J Stroke.
2023 May;25(2):251-265. 10.5853/jos.2022.02327.
Circulating Extracellular-Vesicle-Incorporated MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Ischemic Stroke in Patients With Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2S&E bio Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea
- 3Translational and Stem Cell Research Laboratory on Stroke, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Health Sciences and Technology, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology (SAIHST), Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Hemato-Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Systems Biology, College of Life Science and Biotechnology, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2542476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2022.02327
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate whether extracellular-vesicle-incorporated microRNAs (miRNAs) are potential biomarkers for cancer-related stroke.
Methods
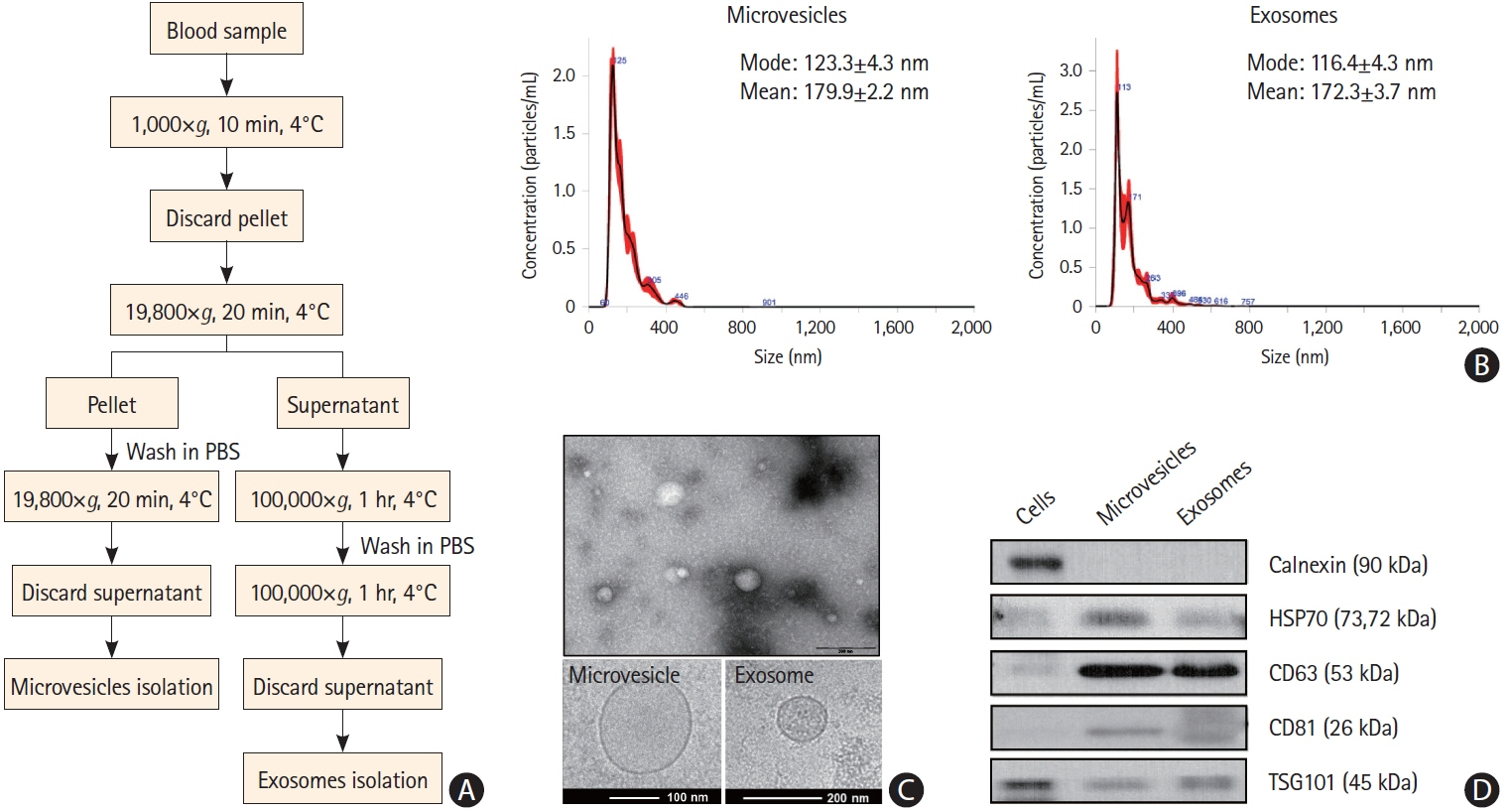
This cohort study compared patients with active cancer who had embolic stroke of unknown sources (cancer-stroke group) with patients with only cancer, patients with only stroke, and healthy individuals (control groups). The expression profiles of miRNAs encapsulated in plasma exosomes and microvesicles were evaluated using microarray and validated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The XENO-QTM miRNA assay technology was used to determine the absolute copy numbers of individual miRNAs in an external validation cohort.
Results
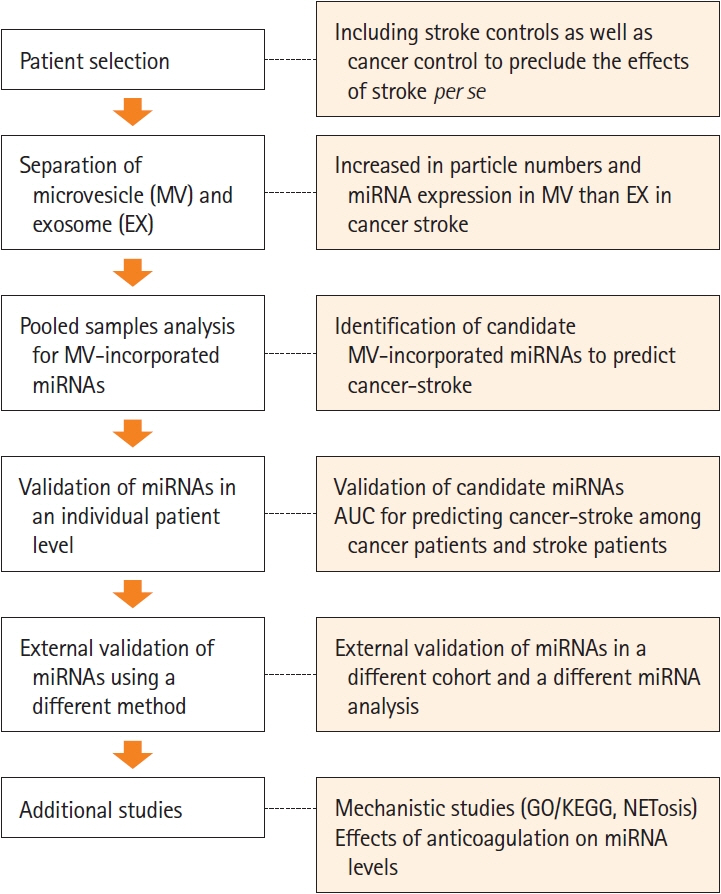
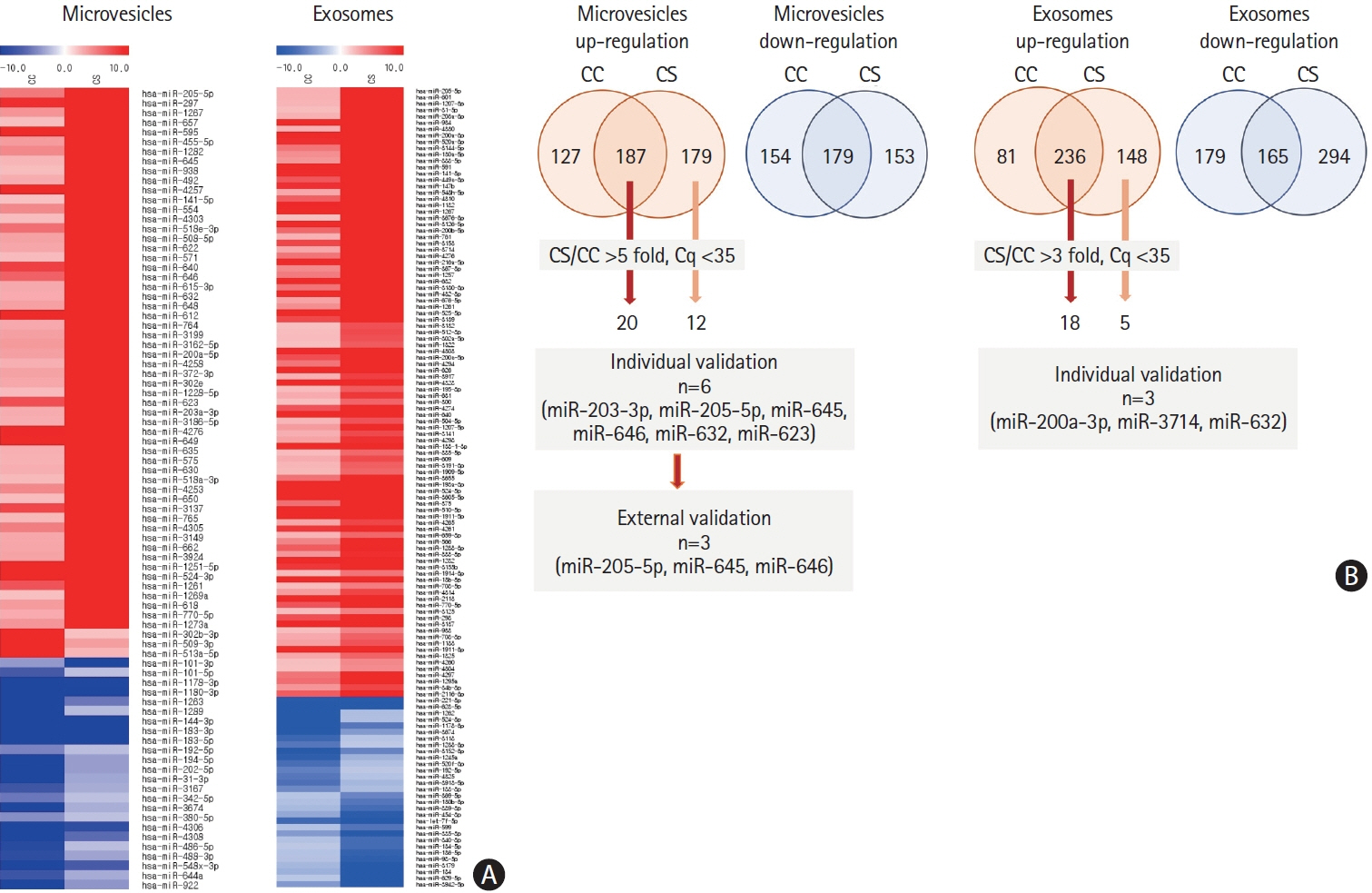
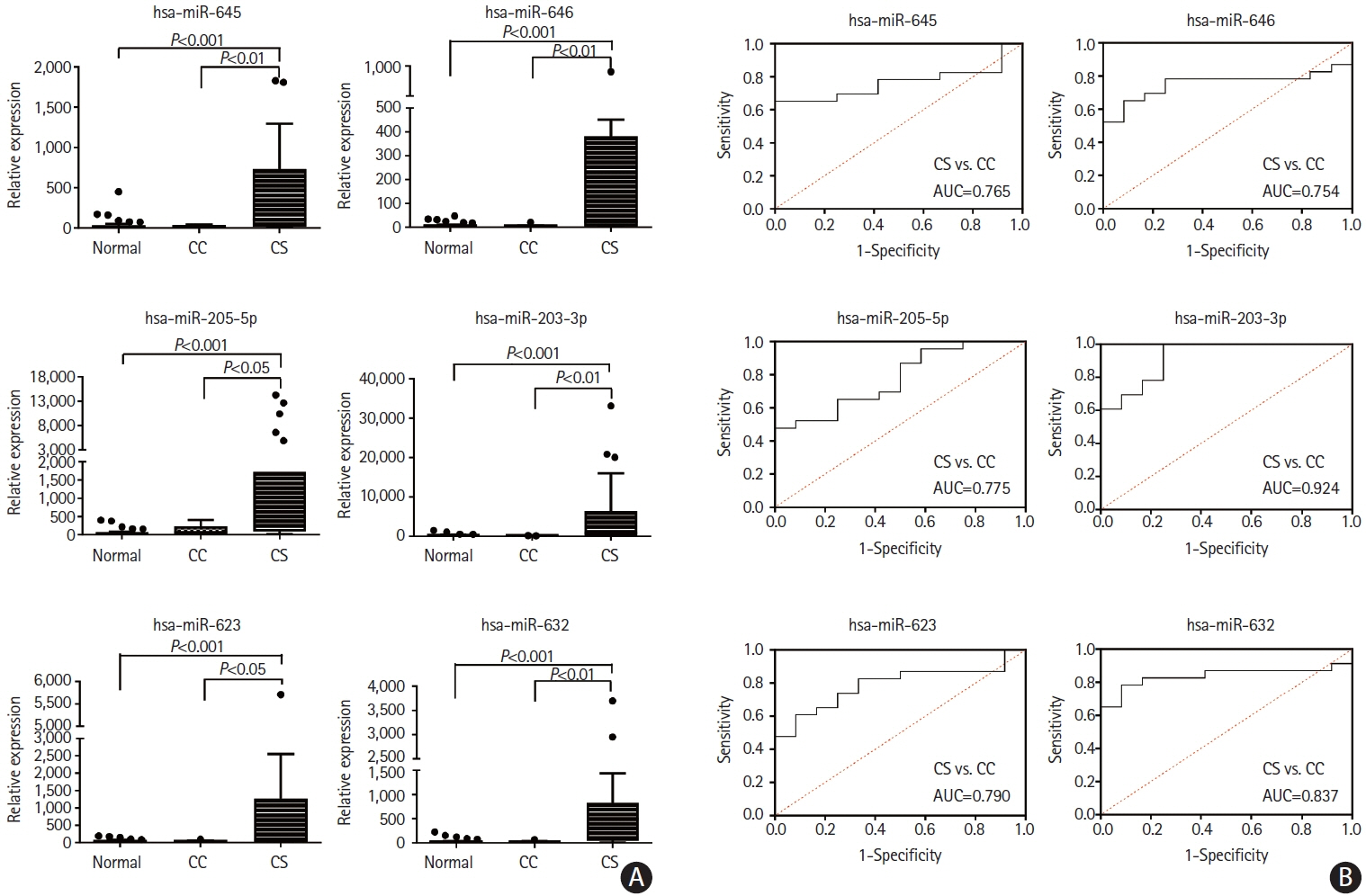
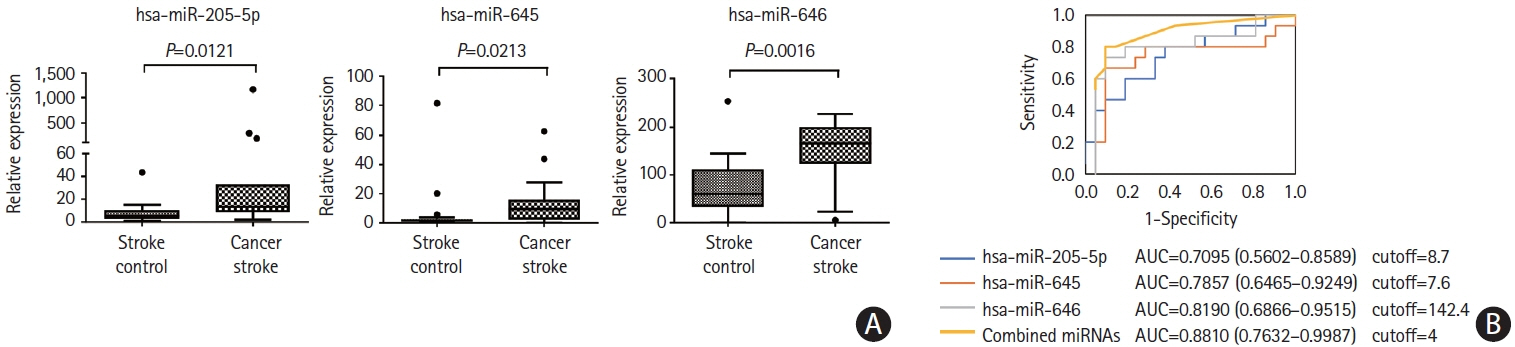
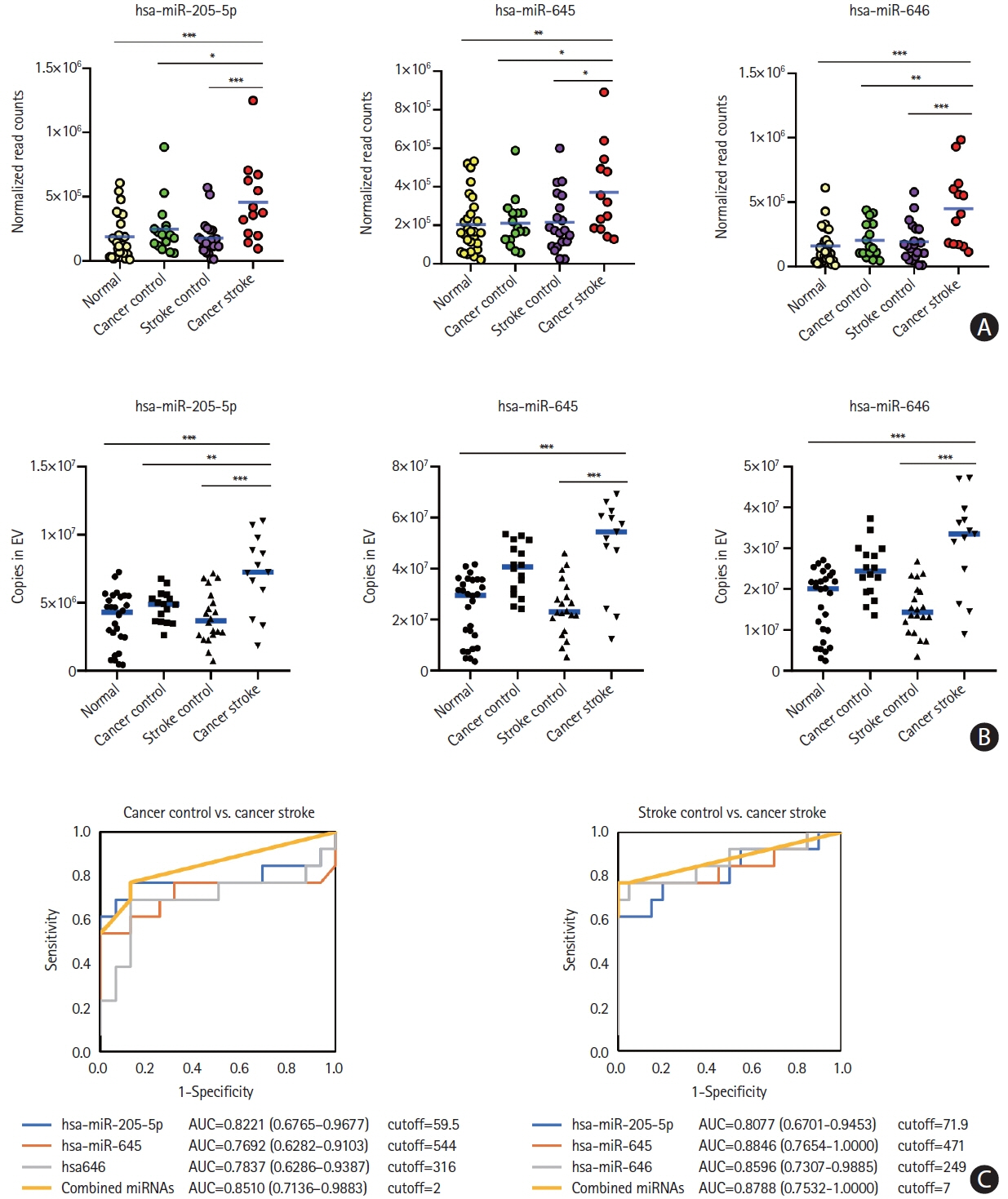
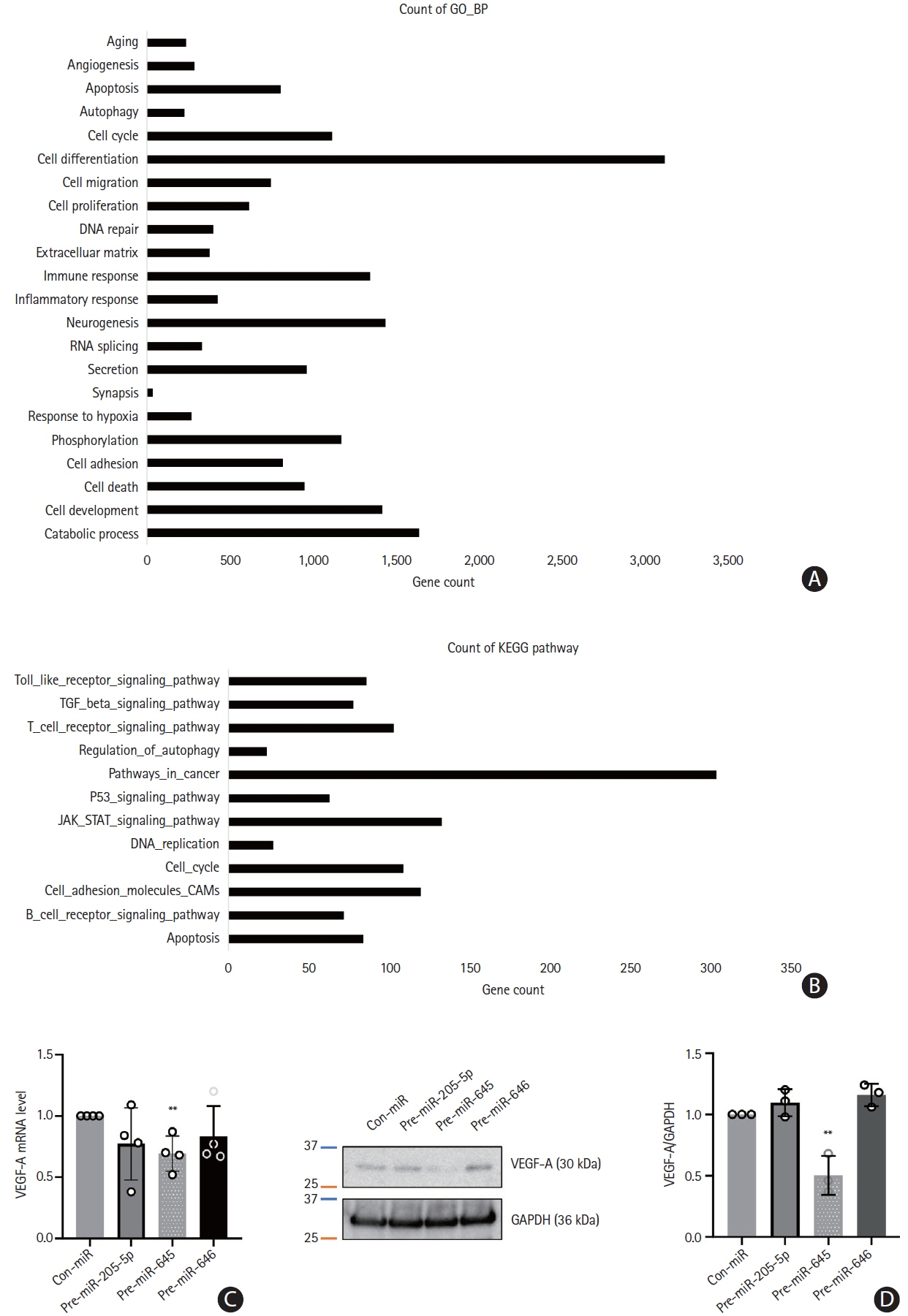
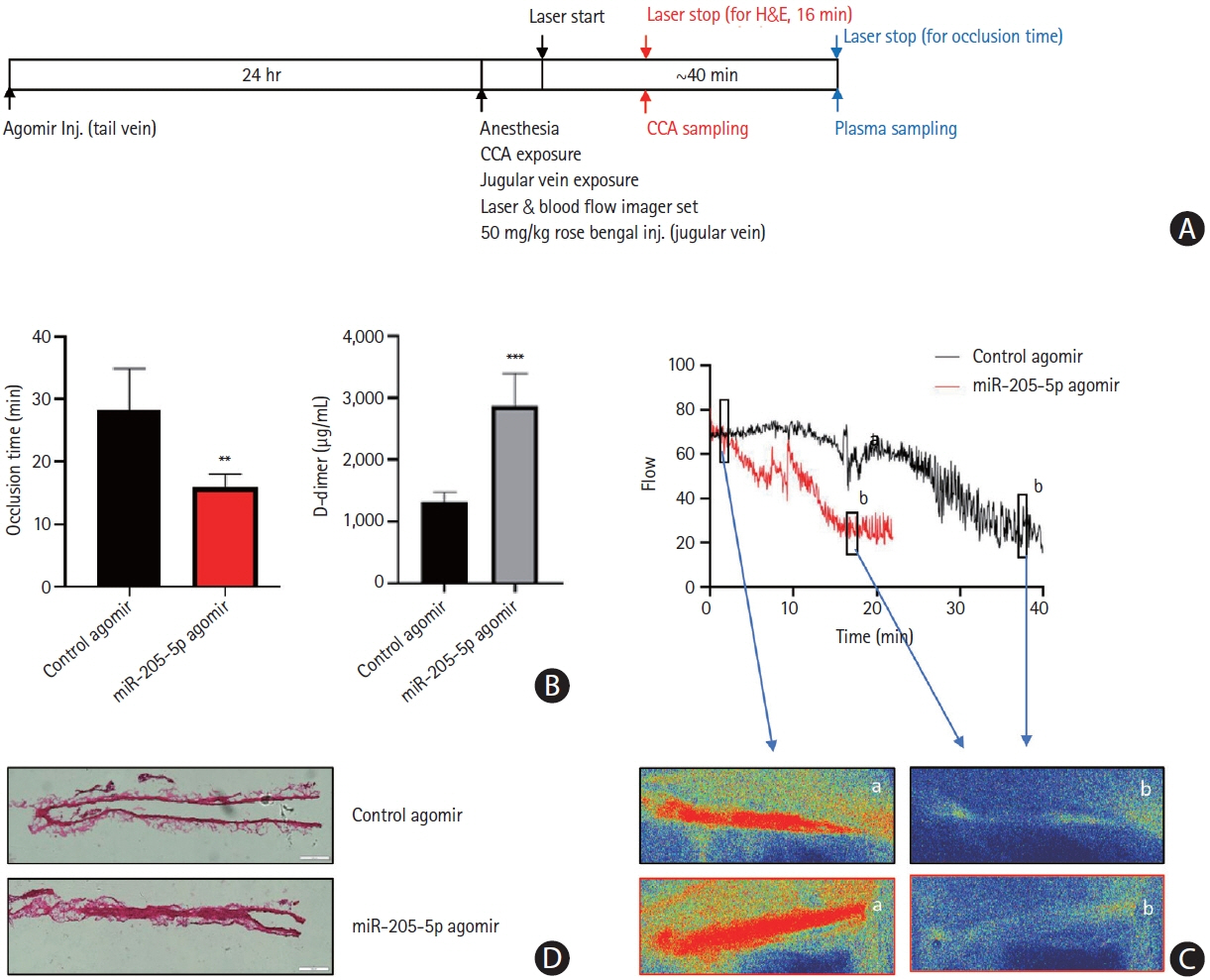
This study recruited 220 patients, of which 45 had cancer-stroke, 76 were healthy controls, 39 were cancer controls, and 60 were stroke controls. Three miRNAs (miR-205-5p, miR-645, and miR-646) were specifically incorporated into microvesicles in patients with cancer-related stroke, cancer controls, and stroke controls. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of these three miRNAs were 0.7692–0.8510 for the differentiation of patients with cancer-stroke from cancer-controls and 0.8077–0.8846 for the differentiation of patients with cancer-stroke from stroke controls. The levels of several miRNAs were elevated in the plasma exosomes of patients with cancer, but were lower than those in plasma microvesicles. An in vivo study showed that systemic injection of miR-205-5p promoted the development of arterial thrombosis and elevation of D-dimer levels.
Conclusion
Stroke due to cancer-related coagulopathy was associated with deregulated expression of miRNAs, particularly microvesicle-incorporated miR-205-5p, miR-645, and miR-646. Further prospective studies of extracellular-vesicle-incorporated miRNAs are required to confirm the diagnostic role of miRNAs in patients with stroke and to screen the roles of miRNAs in patients with cancer.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bang OY, Chung JW, Lee MJ, Seo WK, Kim GM, Ahn MJ; OASIS-Cancer Study Investigators. Cancer-related stroke: an emerging subtype of ischemic stroke with unique pathomechanisms. J Stroke. 2020; 22:1–10.
Article2. Ohara T, Farhoudi M, Bang OY, Koga M, Demchuk AM. The emerging value of serum D-dimer measurement in the workup and management of ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2020; 15:122–131.
Article3. Deng HY, Li G, Luo J, Wang ZQ, Yang XY, Lin YD, et al. MicroRNAs are novel non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 2016; 8:3580–3587.
Article4. Nam GH, Choi Y, Kim GB, Kim S, Kim SA, Kim IS. Emerging prospects of exosomes for cancer treatment: from conventional therapy to immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2020; 32:e2002440.
Article5. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009; 136:215–233.
Article6. van Kralingen JC, McFall A, Ord ENJ, Coyle TF, Bissett M, McClure JD, et al. Altered extracellular vesicle microRNA expression in ischemic stroke and small vessel disease. Transl Stroke Res. 2019; 10:495–508.
Article7. Otero-Ortega L, Alonso-López E, Pérez-Mato M, Laso-García F, Gómez-de Frutos MC, Diekhorst L, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicle proteins and microRNA profiles in subcortical and cortical-subcortical ischaemic stroke. Biomedicines. 2021; 9:786.
Article8. Mills J, Capece M, Cocucci E, Tessari A, Palmieri D. Cancer-derived extracellular vesicle-associated microRNAs in intercellular communication: one cell’s trash is another cell’s treasure. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20:6109.
Article9. Kadota T, Yoshioka Y, Fujita Y, Kuwano K, Ochiya T. Extracellular vesicles in lung cancer-from bench to bedside. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017; 67:39–47.
Article10. Kinoshita T, Yip KW, Spence T, Liu FF. MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: potential cancer biomarkers. J Hum Genet. 2017; 62:67–74.
Article11. Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:581–593.
Article12. Toh CH, Hoots WK. The scoring system of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis: a 5-year overview. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5:604–606.
Article13. Kim SG, Hong JM, Kim HY, Lee J, Chung PW, Park KY, et al. Ischemic stroke in cancer patients with and without conventional mechanisms: a multicenter study in Korea. Stroke. 2010; 41:798–801.
Article14. Demers M, Wagner DD. NETosis: a new factor in tumor progression and cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2014; 40:277–283.
Article15. van Montfoort ML, Stephan F, Lauw MN, Hutten BA, Van Mierlo GJ, Solati S, et al. Circulating nucleosomes and neutrophil activation as risk factors for deep vein thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013; 33:147–151.
Article16. Bang OY, Chung JW, Cho YH, Oh MJ, Seo WK, Kim GM, et al. Circulating DNAs, a marker of neutrophil extracellular traposis and cancer-related stroke: the OASIS-sancer study. Stroke. 2019; 50:2944–2947.
Article17. Lee MJ, Chung JW, Ahn MJ, Kim S, Seok JM, Jang HM, et al. Hypercoagulability and mortality of patients with stroke and active cancer: the OASIS-CANCER study. J Stroke. 2017; 19:77–87.
Article18. Chung JW, Cho YH, Ahn MJ, Lee MJ, Kim GM, Chung CS, et al. Association of cancer cell type and extracellular vesicles with coagulopathy in patients with lung cancer and stroke. Stroke. 2018; 49:1282–1285.
Article19. Bang OY, Chung JW, Lee MJ, Kim SJ, Cho YH, Kim GM, et al. Cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles are associated with coagulopathy causing ischemic stroke via tissue factor-independent way: the OASIS-CANCER study. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0159170.
Article20. Xu Y, Zhang Y, Wang L, Zhao R, Qiao Y, Han D, et al. miR-200a targets Gelsolin: a novel mechanism regulating secretion of microvesicles in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2017; 37:2711–2719.
Article21. Melo SA, Sugimoto H, O’Connell JT, Kato N, Villanueva A, Vidal A, et al. Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2014; 26:707–721.
Article22. Sandvig K, Llorente A. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles released by the human prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012; 11:M111.012914.
Article23. Chen M, Xu R, Rai A, Suwakulsiri W, Izumikawa K, Ishikawa H, et al. Distinct shed microvesicle and exosome microRNA signatures reveal diagnostic markers for colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0210003.
Article24. Manri C, Yokoi T, Nishida H. Size-selective harvesting of extracellular vesicles for strategic analyses towards tumor diagnoses. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017; 182:609–623.
Article25. Rabinowits G, Gerçel-Taylor C, Day JM, Taylor DD, Kloecker GH. Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009; 10:42–46.
Article26. Chu YL, Li H, Ng PLA, Kong ST, Zhang H, Lin Y, et al. The potential of circulating exosomal RNA biomarkers in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020; 20:665–678.
Article27. Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013; 2:20360.
Article28. Gao C, Zhang CC, Yang HX, Hao YN. MALAT1 protected the angiogenesis function of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) under oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R) challenge by interacting with miR-205-5p/ VEGFA pathway. Neuroscience. 2020; 435:135–145.
Article29. Zhu B, Tian T, Zhao M. MiR-645 promotes proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting TP53I11. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24:6150–6156.30. Sun Q, Chen S, Zhao X, Yan M, Fang Z, Wang H, et al. Dysregulated miR-645 affects the proliferation and invasion of head and neck cancer cell. Cancer Cell Int. 2015; 15:87.
Article31. Guo ST, Guo XY, Wang J, Wang CY, Yang RH, Wang FH, et al. MicroRNA-645 is an oncogenic regulator in colon cancer. Oncogenesis. 2017; 6:e335.
Article32. Yuan X, Liu Y, Chen E, Wang J, Deng S, Chen P, et al. MiR-646 regulates proliferation and migration of laryngeal carcinoma through the PI3K/AKT pathway via targeting GPX1. Oral Dis. 2021; 27:1678–1686.
Article33. Wang J, Shu H, Guo S. MiR-646 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by repressing FGF2 and CCND2. Cancer Med. 2020; 9:4360–4370.
Article34. Huang J, Wang X, Wen G, Ren Y. miRNA-205-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating VEGFA and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019; 42:1677–1688.
Article35. Zhang D, Zhang X, Zhao C. Risk of venous and arterial thromboembolic events associated with anti-VEGF agents in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Onco Targets Ther. 2016; 9:3695–3704.
Article36. Almeida VH, Rondon AMR, Gomes T, Monteiro RQ. Novel aspects of extracellular vesicles as mediators of cancer-associated thrombosis. Cells. 2019; 8:716.
Article37. Hisada Y, Mackman N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2017; 130:1499–1506.
Article38. Endzeliņš E, Berger A, Melne V, Bajo-Santos C, Soboļevska K, Ābols A, et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:730.
Article