Diabetes Metab J.
2023 Jul;47(4):559-570. 10.4093/dmj.2022.0226.
Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint University Laboratory of Metabolic and Molecular Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 4Jinan University Institute of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders, Guangzhou, China
- KMID: 2544734
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0226
Abstract
- Background
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert an essential contribution to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the differences of miRNAs in the presence and absence of T2DM in patients with obesity, as well as before and after bariatric surgery in T2DM patients with obesity. Characterization of the common changes in both was further analyzed.
Methods
We enrolled 15 patients with obesity but without T2DM and 15 patients with both obesity and T2DM. Their preoperative clinical data and serum samples were collected, as well as 1 month after bariatric surgery. The serum samples were analyzed by miRNA sequencing, and the miRNAs profiles and target genes characteristics were compared.
Results
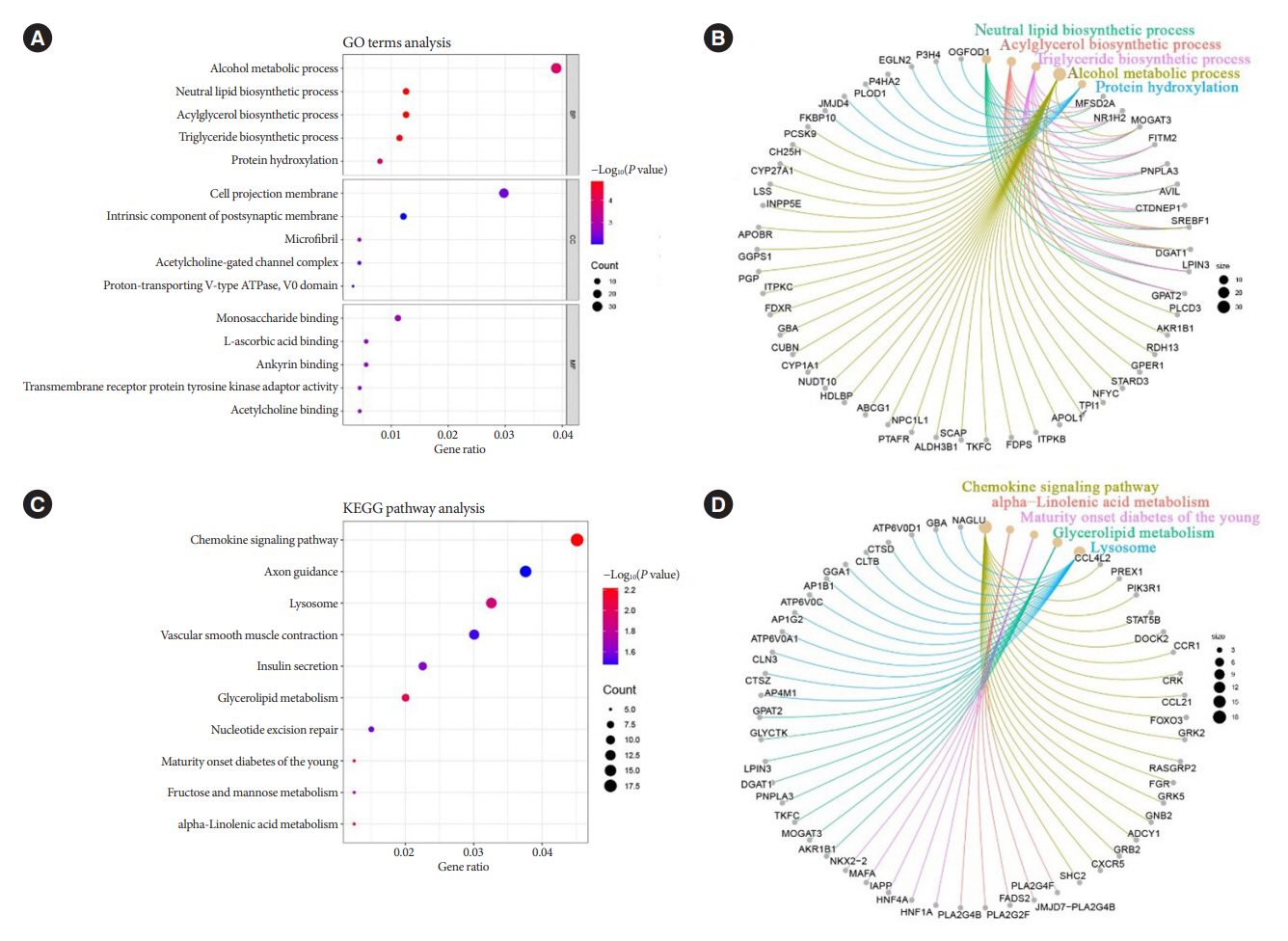
Patients with T2DM had 16 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated miRNAs compared to patients without T2DM. Improvement in metabolic metrics after bariatric surgery of T2DM patients with obesity was correlated with changes in miRNAs, as evidenced by the upregulation of 20 miRNAs and the downregulation of 30 miRNAs. Analysis of the two miRNAs profiles identified seven intersecting miRNAs that showed opposite changes. The target genes of these seven miRNAs were substantially enriched in terms or pathways associated with T2DM.
Conclusion
We determined the expression profiles of miRNAs in the obese population, with and without diabetes, before and after bariatric surgery. The miRNAs that intersected in the two comparisons were discovered. Both the miRNAs discovered and their target genes were closely associated with T2DM, demonstrating that they might be potential targets for the regulation of T2DM.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swinburn BA, Sacks G, Hall KD, McPherson K, Finegood DT, Moodie ML, et al. The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. 2011; 378:804–14.
Article2. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017; 390:2627–42.3. Hu W, Ding Y, Wang S, Xu L, Yu H. The construction and analysis of the aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in adipose tissue from type 2 diabetes individuals with obesity. J Diabetes Res. 2020; 2020:3980742.
Article4. Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Theofilatos K, Barwari T, Gutmann C, Takov K, Singh B, et al. Metabolic recovery after weight loss surgery is reflected in serum microRNAs. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020; 8:e001441.
Article5. Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes: 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:641–51.
Article6. Inge TH, Courcoulas AP, Jenkins TM, Michalsky MP, Helmrath MA, Brandt ML, et al. Weight loss and health status 3 years after bariatric surgery in adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:113–23.
Article7. Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Navaneethan SD, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes: 3-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:2002–13.
Article8. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1577–85.
Article9. Atkin SL, Ramachandran V, Yousri NA, Benurwar M, Simper SC, McKinlay R, et al. Changes in blood microRNA expression and early metabolic responsiveness 21 days following bariatric surgery. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019; 9:773.
Article10. Manoel Alves J, Handerson Gomes Teles R, do Valle Gomes Gatto C, Munoz VR, Regina Cominetti M, Garcia de Oliveira Duarte AC. Mapping research in the obesity, adipose tissue, and microRNA field: a bibliometric analysis. Cells. 2019; 8:1581.
Article11. Hobert O. Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science. 2008; 319:1785–6.
Article12. Arner P, Kulyte A. MicroRNA regulatory networks in human adipose tissue and obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11:276–88.
Article13. Bae YU, Kim Y, Lee H, Kim H, Jeon JS, Noh H, et al. Bariatric surgery alters microRNA content of circulating exosomes in patients with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019; 27:264–71.
Article14. Al-Rawaf HA. Circulating microRNAs and adipokines as markers of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with obesity. Clin Nutr. 2019; 38:2231–8.
Article15. Ji C, Guo X. The clinical potential of circulating microRNAs in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019; 15:731–43.
Article16. Fu X, Dong B, Tian Y, Lefebvre P, Meng Z, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA-26a regulates insulin sensitivity and metabolism of glucose and lipids. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125:2497–509.
Article17. Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M, et al. MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature. 2011; 474:649–53.
Article18. Dehwah MA, Xu A, Huang Q. MicroRNAs and type 2 diabetes/obesity. J Genet Genomics. 2012; 39:11–8.
Article19. Jones A, Danielson KM, Benton MC, Ziegler O, Shah R, Stubbs RS, et al. miRNA signatures of insulin resistance in obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2017; 25:1734–44.
Article20. Zampetaki A, Kiechl S, Drozdov I, Willeit P, Mayr U, Prokopi M, et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res. 2010; 107:810–7.
Article21. Lozano-Bartolome J, Llaurado G, Portero-Otin M, Altuna-Coy A, Rojo-Martinez G, Vendrell J, et al. Altered expression of miR-181a-5p and miR-23a-3p is associated with obesity and TNFα-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 103:1447–58.
Article22. Liu R, Wang M, Li E, Yang Y, Li J, Chen S, et al. Dysregulation of microRNA-125a contributes to obesity-associated insulin resistance and dysregulates lipid metabolism in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020; 1865:158640.
Article23. Villard A, Marchand L, Thivolet C, Rome S. Diagnostic value of cell-free circulating MicroRNAs for obesity and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Mol Biomark Diagn. 2015; 6:251.
Article24. Liao CH, Wang CY, Liu KH, Liu YY, Wen MS, Yeh TS. MiR122 marks the differences between subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues and associates with the outcome of bariatric surgery. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 12:570–7.
Article25. Gentile AM, Lhamyani S, Coin-Araguez L, Clemente-Postigo M, Oliva Olivera W, Romero-Zerbo SY, et al. miR-20b, miR296, and Let-7f expression in human adipose tissue is related to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019; 27:245–54.26. Joglekar MV, Joglekar VM, Hardikar AA. Expression of isletspecific microRNAs during human pancreatic development. Gene Expr Patterns. 2009; 9:109–13.
Article27. Pullen TJ, da Silva Xavier G, Kelsey G, Rutter GA. miR-29a and miR-29b contribute to pancreatic beta-cell-specific silencing of monocarboxylate transporter 1 (Mct1). Mol Cell Biol. 2011; 31:3182–94.28. Wu Q, Li JV, Seyfried F, le Roux CW, Ashrafian H, Athanasiou T, et al. Metabolic phenotype-microRNA data fusion analysis of the systemic consequences of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015; 39:1126–34.
Article29. Rega-Kaun G, Kaun C, Jaegersberger G, Prager M, Hackl M, Demyanets S, et al. Roux-en-Y-bariatric surgery reduces markers of metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2020; 30:391–400.
Article30. Zhu Z, Yin J, Li DC, Mao ZQ. Role of microRNAs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017; 50:e5817.
Article31. Lirun K, Sewe M, Yong W. A pilot study: the effect of Roux-enY gastric bypass on the serum microRNAs of the type 2 diabetes patient. Obes Surg. 2015; 25:2386–92.
Article32. Breininger SP, Sabater L, Malcomson FC, Afshar S, Mann J, Mathers JC. Obesity and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass drive changes in miR-31 and miR-215 expression in the human rectal mucosa. Int J Obes (Lond). 2022; 46:333–41.
Article33. Zhang JJ, Zhang YZ, Peng JJ, Li NS, Xiong XM, Ma QL, et al. Atorvastatin exerts inhibitory effect on endothelial senescence in hyperlipidemic rats through a mechanism involving down-regulation of miR-21-5p/203a-3p. Mech Ageing Dev. 2018; 169:10–8.
Article34. Meng Q, Zhai X, Yuan Y, Ji Q, Zhang P. lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and fibrogenesis by regulating the miR-216a-5p/BMP7 axis in diabetic nephropathy. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020; 53:e9288.
Article35. Wijayatunga NN, Pahlavani M, Kalupahana NS, Kottapalli KR, Gunaratne PH, Coarfa C, et al. An integrative transcriptomic approach to identify depot differences in genes and microRNAs in adipose tissues from high fat fed mice. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:9246–61.
Article36. Langi G, Szczerbinski L, Kretowski A. Meta-analysis of differential miRNA expression after bariatric surgery. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:1220.
Article37. Winnay JN, Boucher J, Mori MA, Ueki K, Kahn CR. A regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase increases the nuclear accumulation of X-box-binding protein-1 to modulate the unfolded protein response. Nat Med. 2010; 16:438–45.
Article38. Bandyopadhyay GK, Yu JG, Ofrecio J, Olefsky JM. Increased p85/55/50 expression and decreased phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase activity in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 2005; 54:2351–9.
Article39. Axelsson L, Hellberg C, Melander F, Smith D, Zheng L, Andersson T. Clustering of beta(2)-integrins on human neutrophils activates dual signaling pathways to PtdIns 3-kinase. Exp Cell Res. 2000; 256:257–63.40. Olah J, Orosz F, Puskas LG, Hackler L, Horanyi M, Polgar L, et al. Triosephosphate isomerase deficiency: consequences of an inherited mutation at mRNA, protein and metabolic levels. Biochem J. 2005; 392(Pt 3):675–83.
Article41. Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Yahagi N, Yoshikawa T, Matsuzaka T, et al. Transcriptional activities of nuclear SREBP-1a, -1c, and -2 to different target promoters of lipogenic and cholesterogenic genes. J Lipid Res. 2002; 43:1220–35.
Article42. Xu D, Wang Z, Xia Y, Shao F, Xia W, Wei Y, et al. The gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 phosphorylates INSIG1/2 for lipogenesis. Nature. 2020; 580:530–5.
Article43. Craig TJ, Anderson D, Evans AJ, Girach F, Henley JM. SUMOylation of Syntaxin1A regulates presynaptic endocytosis. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:17669.
Article44. Romeo S, Sentinelli F, Cavallo MG, Leonetti F, Fallarino M, Mariotti S, et al. Search for genetic variants of the SYNTAXIN 1A (STX1A) gene: the -352 A>T variant in the STX1A promoter associates with impaired glucose metabolism in an Italian obese population. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:413–20.
Article45. Machado AK, Andreazza AC, da Silva TM, Boligon AA, do Nascimento V, Scola G, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) against rotenone in vitro exposure. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:8940850.46. Haack TB, Haberberger B, Frisch EM, Wieland T, Iuso A, Gorza M, et al. Molecular diagnosis in mitochondrial complex I deficiency using exome sequencing. J Med Genet. 2012; 49:277–83.
Article