J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Sep;38(35):e276. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e276.
Association Between Changes in Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Parameter and the Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Heart Failure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Cardiovascular Center, Seoul National University Hospital and Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2545554
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e276
Abstract
- Background
Volume overload is associated not only with clinical manifestations but also with poor outcomes of heart failure (HF). However, there is an unmet need for effective methods for serial monitoring of volume status during HF hospitalization. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic implication of serial measurement of bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) in patients hospitalized with acute HF.
Methods
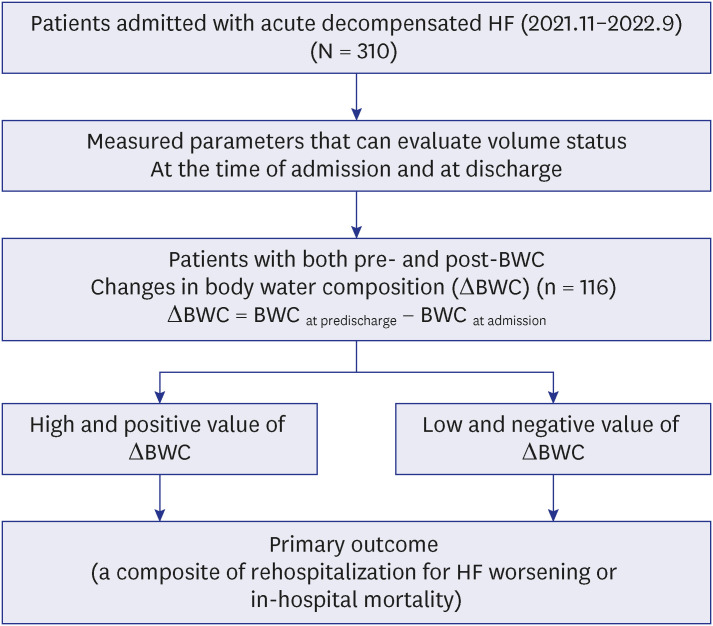
This study is a retrospective observational study and screened 310 patients hospitalized due to acute decompensated HF between November 2021 and September 2022. Among them, 116 patients with acute HF who underwent BIA at the time of admission and at discharge were evaluated. We investigated the correlation between change of BIA parameters and the primary composite outcome (in-hospital mortality or rehospitalization for worsening HF within one month).
Results
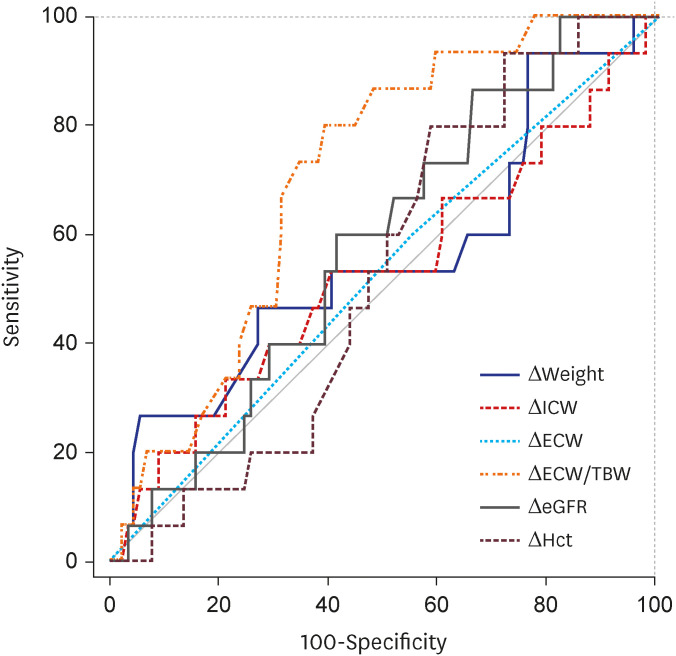
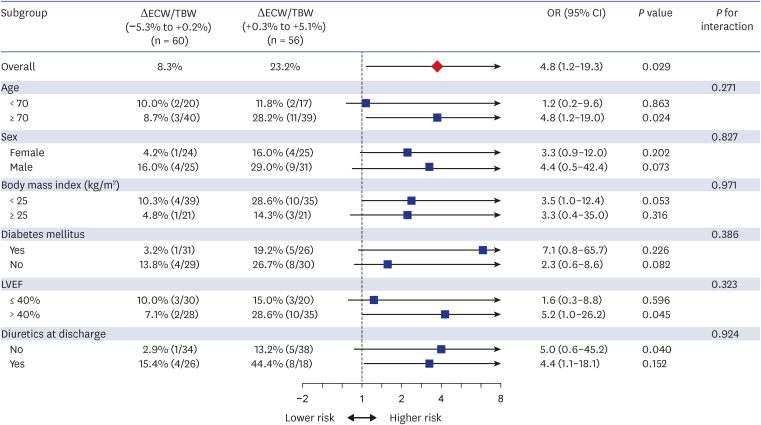
The median (interquartile range) age was 77 years (67–82 years). The mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 40.7 ± 14.6% and 55.8% of HF patients have HF with reduced ejection fraction. The body water composition (intracellular water [ICW], extracellular water [ECW], and total body water [TBW]) showed a statistically significant correlation with body mass index and LV chamber sizes. Furthermore, the ratio of ECW to TBW (ECW/TBW), as an edema index showed a significant correlation with natriuretic peptide levels. Notably, the change of the edema index during hospitalization (ΔECW/TBW) showed a significant correlation with the primary outcome. The area under the curve of ΔECW/TBW for predicting primary outcome was 0.71 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.61–0.79; P = 0.006). When patients were divided into two groups based on the median value of ΔECW/TBW, the group of high and positive ΔECW/TBW (+0.3% to +5.1%) had a significantly higher risk of the primary outcome (23.2% vs. 8.3%, adjusted odds ratio, 4.8; 95% CI, 1.2–19.3; P = 0.029) than those with a low and negative ΔECW/TBW (−5.3% to +0.2%).
Conclusion
BIA is a noninvasive and effective method to evaluate the volume status during the hospitalization of HF patients. The high and positive value of ΔECW/TBW during hospitalization was associated with poor outcomes in patients with HF.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miller WL. Fluid volume overload and congestion in heart failure: time to reconsider pathophysiology and how volume is assessed. Circ Heart Fail. 2016; 9(8):e002922. PMID: 27436837.2. Elhassan MG, Chao PW, Curiel A. The conundrum of volume status assessment: revisiting current and future tools available for physicians at the bedside. Cureus. 2021; 13(5):e15253. PMID: 34188992.
Article3. Craig M, Pereira NL. Right heart catheterization and risk stratification in advanced heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2006; 3(3):143–152. PMID: 16914107.
Article4. Porter TR, Shillcutt SK, Adams MS, Desjardins G, Glas KE, Olson JJ, et al. Guidelines for the use of echocardiography as a monitor for therapeutic intervention in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015; 28(1):40–56. PMID: 25559474.
Article5. Arjamaa O. Physiology of natriuretic peptides: the volume overload hypothesis revisited. World J Cardiol. 2014; 6(1):4–7. PMID: 24527182.
Article6. Park JH, Jo YI, Lee JH. Clinical usefulness of bioimpedance analysis for assessing volume status in patients receiving maintenance dialysis. Korean J Intern Med. 2018; 33(4):660–669. PMID: 29961308.
Article7. Malbrain ML, Huygh J, Dabrowski W, De Waele JJ, Staelens A, Wauters J. The use of bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA) to guide fluid management, resuscitation and deresuscitation in critically ill patients: a bench-to-bedside review. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014; 46(5):381–391. PMID: 25432557.
Article8. Ciumanghel AI, Grigoras I, Siriopol D, Blaj M, Rusu DM, Grigorasi GR, et al. Bio-electrical impedance analysis for perioperative fluid evaluation in open major abdominal surgery. J Clin Monit Comput. 2020; 34(3):421–432. PMID: 31201590.
Article9. Mayne KJ, Shemilt R, Keane DF, Lees JS, Mark PB, Herrington WG. Bioimpedance indices of fluid overload and cardiorenal outcomes in heart failure and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. J Card Fail. 2022; 28(11):1628–1641. PMID: 36038013.
Article10. Pirlich M, Schütz T, Spachos T, Ertl S, Weiss ML, Lochs H, et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a useful bedside technique to assess malnutrition in cirrhotic patients with and without ascites. Hepatology. 2000; 32(6):1208–1215. PMID: 11093726.11. Yu SJ, Kim DH, Oh DJ, Yu SH, Kang ET. Assessment of fluid shifts of body compartments using both bioimpedance analysis and blood volume monitoring. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21(1):75–80. PMID: 16479069.
Article12. Park CS, Lee SE, Cho HJ, Kim YJ, Kang HJ, Oh BH, et al. Body fluid status assessment by bio-impedance analysis in patients presenting to the emergency department with dyspnea. Korean J Intern Med. 2018; 33(5):911–921. PMID: 29241303.
Article13. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021; 42(36):3599–3726. PMID: 34447992.
Article14. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2022; 145(18):e895–1032. PMID: 35363499.15. Ji E, Kim YS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease defined by using CKD-EPI equation and albumin-to-creatinine ratio in the Korean adult population. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31(6):1120–1130. PMID: 27017386.
Article16. Levin A, Stevens PE, Bilous RW, Coresh J, De Francisco AL, De Jong PE, et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) CKD work group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013; 3(1):1–150.17. Choi G, Yoon HJ, Song YJ, Jeong HM, Gu JE, Han M, et al. Consistency of the estimated target weights and ECW/TBW using BIA after hemodialysis in patients between standing and lying-down positions. BMC Nephrol. 2022; 23(1):106. PMID: 35300597.
Article18. Yang EM, Park E, Ahn YH, Choi HJ, Kang HG, Cheong HI, et al. Measurement of fluid status using bioimpedance methods in korean pediatric patients on hemodialysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32(11):1828–1834. PMID: 28960036.
Article19. Liu MH, Wang CH, Huang YY, Tung TH, Lee CM, Yang NI, et al. Edema index established by a segmental multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis provides prognostic value in acute heart failure. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2012; 13(5):299–306. PMID: 22367574.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Validity of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) in Measurement of Human Body Composition
- Home Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Management System in Patients With Heart Failure: Rationale and Study Design
- Comparison of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Obese Women
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) of the Estimation of Total Body Water and Lean Body Mass in Patients with Renal Failure
- Correlation between Percentage of Body Fat by BIA and Other Obesity Indices