Neonatal Med.
2023 May;30(2):49-54. 10.5385/nm.2023.30.2.49.
The Impact of Slow Infusion Intermittent Feeding on Gavage Feeding-Associated Cardiorespiratory Deterioration in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2542547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2023.30.2.49
Abstract
- Purpose
Infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) often show cardiorespiratory deterioration during gavage feeding. We aimed to determine whether slow infusion intermittent feeding (SIIF) can reduce respiratory deterioration during gavage feeding in preterm infants in the NICU.
Methods
Data on preterm infants whose gavage feeding method was changed to SIIF (1-hour infusion with an infusion pump and 2-hour rest within a 3-hour interval) from bolus gravity feeding (2- or 3-hour interval) due to feeding-associated cardiorespiratory deterioration were retrospectively reviewed. A significant cardiorespiratory event was defined as a saturation level below 80% or heart rate below 80 bpm. We compared the frequency of cardiorespiratory events and the level of respiratory support 24 hours before and after the application of SIIF.
Results
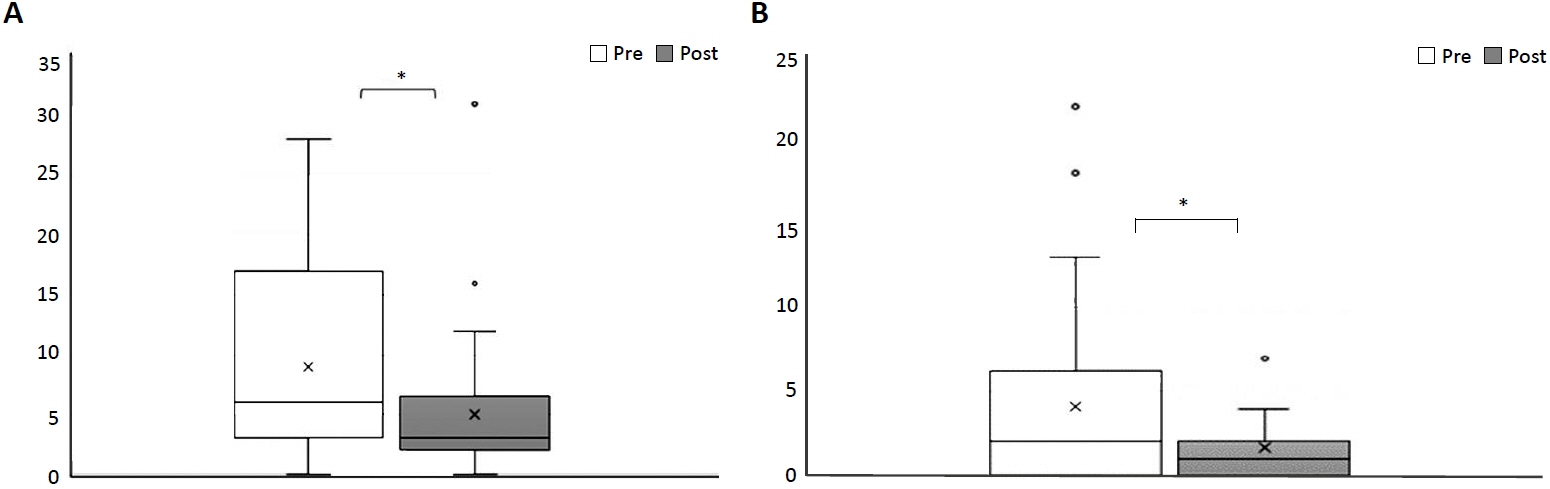
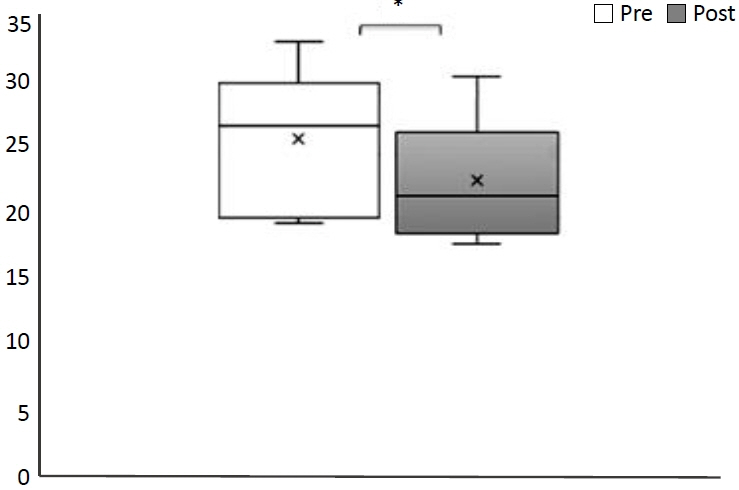
A total of 34 infants were enrolled and analyzed. The total frequency of desaturation or bradycardia significantly decreased after SIIF application (8.94 vs. 5.03, P=0.001). The frequency of feeding-related bradycardia and desaturation also significantly decreased (4.15 vs. 1.68, P=0.008). Out of 34 patients, 11 (32.4%) had a decreased level of ventilator support within 1 day after SIIF. The respiratory severity scores of the 10 patients who received invasive ventilator support decreased significantly after SIIF (5.24 vs. 4.59, P=0.032).
Conclusion
SIIF significantly decreased gavage feeding-associated cardiorespiratory events and reduced respiratory support in approximately one-third of subjects. Therefore, SIIF may be a therapeutic option for gavage feed-associated respiratory deterioration in preterm infants in the NICU.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thoene M, Anderson-Berry A. Early enteral feeding in preterm infants: a narrative review of the nutritional, metabolic, and developmental benefits. Nutrients. 2021; 13:2289.
Article2. Blondheim O, Abbasi S, Fox WW, Bhutani VK. Effect of enteral gavage feeding rate on pulmonary functions of very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 1993; 122(5 Pt 1):751–5.
Article3. Ballard RA, Truog WE, Cnaan A, Martin RJ, Ballard PL, Merrill JD, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide in preterm infants undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:343–53.
Article4. Wang Y, Zhu W, Luo BR. Continuous feeding versus intermittent bolus feeding for premature infants with low birth weight: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020; 74:775–83.
Article5. Sadrudin Premji S, Chessell L, Stewart F. Continuous nasogastric milk feeding versus intermittent bolus milk feeding for preterm infants less than 1500 grams. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021; 6:CD001819.
Article6. Gonzalez JT, Dirks ML, Holwerda AM, Kouw IW, van Loon LJ. Intermittent versus continuous enteral nutrition attenuates increases in insulin and leptin during short-term bed rest. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020; 120:2083–94.
Article7. El-Kadi SW, Boutry C, Suryawan A, Gazzaneo MC, Orellana RA, Srivastava N, et al. Intermittent bolus feeding promotes greater lean growth than continuous feeding in a neonatal piglet model. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018; 108:830–41.
Article8. Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Suryawan A. Bolus vs. continuous feeding to optimize anabolism in neonates. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015; 18:102–8.
Article9. Hrdy O, Vrbica K, Strazevska E, Suk P, Souckova L, Stepanova R, et al. Comparison of continuous versus intermittent enteral nutrition in critically ill patients (COINN): study protocol for a randomized comparative effectiveness trial. Trials. 2020; 21:955.
Article10. Ichimaru S, Amagai T. Intermittent and bolus methods of feeding in critical care. In : Rajendram R, Preedy V, Patel V, editors. Diet and nutrition in critical care. Springer;2014. p. 1–17.11. Lee HY, Lee JK, Kim HJ, Ju DL, Lee SM, Lee J. Continuous versus intermittent enteral tube feeding for critically ill patients: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2022; 14:664.
Article12. O'Connor G, Hartfiel-Capriles Z, Saduera S. Intermittent bolus versus continuous feeding in children receiving an enteral formula with food derived ingredients: a national multicentre retrospective study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023; 54:175–9.13. Heldt GP. The effect of gavage feeding on the mechanics of the lung, chest wall, and diaphragm of preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 1988; 24:55–8.
Article14. Akintorin SM, Kamat M, Pildes RS, Kling P, Andes S, Hill J, et al. A prospective randomized trial of feeding methods in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 1997; 100:E4.
Article15. Priyadarshi A, Hinder M, Badawi N, Luig M, Tracy M. Continuous positive airway pressure belly syndrome: challenges of a changing paradigm. Int J Clin Pediatr. 2020; 9:9–15.
Article16. D'Angelo E, Pecchiari M, Acocella F, Monaco A, Bellemare F. Effects of abdominal distension on breathing pattern and respiratory mechanics in rabbits. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2002; 130:293–304.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: The Impact of Slow Infusion Intermittent Feeding on Gavage Feeding-Associated Cardiorespiratory Deterioration in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Infants
- Developing the Mansoura Early Feeding Skills Assessment Scale for Preterm Infants
- Effects of an Oral Stimulation Program on the Transition from Tube to Bottle Feeding in Premature Infants
- Efficacy of Erythromycin and Metoclopramide in Neonates with Feeding Intolerance
- Nutritional Support in Premature Infants