Ann Rehabil Med.
2023 Jun;47(3):222-227. 10.5535/arm.23015.
Diagnostic Accuracy of Harris Imprint Index, Chippaux-Smirak Index, Staheli Index Compared With Talar-First Metatarsal Angle for Screening Arch of Foot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathum Thani, Thailand
- 2Department of Orthopaedics, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathum Thani, Thailand
- 3Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Thammasat University Hospital, Pathum Thani, Thailand
- KMID: 2543419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.23015
Abstract
Objective
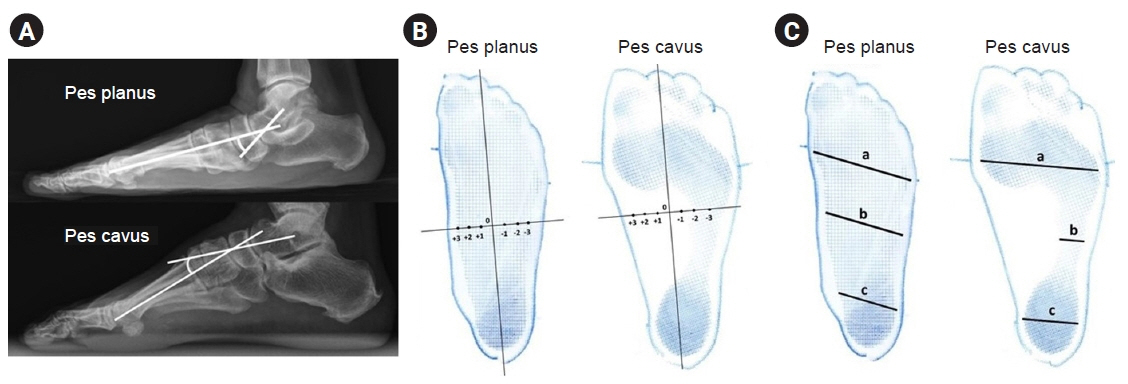
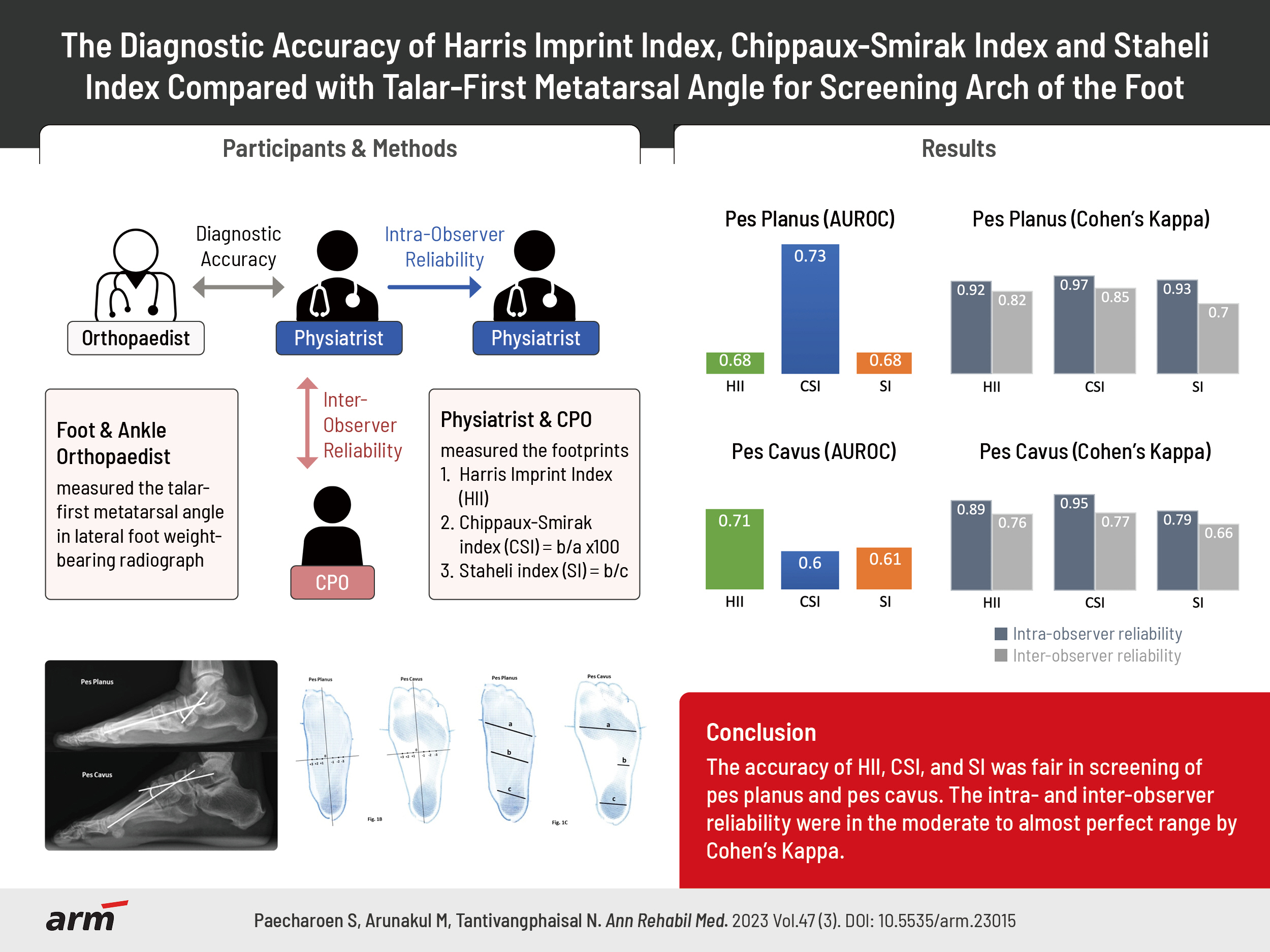
To determine the diagnostic accuracy and reliability of the Harris imprint index (HII), Chippaux-Smirak index (CSI), and Staheli index (SI) compared with the talar-first metatarsal angle.
Methods
Data was collected at the orthotic and prosthetic clinic, Thammasat University Hospital from January 1, 2016 to August 31, 2020. The three footprints were measured by the rehabilitation physician and the orthotist. The talar-first metatarsal angle was measured by the foot and ankle orthopaedist.
Results
The data from 198 patients with 274 feet was analyzed. The diagnostic accuracy of the footprint triad showed that CSI was the most accurate in pes planus prediction, followed by HII and SI (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.73, 0.68, 0.68, respectively). In pes cavus, HII was the most accurate, followed by SI and CSI (AUROC=0.71, 0.61, 0.60, respectively). For pes planus, the intra-observer reliability by Cohen’s Kappa was 0.92 for HII, 0.97 for CSI, and 0.93 for SI, the inter-observer reliability 0.82, 0.85, and 0.70, respectively. For pes cavus, the intra-observer reliability was 0.89 for HII, 0.95 for CSI, and 0.79 for SI, inter-observer reliability of 0.76, 0.77, and 0.66, respectively.
Conclusion
The accuracy of HII, CSI, and SI was fair in screening of pes planus and pes cavus. The intra- and inter-observer reliability were in the moderate to almost perfect range by Cohen’s Kappa.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Change in Plantar Pressure and Plain Radiography in Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sungjoon Kim, Yong Gyun Kim, Jun Yup Kim, Si-Bog Park, Kyu Hoon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2024;48(5):352-359. doi: 10.5535/arm.240041.
Reference
-
1. Tong JW, Kong PW. Association between foot type and lower extremity injuries: systematic literature review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013; 43:700–14.
Article2. Akoh CC, Phisitkul P. Clinical examination and radiographic assessment of the cavus foot. Foot Ankle Clin. 2019; 24:183–93.
Article3. Toullec E. Adult flatfoot. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101(1 Suppl):S11–7.
Article4. Chuckpaiwong B, Nunley JA 2nd, Queen RM. Correlation between static foot type measurements and clinical assessments. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:205–12.
Article5. Coughlin MJ, Kaz A. Correlation of Harris mats, physical exam, pictures, and radiographic measurements in adult flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:604–12.
Article6. Pita-Fernández S, González-Martín C, Seoane-Pillado T, López-Calviño B, Pértega-Díaz S, Gil-Guillén V. Validity of footprint analysis to determine flatfoot using clinical diagnosis as the gold standard in a random sample aged 40 years and older. J Epidemiol. 2015; 25:148–54.
Article7. Meary R. On the measurement of the angle between the talus and the first metatarsal. Symposium: le pied creux essential. Rev Chir Orthop. 1967; 53:390–419.8. Arunakul M, Amendola A, Gao Y, Goetz JE, Femino JE, Phisitkul P. Tripod index: a new radiographic parameter assessing foot alignment. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:1411–20.9. Shariff S, Manaharan T, Shariff A, Merican A. Evaluation of foot arch in adult women: comparison between five different footprint parameters. Sains Malays. 2017; 46:1839–48.
Article10. Shiang TY, Lee SH, Lee SJ, Chu WC. Evaluating different footprint parameters as a predictor of arch height. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1998; 17:62–6.11. Sakalauskaitė R, Satkunskienė D. Inconsistencies of foot type classification. J Sport Health Sci. 2012; 3:81–6.
Article12. Welton EA. The Harris and Beath footprint: interpretation and clinical value. Foot Ankle. 1992; 13:462–8.13. Coughlin MJ, Saltzman CL, Mann RA. Mann’s surgery of the foot and ankle: expert consult - online. St. Louis: Elsevier Health Sciences;2013. p. 2338.14. Arunakul M, Amendola A, Gao Y, Goetz JE, Femino JE, Phisitkul P. Tripod index: diagnostic accuracy in symptomatic flatfoot and cavovarus foot: part 2. Iowa Orthop J. 2013; 33:47–53.15. Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:426–8.
Article16. McHugh ML. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012; 22:276–82.
Article17. Villarroya MA, Esquivel JM, Tomás C, Moreno LA, Buenafé A, Bueno G. Assessment of the medial longitudinal arch in children and adolescents with obesity: footprints and radiographic study. Eur J Pediatr. 2009; 168:559–67.
Article18. Mathieson I, Upton D, Prior TD. Examining the validity of selected measures of foot type: a preliminary study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2004; 94:275–81.19. Queen RM, Mall NA, Hardaker WM, Nunley JA 2nd. Describing the medial longitudinal arch using footprint indices and a clinical grading system. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:456–62.
Article20. Zuil-Escobar JC, Martínez-Cepa CB, Martín-Urrialde JA, Gómez-Conesa A. Evaluating the medial longitudinal arch of the foot: correlations, reliability, and accuracy in people with a low arch. Phys Ther. 2019; 99:364–72.
Article21. Plumarom Y, Imjaijitt W, Chaiphrom N. Comparison between Staheli index on Harris mat footprint and Talar-first metatarsal angle for the diagnosis of flatfeet. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014; 97 Suppl 2:S131–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Foot Deformity according to the Occupational Condition in the Labor of the Industry
- Morphometrics of the Medial Longitudinal Arch of Foot in Korean
- Diagnostic measurements of flatfoot
- The Height and Volume of Medial Longitudinal Arch in Normal and Painful Feet
- Correlation of Foot Posture Index With Plantar Pressure and Radiographic Measurements in Pediatric Flatfoot