J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2023 Jun;25(2):203-207. 10.7461/jcen.2022.E2022.07.003.
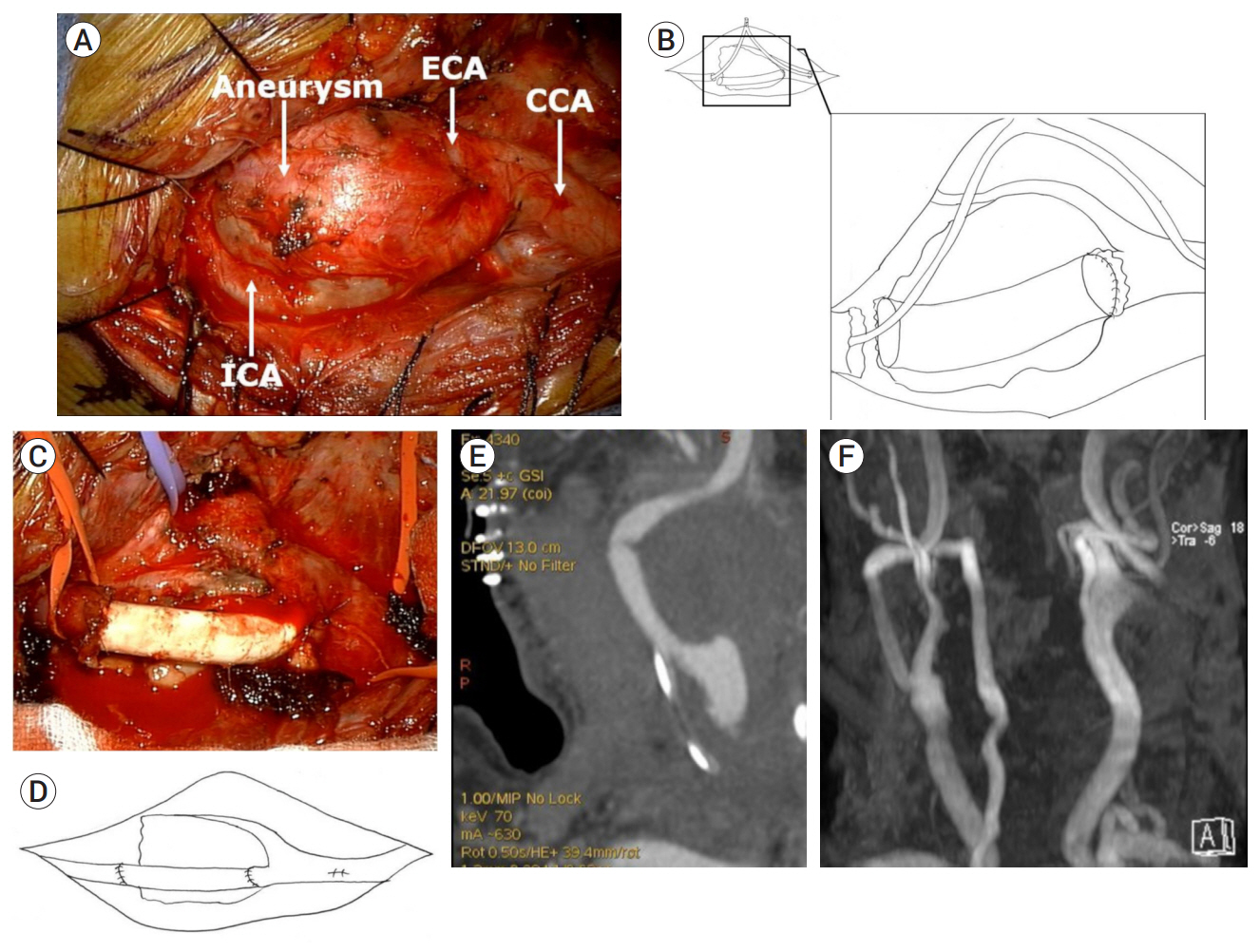
Aneurysmectomy and graft interposition for giant thrombosed proximal internal carotid artery aneurysm: Technical details
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji Universtity, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2543517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2022.E2022.07.003
Abstract
- A giant thrombosed extracranial internal carotid artery aneurysm (ECCA) is extremely rare and its treatment is challenging. Despite the advance of endovascular technique, open surgery is still considered a first-line treatment in giant thrombosed ECCA. We describe a case of giant thrombosed ECCA which was successfully treated by aneurysmectomy and graft interposition with the technical details.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Attigah N, Külkens S, Zausig N, Hansmann J, Ringleb P, Hakimi M, et al. Surgical therapy of extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: long-term results over a 24-year period. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009; Feb. 37(2):127–33.
Article2. de Jong KP, Zondervan PE, van Urk H. Extracranial carotid artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1989; Dec. 3(6):557–62.
Article3. El-Sabrout R, Cooley DA. Extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: Texas Heart Institute experience. J Vasc Surg. 2000; Apr. 31(4):702–12.
Article4. Hosoda K, Fujita S, Kawaguchi T, Shibata Y, Tamaki N. The use of an external-internal shunt in the treatment of extracranial internal carotid artery saccular aneurysms: technical case report. Surg Neurol. 1999; Aug. 52(2):153–5.
Article5. Krings T, Alvarez H, Reinacher P, Ozanne A, Baccin CE, Gandolfo C, et al. Growth and rupture mechanism of partially thrombosed aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol. 2007; Jun. 13(2):117–26.
Article6. Li Z, Chang G, Yao C, Guo L, Liu Y, Wang M, et al. Endovascular stenting of extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; Oct. 42(4):419–26.7. Pourier VEC, Welleweerd JC, Kappelle LJ, Rinkel GJE, Ruigrok YM, van der Worp HB, et al. Experience of single center in the conservative approach of 20 consecutive cases of asymptomatic extracranial carotid artery aneurysms. Eur J Neurol. 2018; Oct. 25(10):1285–89.
Article8. Szopiński P, Ciostek P, Kielar M, Myrcha P, Pleban E, Noszczyk W. A series of 15 patients with extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: surgical and endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; Mar. 29(3):256–61.
Article9. Valentine RJ. Asymptomatic internal carotid artery aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2003; Jan. 37(1):210.
Article10. Welleweerd JC, de Borst GJ, de Groot D, van Herwaarden JA, Lo RT, Moll FL. Bare metal stents for treatment of extracranial internal carotid artery aneurysms: long-term results. J Endovasc Ther. 2015; Feb. 22(1):130–4.
Article11. Welleweerd JC, Nelissen BG, Koole Dave, de Vries JP, Moll FL, Pasterkamp G, et al. Histological analysis of extracranial carotid artery aneurysms. PLoS One. 2015; Jan. 10(1):e0117915.
Article12. Zhou W, Lin PH, Bush RL, Peden E, Guerrero MA, Terramani T, et al. Carotid artery aneurysm: evolution of management over two decades. J Vasc Surg. 2006; Mar. 43(3):493–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Completely Thrombosed Contralateral Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm Combined with Ruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm: Case Report
- A Case of Giant Paraclinoid Aneurysm
- External Carotid Artery to Middle Cerebral Artery Bypass with Saphenous Vein Graft for a Giant Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm at the Cavernous Portion
- Surgical Treatment of a Right Common Carotid Artery Aneurysm
- Stent-Graft Repair of Common Carotid Pseudoaneurysms in Behcet's Syndrome