Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2023 Aug;27(3):277-286. 10.14701/ahbps.23-010.
Histopathological changes in gall bladder mucosa in relation to the number, and size of gallstones, and analysis of the findings in the context of age distribution of the patients: A perspective
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Government Medical College, Amritsar, India
- 2Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Amritsar, India
- 3Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, India
- KMID: 2545774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.23-010
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
To study histopathological changes in gall bladder mucosa in cholelithiasis patients, and analyse their relation to the number and size of gallstones. These findings were evaluated in the context of age distribution of the study population.
Methods
One hundred cases of cholecystectomy were part of the study, which was conducted in collaboration with the pathology department. The time period of the study was January 2020 to June 2021.
Results
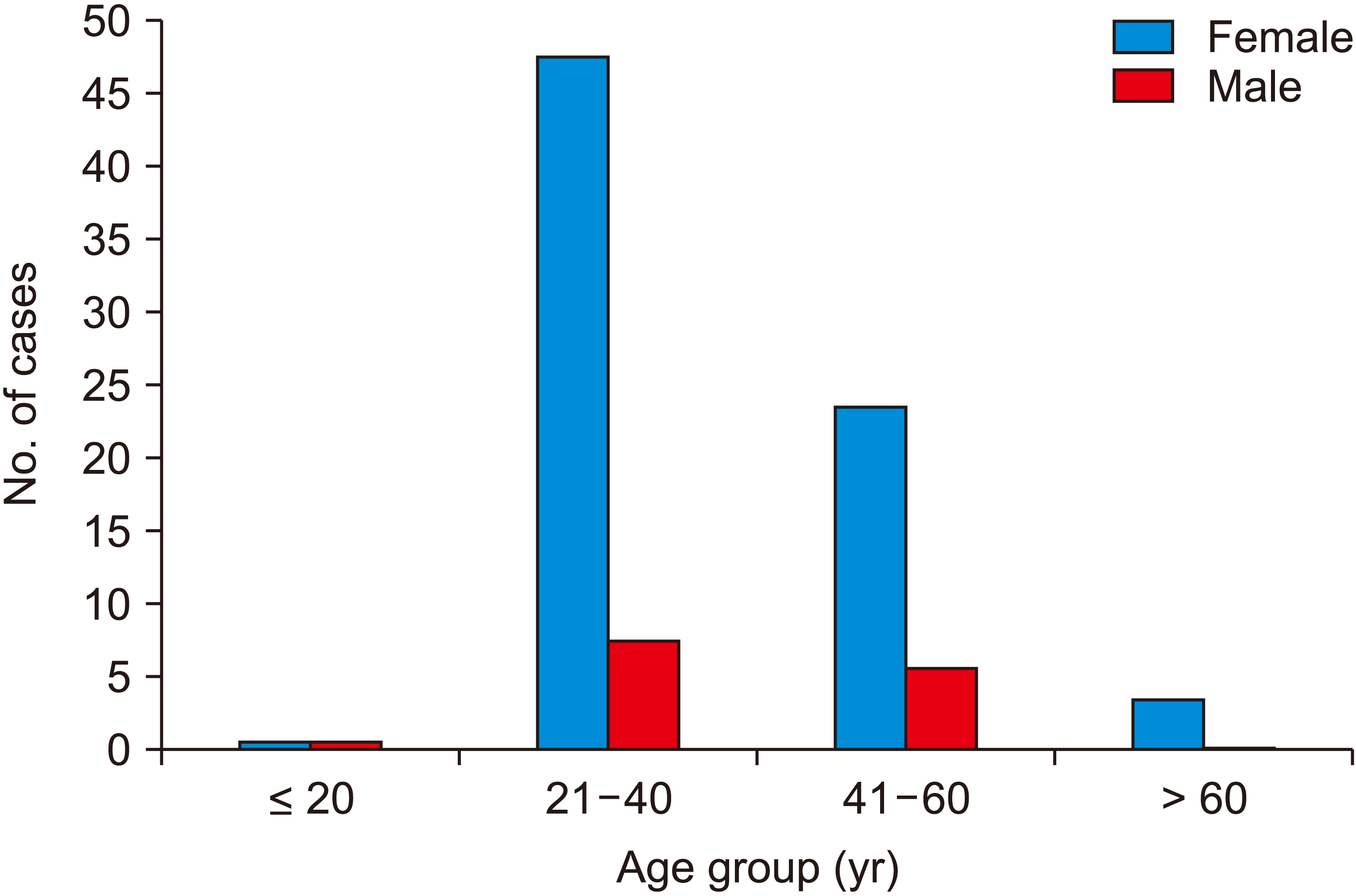
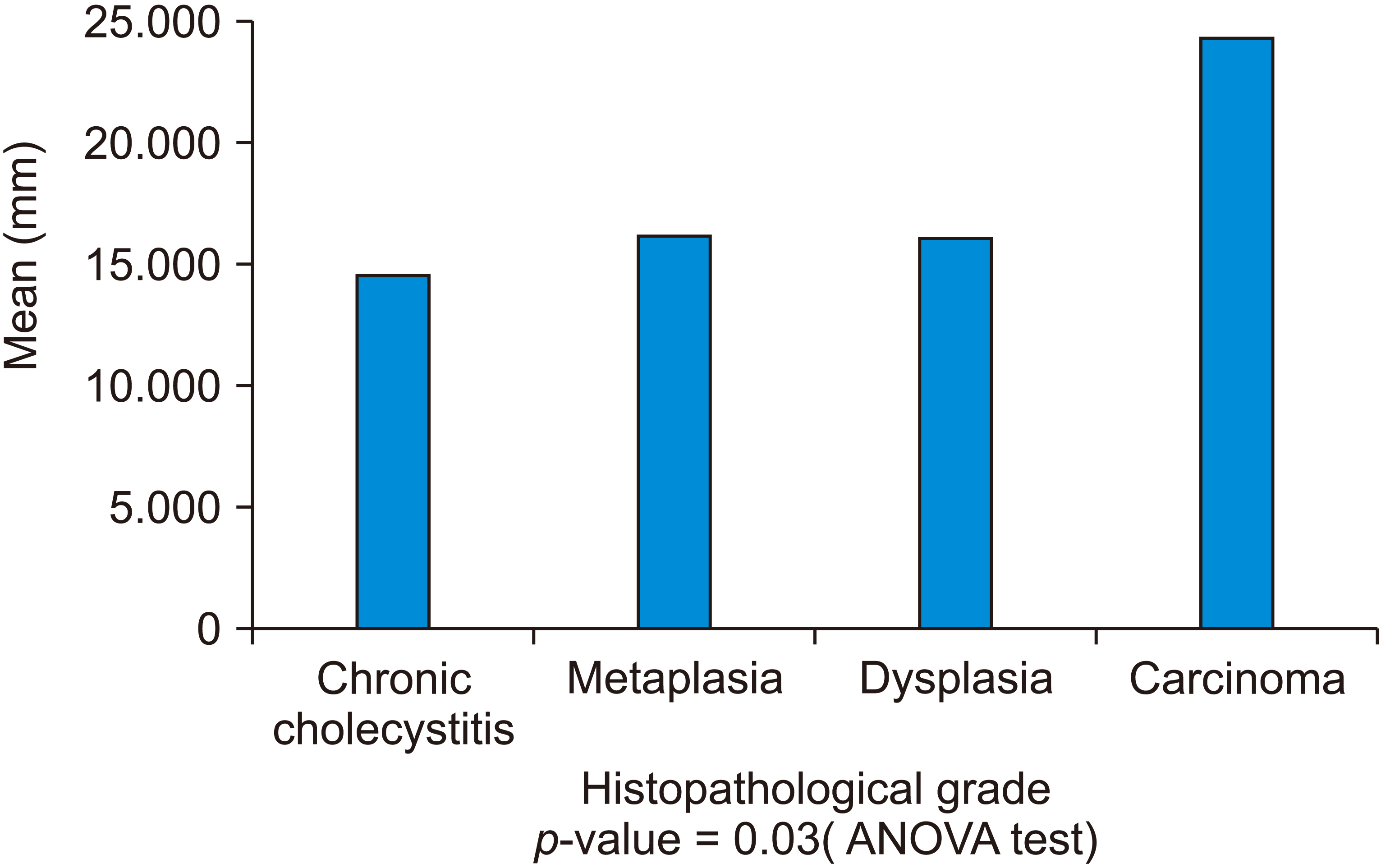
Maximum cases had multiple stones (69.0%), while one third cases (31.0%) had solitary stones. While initial univariate analysis showed age (odds ratio [OR], 6.882; p = 0.043), gallstone number (OR, 9.1; p = 0.050), gallstone size (OR, 17.111; p = 0.013), and duration of symptom (OR, 34.125; p = 0.001) to be significant risk factors associated with gallbladder carcinoma, multivariate analysis found none of these variables to be significant. However, conditional multivariate analysis for the duration of symptom (p = 0.008; OR, 21.118) yielded significant p-value. With histopathological diagnoses, 5% of cases had gallbladder cancer.
Conclusions
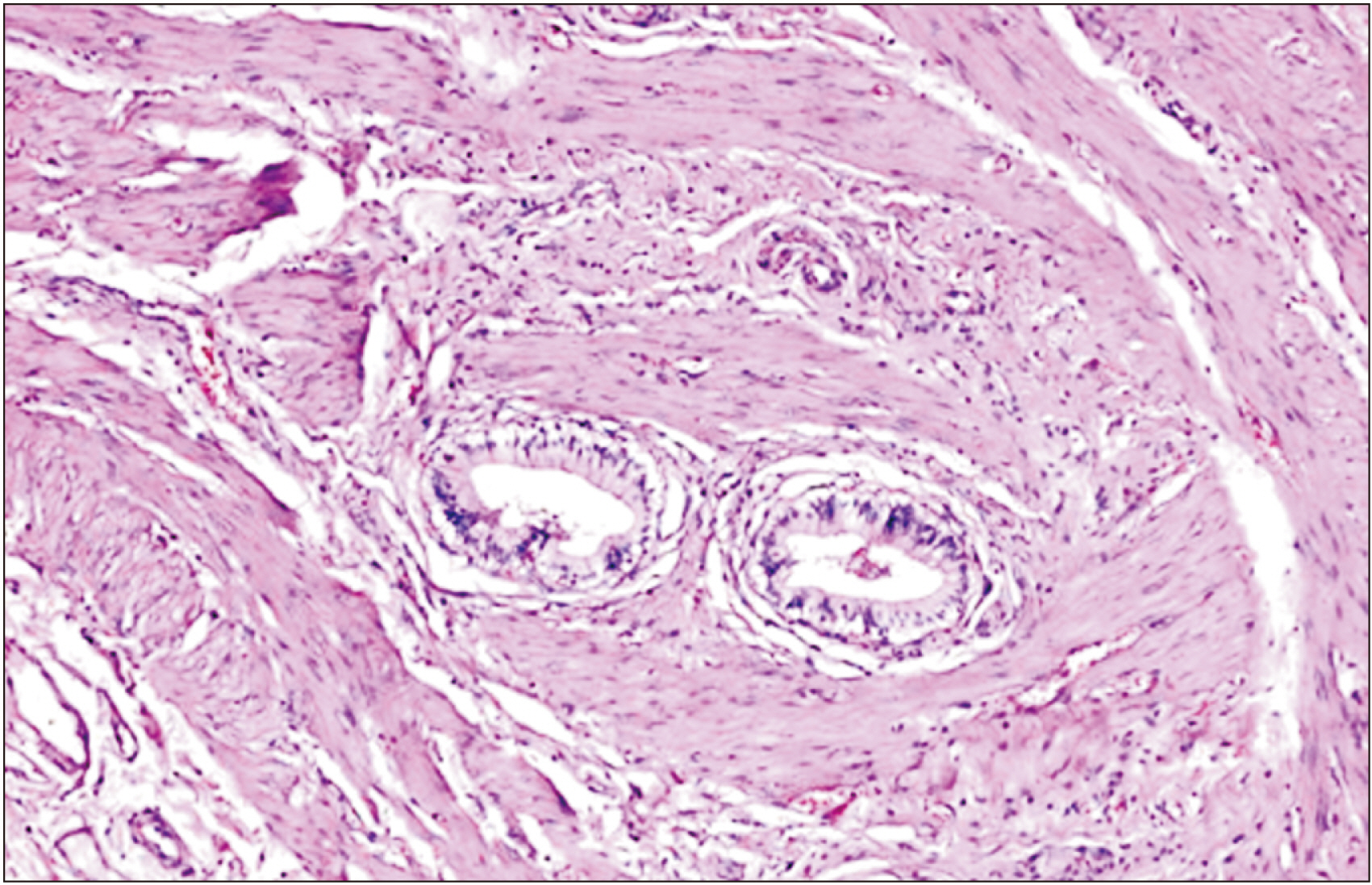
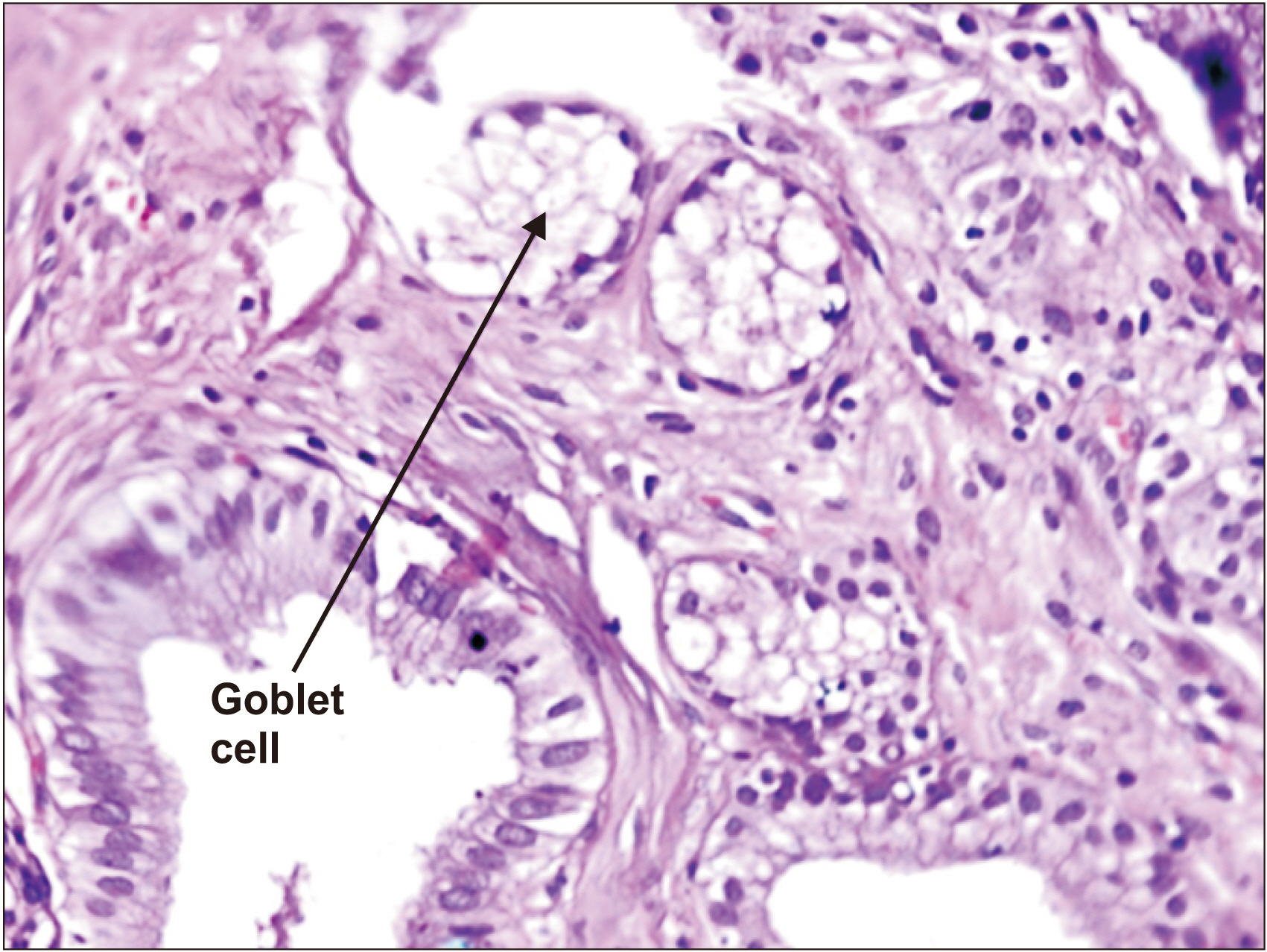
This study shed light on the rising incidence of cholelithiasis in the young population and the high rate of gallbladder carcinoma in Punjab, India. Although gall stone characteristics (size, number) and patient age appeared to be significant risk factors when their individual relation with gallbladder carcinoma was studied, multivariate analysis, could not prove that. Conditional multivariate analysis showed the duration of symptom to be the only significant risk factor associated with gallbladder carcinoma. Further research with larger sample size is needed to study the rising incidence of gallbladder carcinoma, and the risk factors associated with it.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rakesh Tendon. Siddharth N Shah, editor. 2003. Diseases of gallbladder and biliary tract. API text of Medicine. 7th ed. Association physicians india;p. 642–644.2. Narang S, Goyal P, Bal MS, Bandlish U, Goyal S. 2014; Gall stones size, number, biochemical analysis and lipidogram-an association with gall bladder cancer: a study of 200 cases. Int J Cancer Ther Oncol. 2:0203103. DOI: 10.14319/ijcto.0203.10.3. Bansal A, Akhtar M, Bansal AK. A clinical study: prevalence and management of cholelithiasis. International Surgery Journal. 2014; 1:134–9. DOI: 10.5455/2349-2902.isj20141105.4. Tyagi SP, Tyagi N, Maheshwari V, Ashraf SM, Sahoo P. 1992; Morphological changes in diseased gall bladder: a study of 415 cholecystectomies at Aligarh. J Ind Med Assoc. 90:178–181. PMID: 1401974.5. Koebnick C, Smith N, Black MH, Porter AH, Richie BA, Hudson S, et al. 2012; Pediatric obesity and gallstone disease: results from a cross-sectional study of over 510,000 youth. J Ped Gastroenterol Nutr. 55:328–333. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31824d256f. PMID: 22314396. PMCID: PMC3401629.6. Shafique MS, Ahmad R, Ahmad SH, Hassan SW, Khan JS. 2018; Gallstones in young population. J Ulutas Med. 4:131–138. DOI: 10.5455/umj.20180324011035.7. Rakesh BH, Rajendra GC. 2013; A prospective clinicopathological study of 50 cases of chronic calculous cholecystitis in the local population. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2:6706–6717. DOI: 10.14260/jemds/1197.8. Khan MK, Jalil MA, Khan MS. 2007; Oral contraceptives in gall stone diseases. Mymensingh Med J. 16(2 Suppl):S40–45. PMID: 17917630.9. Graewin SJ, Kiely JM, Lee KH, Svatek CL, Nakeeb A, Pitt HA. 2004; Nonobese diabetic mice have diminished gallbladder motility and shortened crystal observation time. J Gastrointe Surg. 8:824–829. discussion 829–830. DOI: 10.1016/j.gassur.2004.06.014. PMID: 15531235.10. Agunloye AM, Adebakin AM, Adeleye JO, Ogunseyinde AO. 2013; Ultrasound prevalence of gallstone disease in diabetic patients at Ibadan, Nigeria. Nigerian J Clin Pract. 16:71–75. DOI: 10.4103/1119-3077.106770. PMID: 23377475.11. Gupta A, Gupta S, Siddeek RA, Chennatt JJ, Singla T, Rajput D, et al. 2021; Demographic and clinicopathological profile of gall bladder cancer patients: study from a tertiary care center of the Sub-Himalayan region in Indo-Gangetic Belt. J Carcinog. 20:6. DOI: 10.4103/jcar.JCar_3_21. PMID: 34321956. PMCID: PMC8312375.12. Rathore A, Pathak A, Ranjan S, Sud R, Shivshankara MS, Pandaya T, et al. 2022; A clinicoepidemiological and management profile of metastatic carcinoma gallbladder in the northeast part of Indian patients in a tertiary care center. J Cancer Res Ther. 18(Supplement):S428–S433. DOI: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1213_20. PMID: 36510998.13. Batra Y, Pal S, Dutta U, Desai P, Garg PK, Makharia G, et al. 2005; Gallbladder cancer in India: a dismal picture. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:309–314. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.03576.x. PMID: 15683437.14. Dutta U, Garg PK, Kumar R, Tandon RK. 2000; Typhoid carriers among patients with gallstones are at increased risk for carcinoma of the gallbladder. Am J Gastroenterol. 95:784–787. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01860.x. PMID: 10710075.15. Valdivieso V, Covarrubias C, Siegel F, Cruz F. 1993; Pregnancy and cholelithiasis: pathogenesis and natural course of gallstones diagnosed in early puerperium. Hepatology. 17:1–4. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840170102. PMID: 8423030.16. Nakagaki M, Nakayama F. 1982; Effect of female sex hormones on lithogenicity of bile. Jap J Surg. 12:13–18. DOI: 10.1007/BF02469009. PMID: 7069944.17. Dutta U, Nagi B, Garg PK, Sinha SK, Singh K, Tandon RK. 2005; Patients with gallstones develop gallbladder cancer at an earlier age. Eur J Cancer Prev. 14:381–385. DOI: 10.1097/00008469-200508000-00011. PMID: 16030429.18. Konstantinidis IT, Deshpande V, Genevay M, Berger D, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Tanabe KK, et al. 2009; Trends in presentation and survival for gallbladder cancer during a period of more than 4 decades: a single-institution experience. Arch Surg. 144:441–447. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.46. PMID: 19451486.19. Gupta P, Agarwal A, Gupta V, Singh PK, Pantola C, Amit S. 2012; Expression and clinicopathological significance of estrogen and progesterone receptors in gallbladder cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 5:41–47. PMID: 22690257. PMCID: PMC3369597.20. Goyal S, Singla S, Duhan A. 2014; Correlation between gallstones characteristics and gallbladder mucosal changes: a retrospective study of 313 patients. Clin Cancer Investig J. 3:157–161. DOI: 10.4103/2278-0513.130215.21. Nair B, Malhotra K, Kaundal AK, Malhotra A. 2020; A study of chemical composition of gall stones in a tertiary care hospital. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 9:2422–2427. DOI: 10.14260/jemds/2020/527.22. Alshoabi S. 2016; Gallstones: site, size, number, prevalence and complications by ultrasonography. Int J Med Ima. 4:52–56.23. Mathur SK, Duhan A, Singh S, Aggarwal M, Aggarwal G, Sen R, et al. 2012; Correlation of gallstone characteristics with mucosal changes in gall bladder. Trop Gastroenterol. 33:39–44. DOI: 10.7869/tg.2012.6. PMID: 22803294.24. Khanna R, Chansuria R, Kumar M, Shukla HS. Histological changes in gallbladder due to stone disease. Indian J Surg. 2006; 1;68:201–204.25. Seretis C, Lagoudianakis E, Gemenetzis G, Seretis F, Pappas A, Gourgiotis S. 2014; Metaplastic changes in chronic cholecystitis: implications for early diagnosis and surgical intervention to prevent the gallbladder metaplasia-dysplasia-carcinoma sequence. J Clin Med Res. 6:26–29. DOI: 10.4021/jocmr1689w. PMID: 24400028. PMCID: PMC3881986.26. Phadke PR, Mhatre SS, Budukh AM, Dikshit RP. 2019; Trends in gallbladder cancer incidence in the high-and low-risk regions of India. Ind J Med Paediatr Oncol. 40:90–3. DOI: 10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_164_18.27. Nandakumar A. 1990. National cancer registry programme. Consolidated report of the population based cancer registries. Indian Council of Medical Research;p. 96.28. Yaqub F. 2013; Punjab's cancer awareness campaign. Lancet Oncol. 14:e92. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70051-2. PMID: 23580962.29. Aggarwal R, Manuja KA, Aditya K, Singh GP. 2015; Pattern of cancer in a tertiary care hospital in Malwa region of Punjab, in comparison to other regions in India. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:XC05–XC07. DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/11171.5685. PMID: 25954691. PMCID: PMC4413141.30. Budukh AM, Chaudhary D, Sancheti S, Dora T, Goel AK, Singla A, et al. 2021; Determinants of completion of cancer directed treatment: an experience from a rural cancer centre, Sangrur, Punjab state, India. Ecancermedicalscience. 15:1313. DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2021.1313. PMID: 35047064. PMCID: PMC8723738.31. Hundal R, Shaffer EA. 2014; Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol. 6:99–109. DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S37357. PMID: 24634588. PMCID: PMC3952897.32. Mishra G, Conway JD. 2009; Endoscopic ultrasound in the evaluation of radiologic abnormalities of the liver and biliary tree. Current Gastroenterol Rep. 11:150–154. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-009-0023-5. PMID: 19281703.33. Siegel RL, Torre LA, Soerjomataram I, Hayes RB, Bray F, Weber TK, et al. 2019; Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence in young adults. Gut. 68:2179–2185. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319511. PMID: 31488504.34. Roa I, Ibacache G, Roa J, Araya J, de Aretxabala X, Muñoz S. 2006; Gallstones and gallbladder cancer-volume and weight of gallstones are associated with gallbladder cancer: a case-control study. J Surg Oncol. 93:624–628. DOI: 10.1002/jso.20528. PMID: 16724353.35. Diehl AK. 1983; Gallstone size and the risk of gallbladder cancer. JAMA. 250:2323–2326. DOI: 10.1001/jama.1983.03340170049027. PMID: 6632129.36. Lowenfels AB, Walker AM, Althaus DP, Townsend G, Domellöf L. 1989; Gallstone growth, size, and risk of gallbladder cancer: an interracial study. Int J Epidemiol. 18:50–54. DOI: 10.1093/ije/18.1.50. PMID: 2722383.37. Csendes A, Becerra M, Rojas J, Medina E. 2000; Number and size of stones in patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic gallstones and gallbladder carcinoma: a prospective study of 592 cases. J Gastrointest Sur. 4:481–485. DOI: 10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80090-6. PMID: 11077323.38. Andrea C, Enzo A. 2016; Cholesterol gallstones larger than 3 cm appear to be associated with gallbladder cancer: identification of a high risk group of patients that could benefit from preventive cholecystectomy. Ann Surg. 263:e56. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001082. PMID: 25793627.39. Vitetta L, Sali A, Little P, Mrazek L. 2000; Gallstones and gall bladder carcinoma. Aust N Z J Surg. 70:667–673. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2000.01926.x. PMID: 10976897.40. Moerman CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Bueno de Mesquita HB, van Dalen A, van Leeuwen MS, Schrover PA. 1993; Gallstone size and the risk of gallbladder cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 28:482–486. DOI: 10.3109/00365529309098253. PMID: 8322023.41. Verma GR, Bose SM, Wig JD. 2001; Pericholecystic adhesions in single v multiple gallstones and their consequences for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Laparoendoscop Adv Surg Tech A. 11:275–279. DOI: 10.1089/109264201317054555. PMID: 11642662.42. Mukhopadhyay S, Landas SK. 2005; Putative precursors of gallbladder dysplasia: a review of 400 routinely resected specimens. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 129:386–390. DOI: 10.5858/2005-129-386-PPOGDA. PMID: 15737036.43. Rao I, Araya JC, Valiaseca M, De Aretxabala X, Riedemann P, Endoh K, et al. Preneoplastic lesions and gallbladder cancer: an estimate of the period required for progression. Gastroenterology. 1976; 111:232–236. DOI: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8698204. PMID: 8698204.44. Mishra K, Behari A, Shukla P, Tsuchiya Y, Endoh K, Asai T, et al. 2021; Risk factors for gallbladder cancer development in northern India: a gallstones-matched, case-control study. Indian J Med Res. 154:699–706. DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_201_19. PMID: 35532588. PMCID: PMC9210525.45. Serra I, Calvo A, Báez S, Yamamoto M, Endoh K, Aranda W. 1996; Risk factors of gallbladder cancer. An international collaborative case-contol study. Cancer. 78:1515–1517. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19961001)78:7<1515::AID-CNCR21>3.0.CO;2-1.46. Scott TE, Carroll M, Cogliano FD, Smith BF, Lamorte WW. 1999; A case-control assessment of risk factors for gallbladder carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 44:1619–1625. DOI: 10.1023/A:1026675329644. PMID: 10492143.47. Sharma M, Singh R. Carcinoma of the gall bladder: 8 year experience from a tertiary care centre, Punjab, India. International Surgery Journal. 2019; May. 28. 6:1912–6. DOI: 10.18203/2349-2902.isj20192059.48. Narula MK. 2023. Chandigarh: hope for gallbladder cancer patients not eligible for surgery [Internet]. Available from: https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/chandigarh-news/chandigarhhope-for-gallbladder-cancer-patients-not-eligible-for-surgery-101679182426962.html. cited Mar 19.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Roentgenological observation in the disease of biliary tract by plain film study of abdomen
- Biliary manometry in patients with gall stones: a comparison between patients with common bile duct stones, gall bladder stones, intra-hepatic duct stones, previous cholecystectomy, and controls
- Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis
- Gall bladder wal varices:Easy diagnosis with multiphase incremental bolus dynamic CT
- A case of eosinophilic cholecystitis associated with gallstones