely to be delayed. Among ruptures of the tibialis anterior tendon, longitudinal ruptures are less common and difficult to diagnose. Thus far, there are no reports of ruptures of the tibialis anterior tendon caused by direct trauma in Korea. This paper reports a case of chronic longitudinal tear of the tibialis anterior tendon caused by trauma in a 50-year-old male patient with no specific history of the disease, along with a review of the relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kweon SH, Kang HJ, Lee SI. 2015; Complete rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon due to intratendinous ganglion cyst. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 50:412–7. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.5.412. DOI: 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.5.412.
Article2. Anzel SH, Covey KW, Weiner AD, Lipscomb PR. 1959; Disruption of muscles and tendons; an analysis of 1, 014 cases. Surgery. 45:406–14. PMID: 13635217.3. Markarian GG, Kelikian AS, Brage M, Trainor T, Dias L. 1998; Anterior tibialis tendon ruptures: an outcome analysis of operative versus nonoperative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 19:792–802. doi: 10.1177/107110079801901202. DOI: 10.1177/107110079801901202. PMID: 9872465.
Article4. Seo JH, Jeong JS. 2014; Curvilinear incision in total ankle arthroplasty: a case report. J Korean Orthop Res Soc. 17:41–5. doi: 10.0000/jkors.2014.17.2.41. DOI: 10.0000/jkors.2014.17.2.41.5. Kim J, Kim BS. 2022; Patient-reported outcome measures of the foot and ankle. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 26:1–8. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.1. DOI: 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.1.1.
Article6. Jung HG. 2008; Diagnosis and treatment of the peroneal tendon and tibialis anterior tendon disorders. J Korean Orthop Ultrasound Soc. 1:58–63.7. Hamilton GA, Ford LA. 2005; Longitudinal tear of the tibialis anterior tendon. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 95:390–3. doi: 10.7547/0950390. DOI: 10.7547/0950390. PMID: 16037556.
Article8. Grundy JR, O'Sullivan RM, Beischer AD. 2010; Operative management of distal tibialis anterior tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int. 31:212–9. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0212. DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0212. PMID: 20230699.9. Kopp FJ, Backus S, Deland JT, O'Malley MJ. 2007; Anterior tibial tendon rupture: results of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 28:1045–7. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2007.1045. DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2007.1045. PMID: 17923052.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Tibialis Anterior Tendon Rupture Treated with Semitendinosus Autograft: A Report of Two Cases
- Complete Rupture of the Tibialis Anterior Tendon Due to Intratendinous Ganglion Cyst
- Avulsion Fracture of Medial Cuneiform by Tibialis Anterior Tendon (A Case Report)
- Tenodesis after Tendon Lengthening for Irreparable Tibialis Anterior Tendon Avulsion Injury: A Case Report
- Clinical Features of Tibialis Anterior Tendon Rupture