J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2023 Apr;49(2):86-90. 10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.2.86.
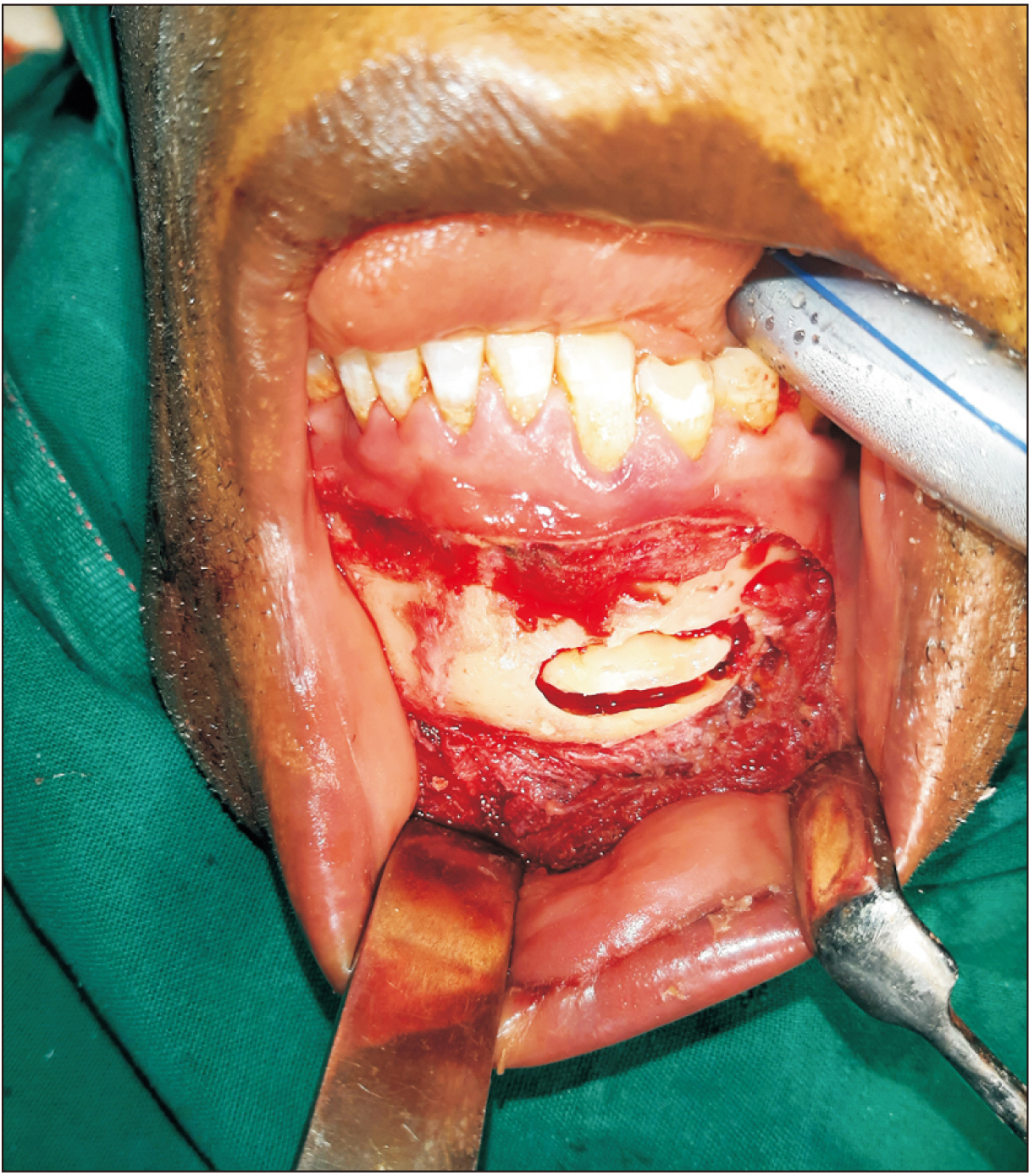
Management of rare ectopic teeth eruption: case series
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dental Sciences, College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Lagos, Nigeria
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital, Maiduguri, Maiduguri, Nigeria
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Pathology, Faculty of Dentistry, College of Medical Sciences, University of Maiduguri, Maiduguri, Nigeria
- KMID: 2542214
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.2.86
Abstract
Objectives
An ectopic tooth is a rare eruption of a tooth out of the normal dental apparatus and occurs commonly with the third molar. Thus, in this study, we reported a case series of ectopic teeth in rare jaw locations and highlight the associated pathology and our experience in the surgical management.
Patients and Methods
All cases of ectopic tooth managed at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University of Maiduguri Teaching Hospital from January 2011 to December 2020 were reviewed. The information retrieved includes biodata, location of the ectopic tooth, signs, symptoms, type of tooth and associated pathology, surgical approach and complications.
Results
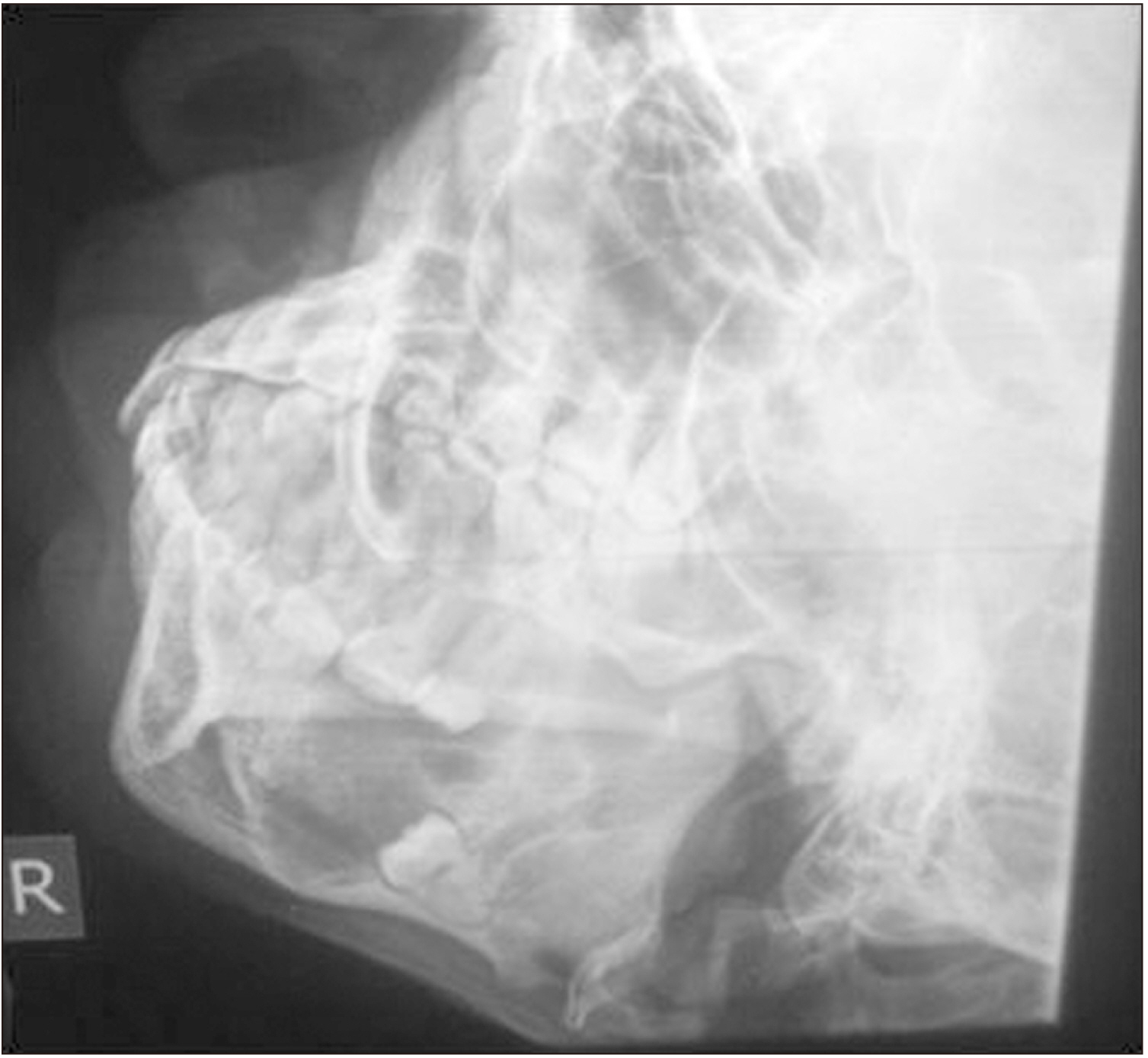
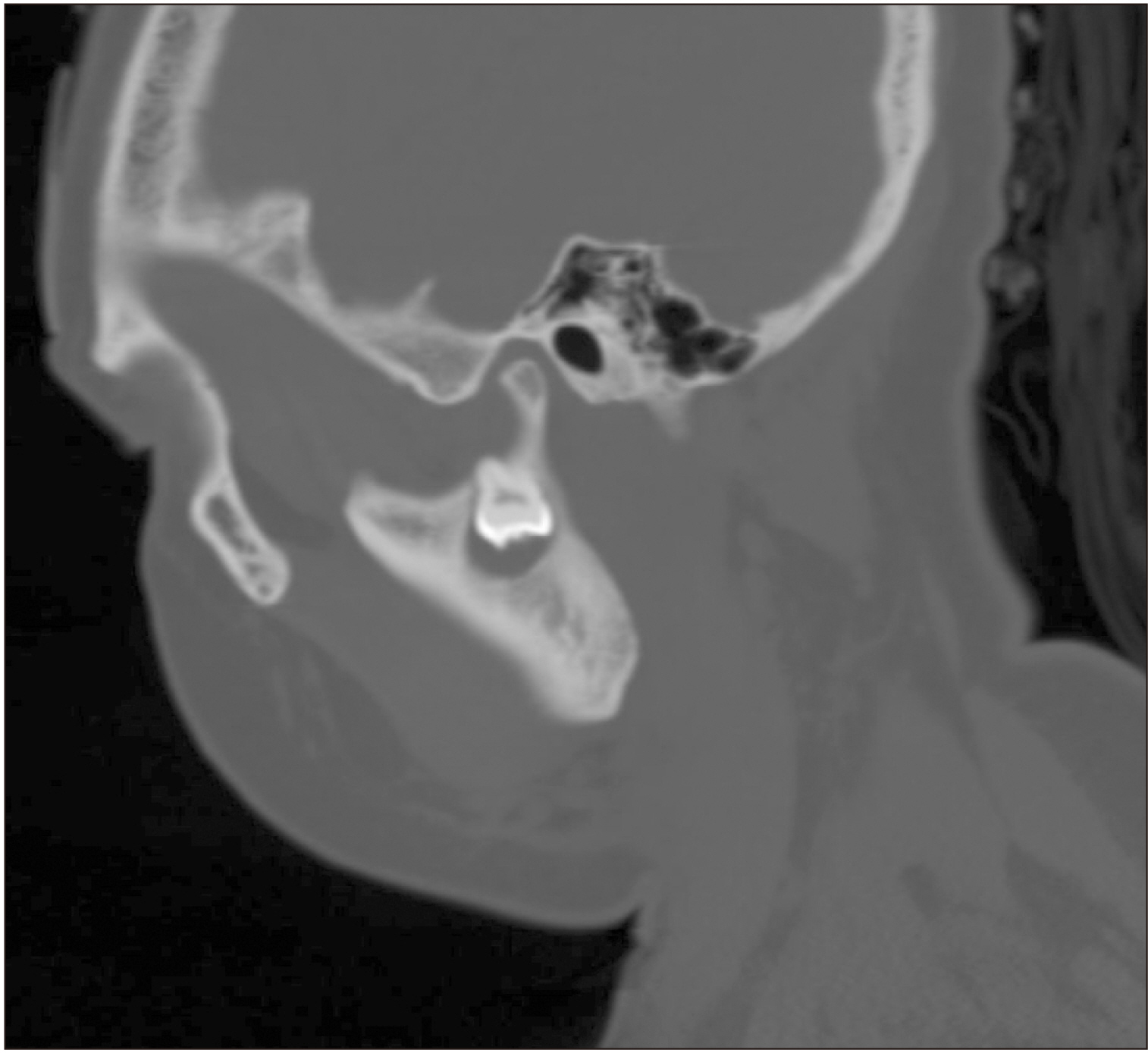
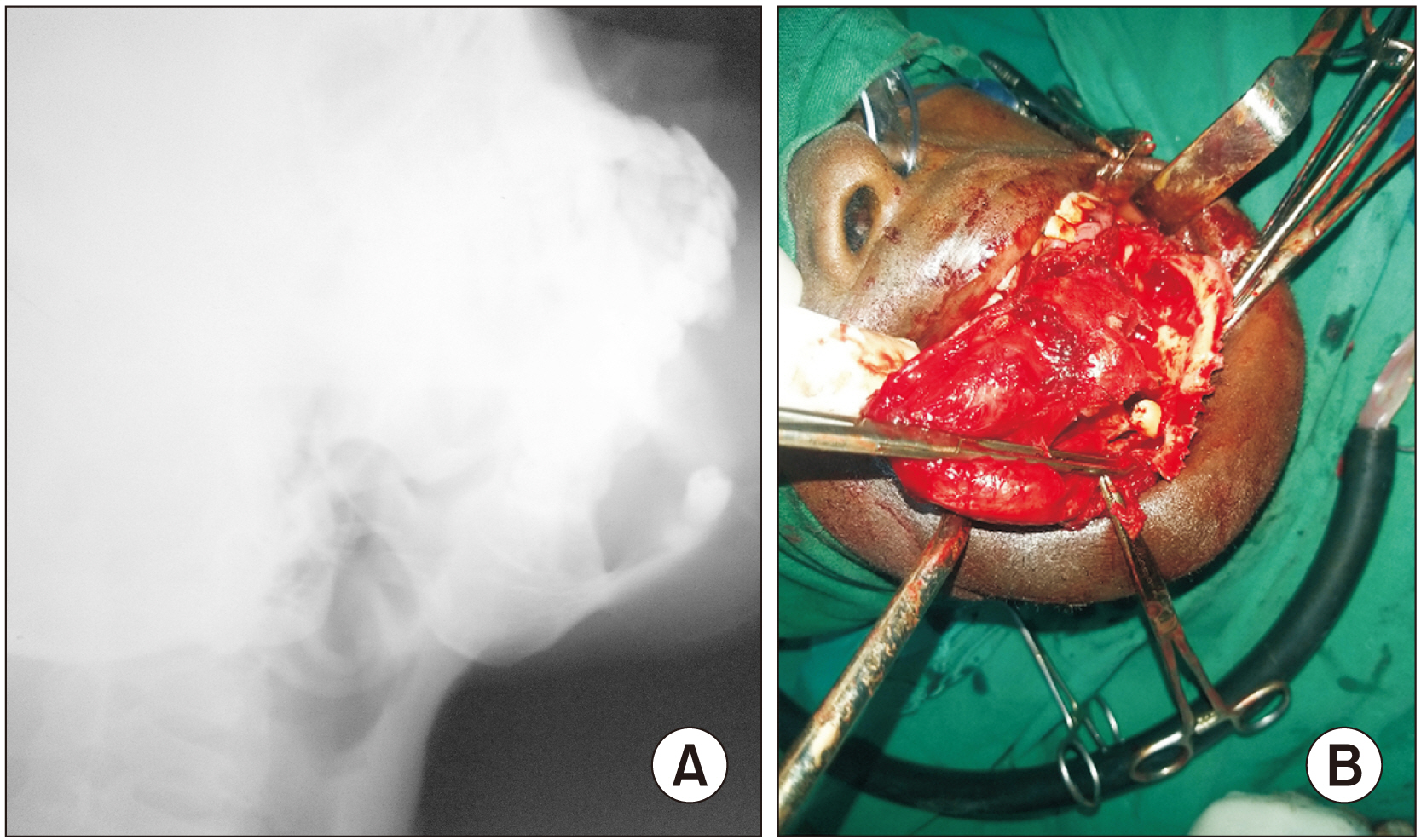
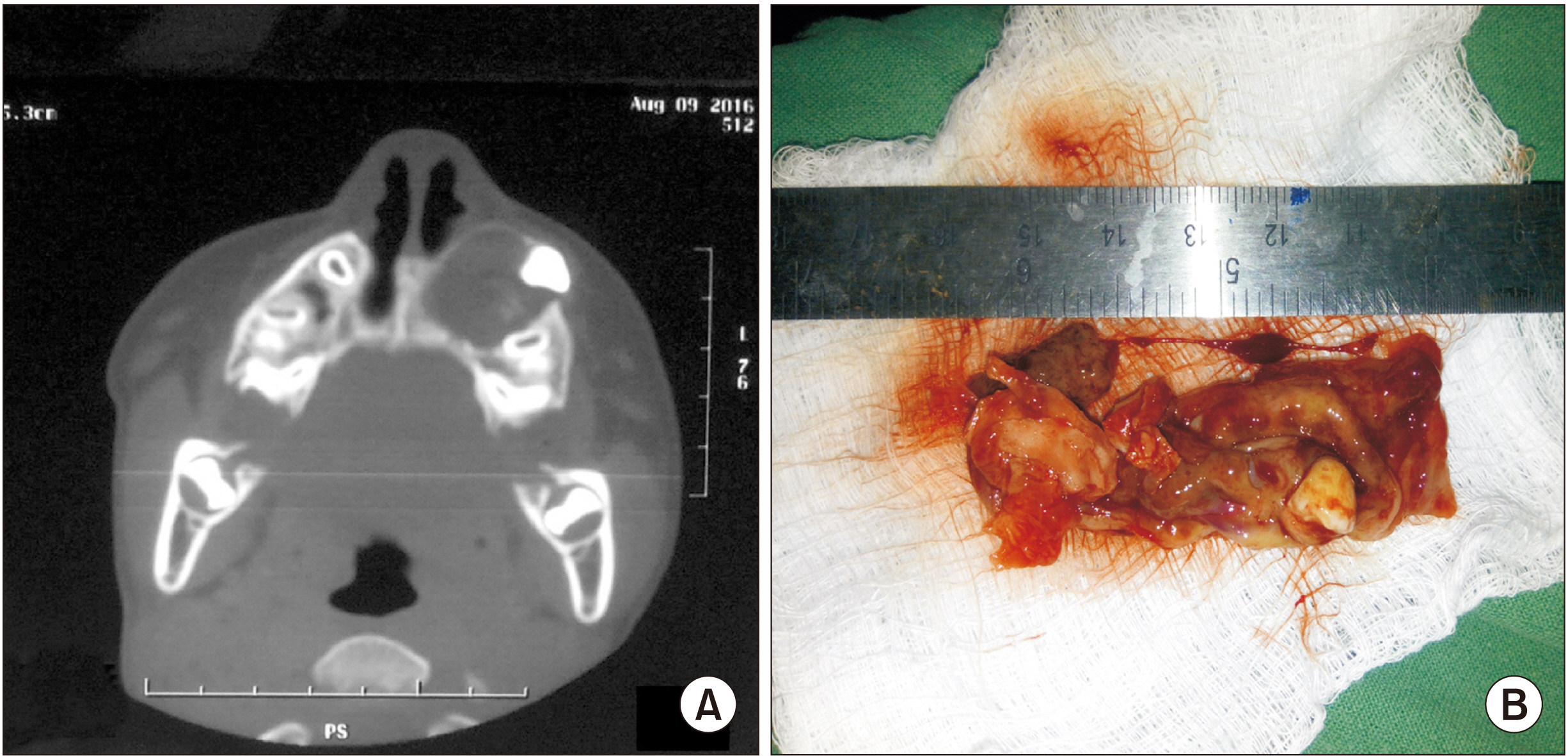
Ten cases of ectopic teeth were identified over the study period. This comprised 80.0% males with a mean age was 23.3 years. The antrum and lower border of the mandible accounted for 50.0% and 40.0% of the ectopic locations, respectively. Dentigerous cyst was the most associated pathology (70%) and usually presented with pain and swelling. Surgical intervention predominantly via the intraoral route was performed if indicated.
Conclusion
Ectopic teeth are rare and not always associated with pathology. A high index of suspicion and radiological investigation are necessary for diagnosis. A more extensive multi-center study is however recommended to determine the prevalence of ectopic teeth other than the third molar.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Iglesias-Martin F, Infante-Cossio P, Torres-Carranza E, Prats-Golczer VE, Garcia-Perla-Garcia A. 2012; Ectopic third molar in the mandibular condyle: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 17:e1013–7. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.17864. DOI: 10.4317/medoral.17864. PMID: 22926463. PMCID: PMC3505695.
Article2. Wu Y, Song Y, Huang R, Hu J, He X, Wang Y, et al. 2017; Comprehensive analysis of ectopic mandibular third molar: a rare clinical entity revisited. Head Face Med. 13:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13005-017-0157-x. DOI: 10.1186/s13005-017-0157-x. PMID: 29229002. PMCID: PMC5725881.
Article3. Gadre KS, Waknis P. 2010; Intra-oral removal of ectopic third molar in the mandibular condyle. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 39:294–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2009.10.002. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.10.002. PMID: 19892523.
Article4. Kheir MK, Sheikhi M. 2019; Ectopic third molar in maxillary sinus: an asymptomatic accidental finding. Egypt J Otolaryngol. 35:219–21. https://doi.org/10.4103/ejo.ejo_80_18.
Article5. Bello SA, Oketade IO, Osunde OD. 2014; Ectopic 3rd molar tooth in the maxillary antrum. Case Rep Dent. 2014:620741. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/620741. DOI: 10.1155/2014/620741. PMID: 25132999. PMCID: PMC4123483.
Article6. Cho JY, Nam KY. 2012; Expansile dentigerous cyst invading the entire maxillary sinus: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 38:245–8. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.4.245. DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.4.245.
Article7. Buyukkurt MC, Omezli MM, Miloglu O. 2010; Dentigerous cyst associated with an ectopic tooth in the maxillary sinus: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 109:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.043. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.043. PMID: 19875313.
Article8. Payne K, Dickenson A, Patel M. 2012; An unusually placed ectopic mandibular third molar: case report and discussion of management. Oral Sug. 5:155–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-248X.2012.01159.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-248X.2012.01159.x.
Article9. Fındık Y, Baykul T. 2015; Ectopic third molar in the mandibular sigmoid notch: report of a case and literature review. J Clin Exp Dent. 7:e133–7. https://doi.org/10.4317/jced.51871. DOI: 10.4317/jced.51871. PMID: 25810825. PMCID: PMC4368001.
Article10. Veerabhadrappa SK, Hesarghatta Ramamurthy P, Yadav S, Bin Zamzuri AT. 2021; Analysis of clinical characteristics and management of ectopic third molars in the mandibular jaw: a systematic review of clinical cases. Acta Odontol Scand. 79:514–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2021.1901984. DOI: 10.1080/00016357.2021.1901984. PMID: 33764264.
Article11. Sharma S, Chauhan JS. 2019; Bilateral ectopic third molars in maxillary sinus associated with dentigerous cyst-a rare case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 61:298–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.07.072. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.07.072. PMID: 31401439. PMCID: PMC6699555.
Article12. Sivolella S, Ricci S, Busca M, Stellini E, Valente M. 2014; Maxillary dentigerous cyst and ectopic third molar. Oral Surg. 7:72–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ors.12111. DOI: 10.1111/ors.12111.
Article13. Zhang LL, Yang R, Zhang L, Li W, MacDonald-Jankowski D, Poh CF. 2010; Dentigerous cyst: a retrospective clinicopathological analysis of 2082 dentigerous cysts in British Columbia, Canada. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 39:878–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2010.04.048. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.04.048. PMID: 20605411.
Article14. Tilakraj TN, Kiran NK, Mukunda KS, Rao S. 2011; Non syndromic unilateral dentigerous cyst in a 4-year-old child: a rare case report. Contemp Clin Dent. 2:398–401. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-237x.91813. DOI: 10.4103/0976-237X.91813. PMID: 22346177. PMCID: PMC3276877.
Article15. Suarez-Cunqueiro MM, Schoen R, Schramm A, Gellrich NC, Schmelzeisen R. 2003; Endoscopic approach to removal of an ectopic mandibular third molar. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:340–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-4356(03)00111-6. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-4356(03)00111-6. PMID: 14581030.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ectopic teeth with disparate migration: A literature review and new case series
- Ectopic Eruption of a Tooth into the Nasal Cavity with Sinusitis: A Case Report
- Eruption failure of teeth
- Clinical Management and Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis of Supernumerary Teeth in Infancy: A Case Report
- Early Eruption of Maxillary Permanent Canines : Report of 2 Cases