Ann Surg Treat Res.
2023 Sep;105(3):148-156. 10.4174/astr.2023.105.3.148.
The prognostic and predictive value of plasma D-dimer in children with neuroblastoma: a 7-year retrospective analysis at a single institution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgical Oncology, Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2National International Science and Technology Cooperation Base for Critical Children’s Developmental Diseases, Chongqing, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Child Developmental Diseases Research of Ministry of Education, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Pediatrics, Chongqing, China
- KMID: 2545906
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2023.105.3.148
Abstract
- Purpose
Elevated plasma D-dimer level is a poor prognostic factor for many solid tumors. However, limited research has been conducted on D-dimer in children with neuroblastoma (NB), and its clinical significance remains unclear. The present study investigated the clinical and prognostic significance of D-dimer in pediatric NB patients.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of all newly admitted NB patients was conducted from January 2014 to December 2020. Baseline clinicopathological features, preoperative laboratory parameters, and follow-up information were collected. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to determine the relationship between D-dimer level, clinical features, and the prognostic value.
Results
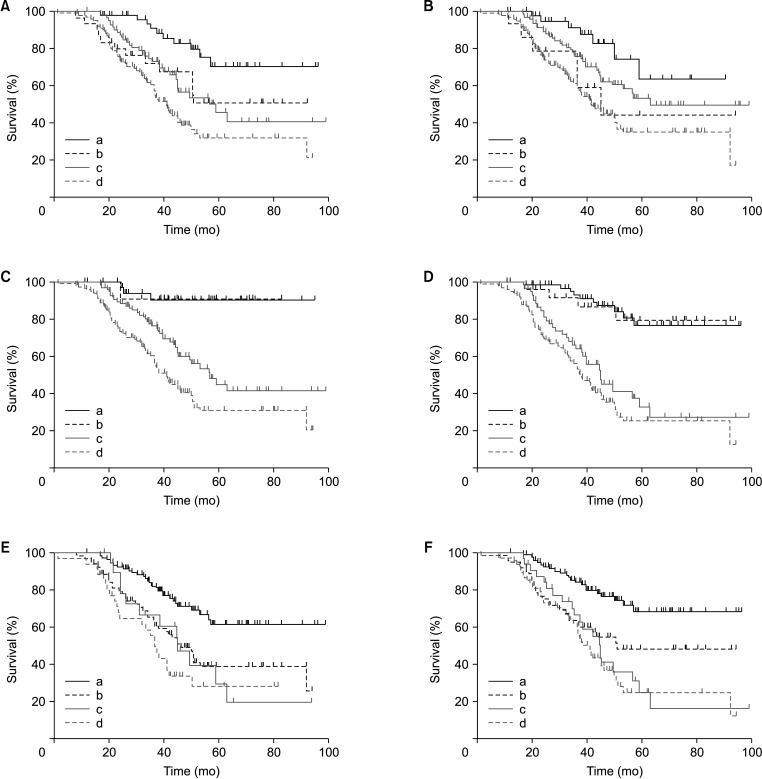
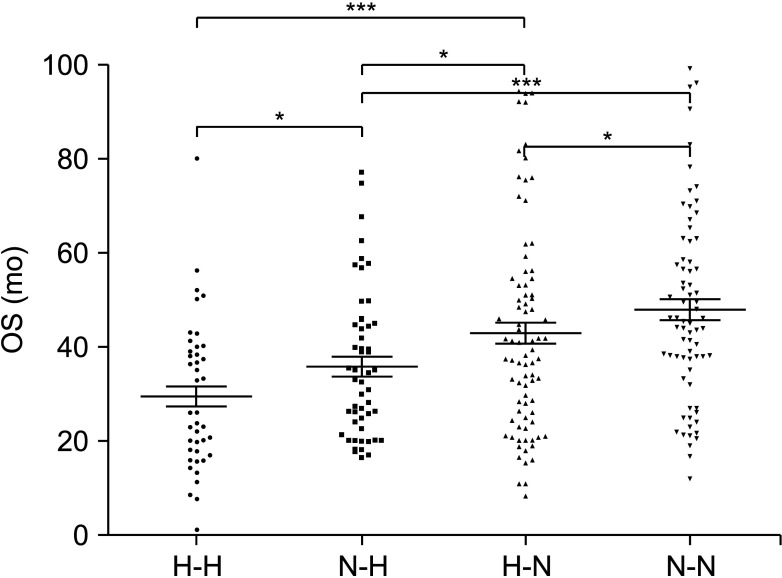
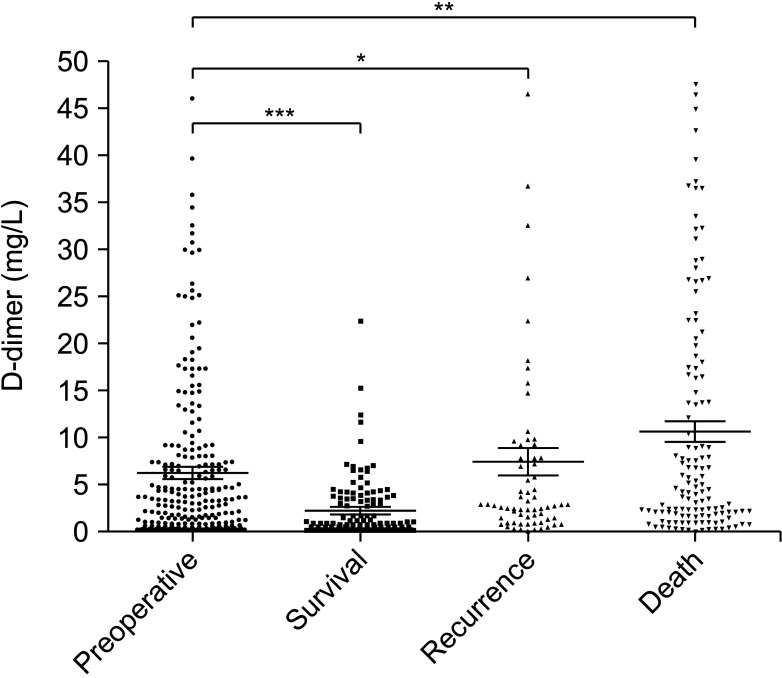
Among 266 patients, the median value of D-dimer was 2.98 ng/mL, of which 132 patients showed elevated D-dimer levels before surgery (>2.98 ng/mL). Univariate analysis revealed that elevated D-dimer was significantly associated with age, hemoglobin, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, neuron-specific enolase, 24-hour vanillylmandelic acid, overall survival, and so on (P < 0.05). Patients with elevated D-dimer levels had shorter median overall survival time when compared with normal D-dimer levels (P = 0.01). The prognosis was better in patients with normal D-dimer levels when combined with lower age, ganglioneuroblastoma tumor type, lower stage on International Neuroblastoma Staging System, low-risk group, and without bone metastasis or bone marrow metastasis. The continuous increase of D-dimer level after treatment indicated tumor recurrence or progression.
Conclusion
A high D-dimer level is associated with low overall survival, and an elevated D-dimer level after treatment indicates tumor recurrence and progression. D-dimer can be used as one of the evaluation factors for NB treatment or prognosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park JR, Eggert A, Caron H. Neuroblastoma: biology, prognosis, and treatment. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010; 24:65–86. PMID: 20113896.
Article2. Johnsen JI, Dyberg C, Wickström M. Neuroblastoma: a neural crest derived embryonal malignancy. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019; 12:9. PMID: 30760980.3. Cheung NK, Dyer MA. Neuroblastoma: developmental biology, cancer genomics and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013; 13:397–411. PMID: 23702928.
Article4. Park JR, Bagatell R, Cohn SL, Pearson AD, Villablanca JG, Berthold F, et al. Revisions to the international neuroblastoma response criteria: A Consensus Statement from the National Cancer Institute Clinical Trials Planning Meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:2580–2587. PMID: 28471719.
Article5. Schulte M, Köster J, Rahmann S, Schramm A. Cancer evolution, mutations, and clonal selection in relapse neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018; 372:263–268. PMID: 29478075.
Article6. von Stedingk K, Gisselsson D, Bexell D. Multidimensional intratumour heterogeneity in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 2019; 10:3–5. PMID: 30713595.
Article7. Bosse KR, Maris JM. Advances in the translational genomics of neuroblastoma: from improving risk stratification and revealing novel biology to identifying actionable genomic alterations. Cancer. 2016; 122:20–33. PMID: 26539795.
Article9. Eisenhofer G, Peitzsch M, Bechmann N, Huebner A. Biochemical diagnosis of catecholamine-producing tumors of childhood: neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:901760. PMID: 35957826.
Article10. Zhu FY, Yan J, Cao YN, Jin Y, Li J, Zhao Q. Early decline of neuron-specific enolase during neuroblastoma chemotherapy is a predictive factor of clinical outcome. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2021; 38:543–554. PMID: 34106032.
Article11. Moroz V, Machin D, Hero B, Ladenstein R, Berthold F, Kao P, et al. The prognostic strength of serum LDH and serum ferritin in children with neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) project. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020; 67:e28359. PMID: 32472746.
Article12. Deme D, Telekes A. Prognostic importance of cross-linked fibrin degradation products (D-dimer) in oncology. Magy Onkol. 2017; 61:319–326. PMID: 29257150.13. Kim EY, Song KY. Prognostic value of D-dimer levels in patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy. Surg Oncol. 2021; 37:101570. PMID: 33839443.
Article14. Ma M, Cao R, Wang W, Wang B, Yang Y, Huang Y, et al. The D-dimer level predicts the prognosis in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021; 16:243. PMID: 34454552.
Article15. Fang P, Du L, Cai D. Evaluation of plasma D-dimer for the diagnosis in Chinese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99:e19461. PMID: 32195943.16. Lu Y, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Chen D, Lou J, et al. The association of D-dimer with clinicopathological features of breast cancer and its usefulness in differential diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0221374. PMID: 31487295.
Article17. Lin Y, Liu Z, Qiu Y, Zhang J, Wu H, Liang R, et al. Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen in digestive cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44:1494–1503. PMID: 30100361.
Article18. Nakashima J, Tachibana M, Ueno M, Baba S, Tazaki H. Tumor necrosis factor and coagulopathy in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:4881–4885. PMID: 7585524.19. Luo YL, Chi PD, Zheng X, Zhang L, Wang XP, Chen H. Preoperative D-dimers as an independent prognostic marker in cervical carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36:8903–8911. PMID: 26071675.
Article20. Aravindan N, Herman T, Aravindan S. Emerging therapeutic targets for neuroblastoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020; 24:899–914. PMID: 33021426.
Article21. Castel V, Cañete A, Navarro S, García-Miguel P, Melero C, Acha T, et al. Outcome of high-risk neuroblastoma using a dose intensity approach: improvement in initial but not in long-term results. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2001; 37:537–542. PMID: 11745893.
Article22. London WB, Castel V, Monclair T, Ambros PF, Pearson AD, Cohn SL, et al. Clinical and biologic features predictive of survival after relapse of neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group project. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3286–3292. PMID: 21768459.
Article23. Nasser NJ, Fox J, Agbarya A. Potential mechanisms of cancer-related hypercoagulability. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12:566. PMID: 32121387.
Article24. Nadir Y. Decreasing tumor growth and angiogenesis by inhibition of coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2019; 45:622–628. PMID: 31398734.
Article25. Palumbo JS, Talmage KE, Massari JV, La Jeunesse CM, Flick MJ, Kombrinck KW, et al. Platelets and fibrin(ogen) increase metastatic potential by impeding natural killer cell-mediated elimination of tumor cells. Blood. 2005; 105:178–185. PMID: 15367435.
Article26. Ward MP, Kane LE, Norris LA, Mohamed BM, Kelly T, Bates M, et al. Platelets, immune cells and the coagulation cascade: friend or foe of the circulating tumour cell? Mol Cancer. 2021; 20:59. PMID: 33789677.
Article27. Lee AY. Cancer and thromboembolic disease: pathogenic mechanisms. Cancer Treat Rev. 2002; 28:137–140. PMID: 12234564.
Article28. Chen Y, Chai Y, Huang H, Zhang M, Zhang S. Circulating D-dimer level is a predictor of overall survival and correlates with clinicopathologic characteristics of patients with neuroblastoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018; 11:5436–5440. PMID: 31949627.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between plasma D-dimer levels and the severity of patients with chronic urticaria
- The Influence of Anticoagulants and Time of Measurements on D-Dimer Determinations
- Plasma D-dimer Determination in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
- Plasma Fibrin D-dimer for Detection of Acute Aortic Syndrome in the Emergency Department
- One Case of Retroperitoneal Neuroblastoma in an Adult