Kosin Med J.
2023 Jun;38(2):151-155. 10.7180/kmj.22.141.
A case report of a carotid space abscess due to extraluminal migration of a fishbone into the deep cervical space
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
- 2Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2543336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.22.141
Abstract
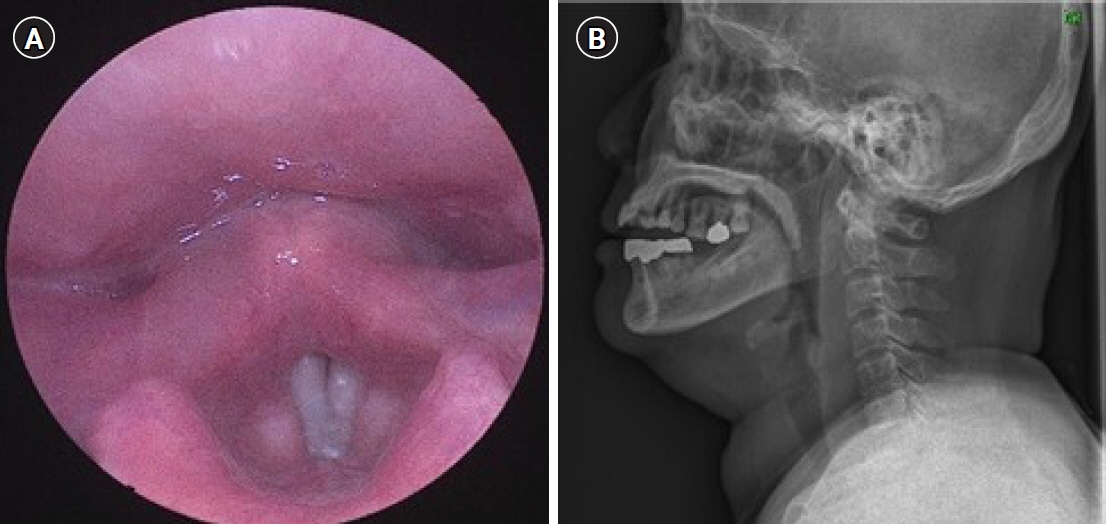
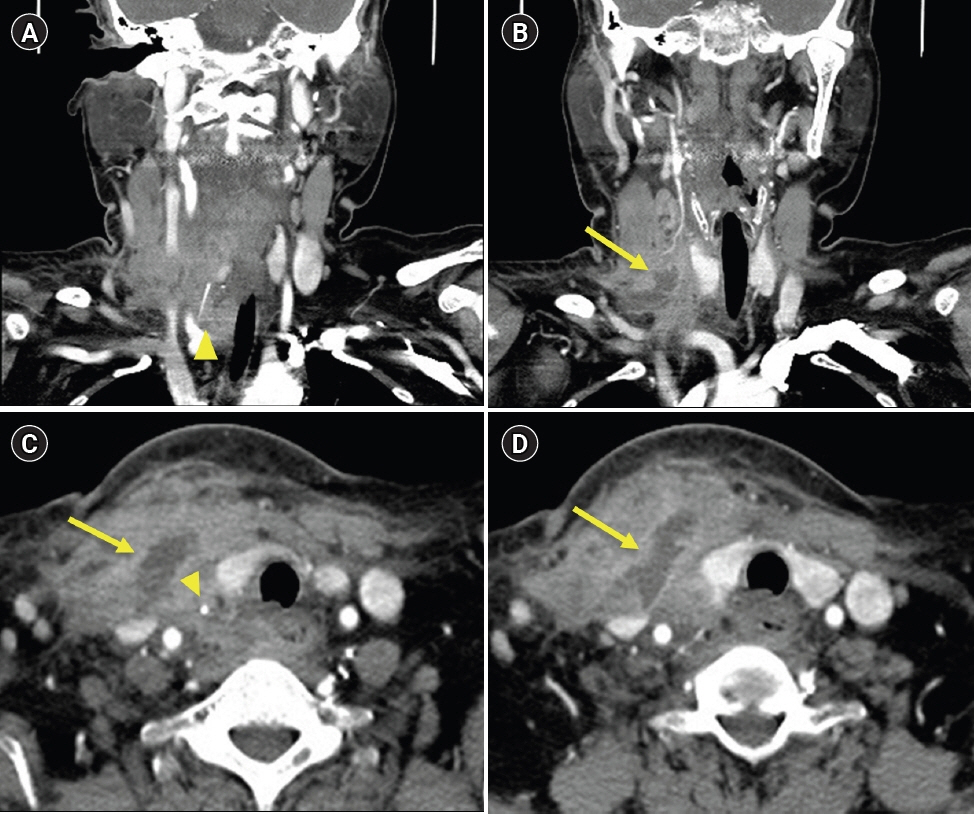
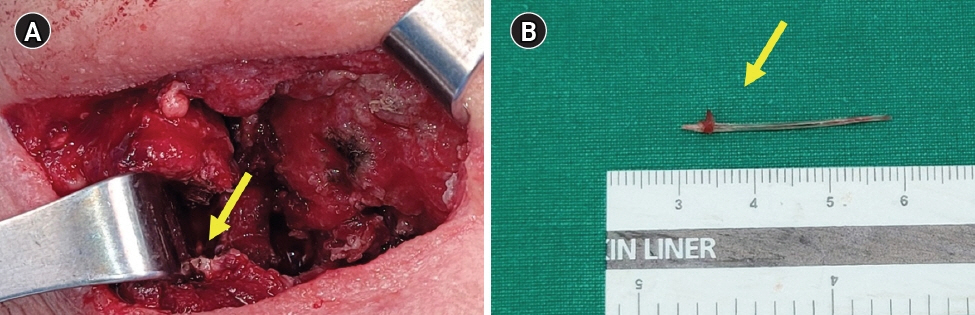
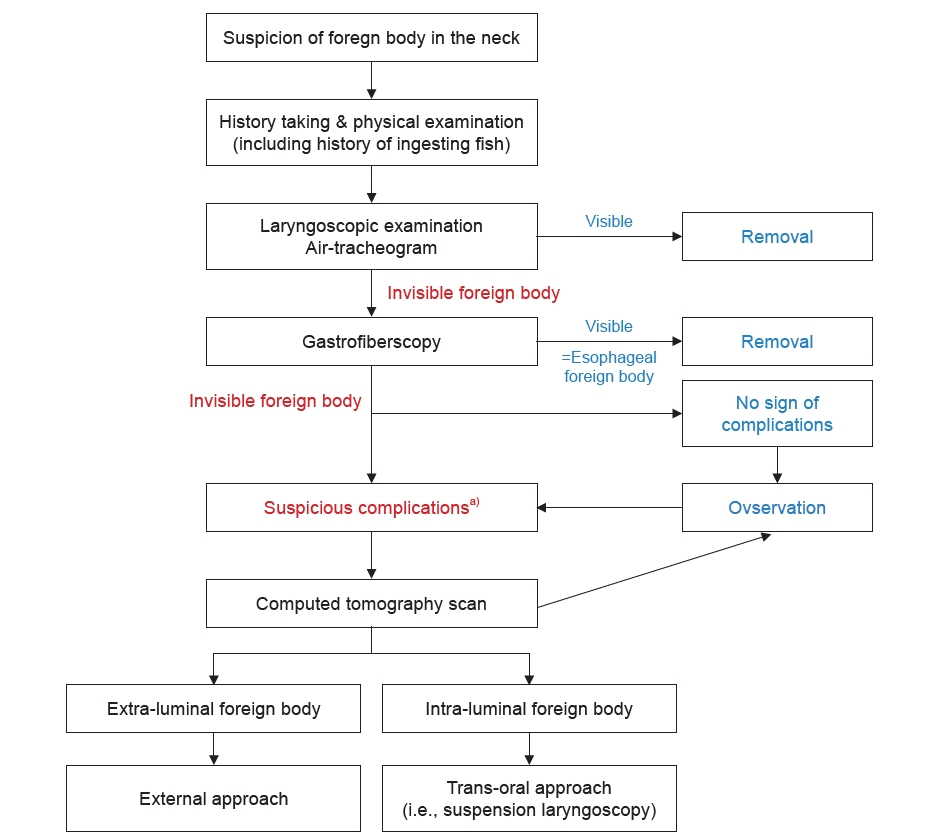
- Laryngopharyngeal foreign bodies are among the cases most frequently encountered by otolaryngologists. Most foreign bodies can be easily removed without any complications. However, surgical removal is required in some cases. Therefore, a delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis could cause fatal complications for patients who need a surgical approach. We report a rare case of extraluminal migration of a foreign body to the deep cervical space. The foreign body (a fishbone) was removed by a surgical approach. With a literature review, we also propose an algorithm for the management of suspicious foreign bodies in the neck.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Shim WY, Jeong WH, Park JB, Kim CA, Baik SK. Two cases of fish bone foreign body presenting as tongue and neck mass. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2001; 44:556–9.2. Chee LW, Sethi DS. Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to migrating foreign bodies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 108:177–80.3. Ma DH, Lee YS, Lee MJ, Yim JS, Kim BC. A clinical study of foreign bodies in the food and air passages: in 649 cases for 8 years. Korean J Otolaryngol. 1989; 32:923–8.4. Kim JP, Kwon OJ, Shim HS, Kim RB, Kim JH, Woo SH. Analysis of clinical feature and management of fish bone ingestion of upper gastrointestinal tract. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 8:261–7.5. Chung SM, Kim HS, Park EH. Migrating pharyngeal foreign bodies: a series of four cases of saw-toothed fish bones. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008; 265:1125–9.6. Hong JC, Lee HS, Kim JY, Lee KD. A case of fish bone foreign body presenting as tongue base abscess. J Clin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 17:270–2.7. Bendet E, Horowitz Z, Heyman Z, Faibel M, Kronenberg J. Migration of fishbone following penetration of the cervical esophagus presenting as a thyroid mass. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1992; 19:193–7.8. Feldhusen F, Braunbeck T, Wallner F. Dysphagia after eating sea foods: pyriform sinus foreign body with perforation and abscess of the parapharyngeal space. HNO. 1999; 47:746–7.9. Kim HU. Oroesophageal fish bone foreign body. Clin Endosc. 2016; 49:318–26.10. Park JH, Park CH, Park JH, Lee SJ, Lee WS, Joo YE, et al. Review of 209 cases of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract and clinical factors for successful endoscopic removal. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:226–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep cervical space abscess: Role of CT for guiding surgical approach
- Deep Neck Space Infection Along with Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenitis in an HIV Patient
- A Case of Cryptococcal Abscess Involving Deep Neck Space in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Oropharyngeal Carotid Space Mass Presenting with Isolated Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy
- Deep Neck Space Infection Caused by Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor