Arch Hand Microsurg.
2023 Sep;28(3):158-165. 10.12790/ahm.23.0023.
Risk factors for bacterial infection following replantation of zone 1 amputation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea
- KMID: 2545526
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.23.0023
Abstract
- Purpose
Bacterial infection is a critical complication influencing the survival of a replanted digit. This study aimed to identify risk factors for bacterial infection following zone 1 replantation.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted on patients who underwent zone 1 replantation from January 2016 to November 2022. The factors included in the comparative analysis were patient demographics (age, sex), past medical history (hypertension, diabetes mellitus), smoking, types of injury, degree of contamination, source of trauma, fractures, number of vascular anastomoses, use of salvage therapies, and the use of vein grafts. A bacterial infection was diagnosed based on observation of visible inflammatory signs with the results of culture studies.
Results
In total, 313 patients were selected. Thirty-eight cases of bacterial infection were identified, which accounted for 12.1% of total patients. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) was the most prevalent bacterium (63.2%, 24 of 38 cases). The patient and injury-related factors showed no significant differences, but the number of vein anastomoses and use of salvage therapy were significantly correlated with the occurrence of bacterial infection.
Conclusion
Performing fewer vein anastomoses appears to increase the likelihood of a salvage procedure, and subsequently increases the risk of bacterial infection by an increased need for direct wound manipulation after zone 1 replantation. Infections caused by MRSE were more commonly identified than those by Aeromonas hydrophilia, which is a commonly known pathogen in medicinal leeches.
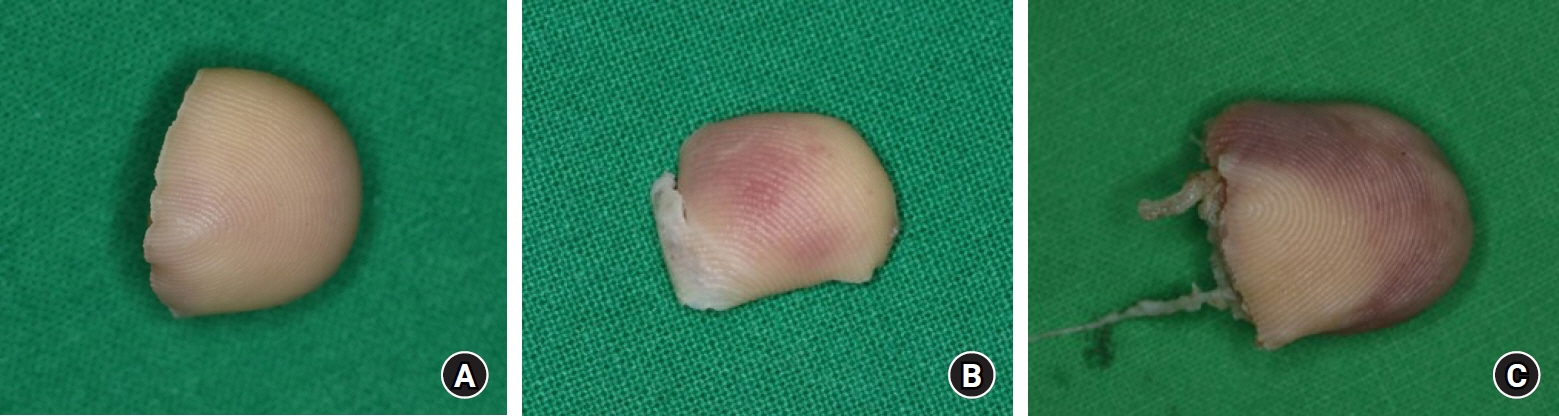
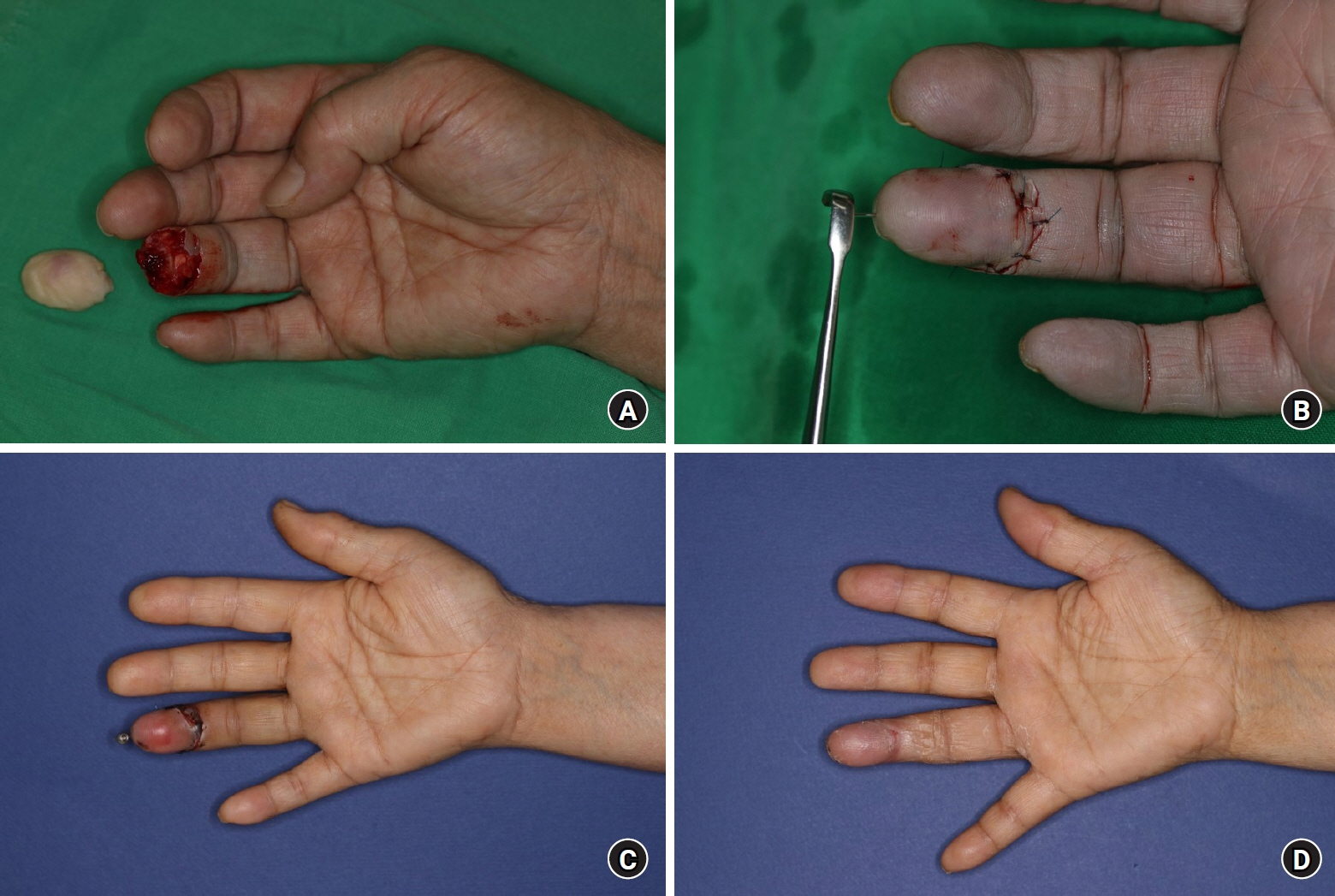
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sebastin SJ, Chung KC. A systematic review of the outcomes of replantation of distal digital amputation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 128:723–37.
Article2. Komatsu S, Tamai S. Successful replantation of a completely cut-off thumb. Plast Reconst Surg. 1968; 42:374–7.
Article3. Yamano Y. Replantation of the amputated distal part of the fingers. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:211–8.
Article4. Buntic RF, Brooks D. Standardized protocol for artery-only fingertip replantation. J Hand Surg Am. 2010; 35:1491–6.
Article5. Chen KK, Hsieh TY, Chang KP. Tamai zone I fingertip replantation: is external bleeding obligatory for survival of artery anastomosis-only replanted digits? Microsurgery. 2014; 34:535–9.
Article6. Barnett GR, Taylor GI, Mutimer KL. The "chemical leech": intra-replant subcutaneous heparin as an alternative to venous anastomosis. Report of three cases. Br J Plast Surg. 1989; 42:556–8.
Article7. Foucher G, Norris RW. Distal and very distal digital replantations. Br J Plast Surg. 1992; 45:199–203.
Article8. Kim SW, Han HH, Jung SN. Use of the mechanical leech for successful zone I replantation. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014; 2014:105234.
Article9. Lee NH, Yang KM. The problem of leech application in digital replantation. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2000; 9:158–63.10. Busing KH, Doll W, Freytag K. Bacterial flora of the medicinal leech. Arch Mikrobiol. 1953; 19:52–86.11. Daane S, Zamora S, Rockwell WB. Clinical use of leeches in reconstructive surgery. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1997; 26:528–32.12. Prsic A, Friedrich JB. Postoperative management and rehabilitation of the replanted or revascularized digit. Hand Clin. 2019; 35:221–9.
Article13. Boulas HJ. Amputations of the fingers and hand: indications for replantation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998; 6:100–5.14. Hong MK, Park J, Koh SH, et al. Analysis of outcomes of Tamai zone I digital replantation in cases of severe crushing injury. Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020; 25:297–303.15. Hattori Y, Doi K, Ikeda K, Abe Y, Dhawan V. Significance of venous anastomosis in fingertip replantation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 111:1151–8.16. Efanov JI, Rizis D, Landes G, Bou-Merhi J, Harris PG, Danino MA. Impact of the number of veins repaired in short-term digital replantation survival rate. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016; 69:640–5.17. Ryu DH, Roh SY, Kim JS, Lee DC, Lee KJ. Multiple venous anastomoses decrease the need for intensive postoperative management in tamai zone I replantations. Arch Plast Surg. 2018; 45:58–61.
Article18. Han SK, Lee BI, Kim WK. Topical and systemic anticoagulation in the treatment of absent or compromised venous outflow in replanted fingertips. J Hand Surg Am. 2000; 25:659–67.
Article19. Foucher G, Merle M, Braun JB. Distal digital replantation-one of the best indications for microsurgery. Int J Microsurg. 1981; 3:263–70.20. Whitlock MR, O'Hare PM, Sanders R, Morrow NC. The medicinal leech and its use in plastic surgery: a possible cause for infection. Br J Plast Surg. 1983; 36:240–4.
Article21. Mercer NS, Beere DM, Bornemisza AJ, Thomas P. Medical leeches as sources of wound infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987; 294:937.
Article22. Tepas JJ. Editor's foreword. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 73:S235.
Article23. Tran PA, O'Brien-Simpson N, Palmer JA, et al. Selenium nanoparticles as anti-infective implant coatings for trauma orthopedics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis: in vitro and in vivo assessment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019; 14:4613–24.24. Hospenthal DR, Murray CK, Andersen RC, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of infection after combat-related injuries. J Trauma. 2008; 64(3 Suppl):S211–20.25. Haque N, Bari MS, Haque N, et al. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Mymensingh Med J. 2011; 20:326–31.26. Kalani BS, Khodaei F, Moghadampour M, et al. TRs analysis revealed Staphylococcus epidermidis transmission among patients and hospital. Ann Ig. 2019; 31:52–61.27. Inweregbu K, Dave J, Pittard A. Nosocomial infections. Cont Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2005; 5:14–7.
Article28. Ziebuhr W, Hennig S, Eckart M, Kränzler H, Batzilla C, Kozitskaya S. Nosocomial infections by Staphylococcus epidermidis: how a commensal bacterium turns into a pathogen. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 28 Suppl 1:S14–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Review Article Fingertip Replantation
- Replantation for Segmental Amputation of the Digits and Hand: A Case Report
- Replantation of a Completely Amputated Penis, which Occurred in a Child during Circumcision
- A Case of Successful Penile Replantation
- Clinical Evaluation of Microreplantation in the Digital Amputation