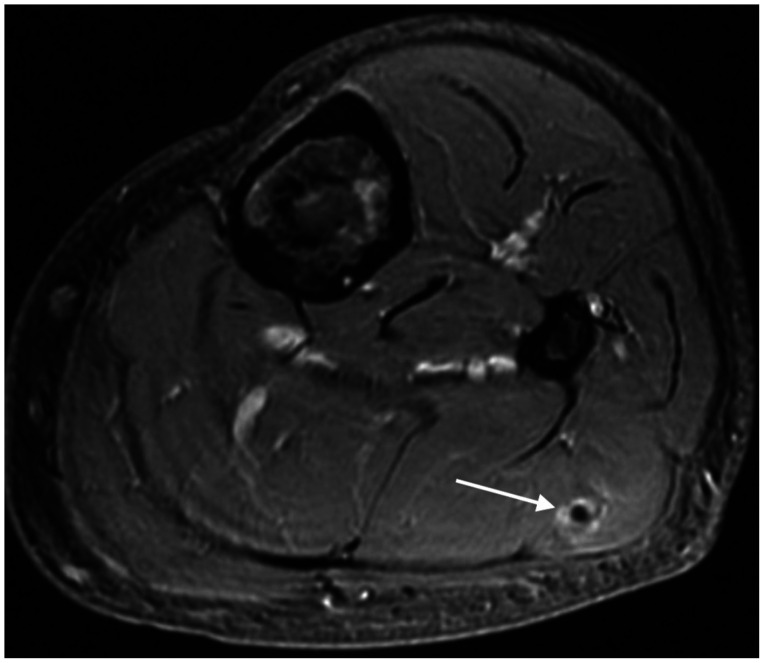
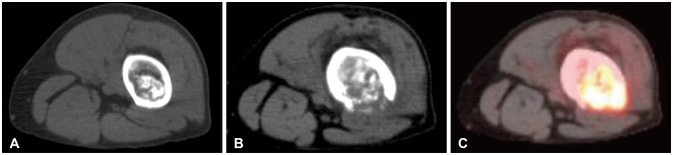
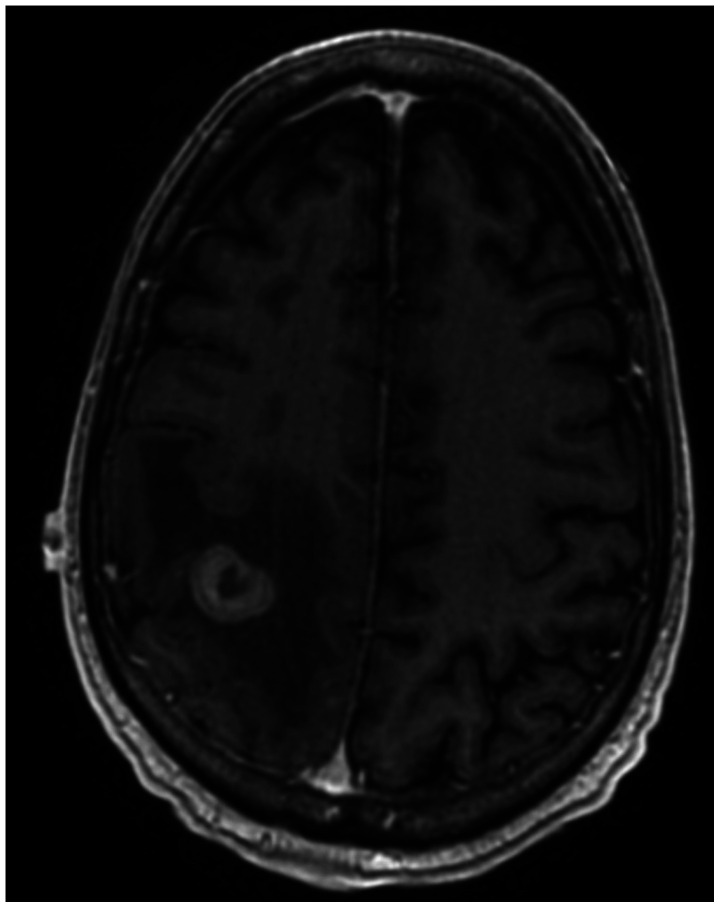
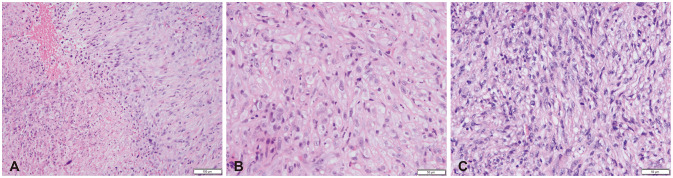
Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2023 Apr;11(2):103-113. 10.14791/btrt.2023.0003.
Intracranial Metastasis of Extracranial Chondrosarcoma: Systematic Review With Illustrative Case
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- 2Department of Pathology, Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- 3Department of Neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- KMID: 2542082
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2023.0003
Abstract
- Background
Cerebral chondrosarcoma metastases are rare and aggressive neoplasms. The rarity of presentation has precluded rigorous analysis of diagnosis, risk factors, treatment, and survival. We analyzed every reported case through exhaustive literature review. We further present the first case with Maffucci syndrome.
Methods
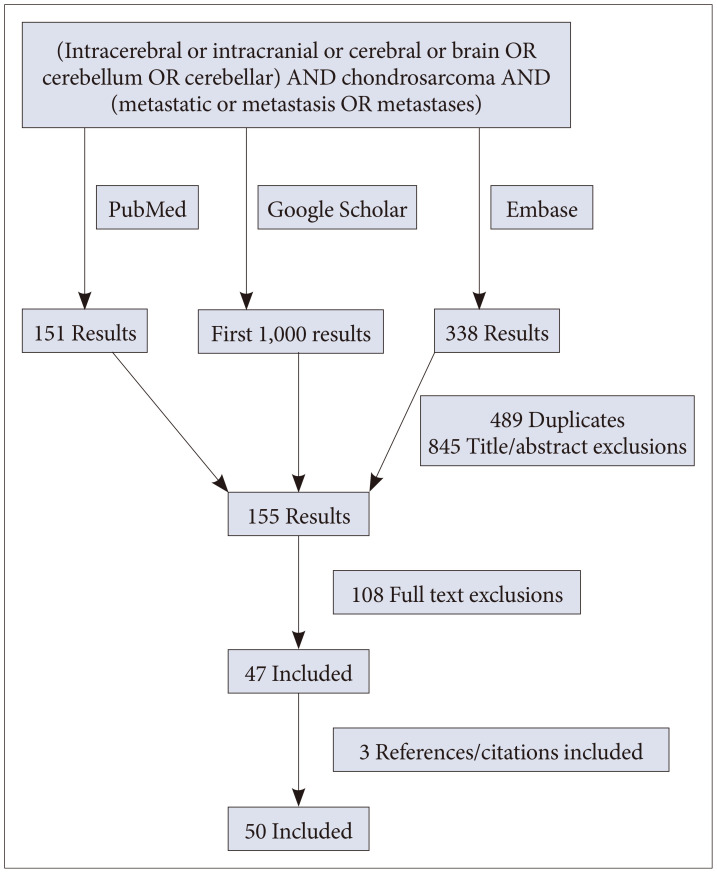
Three databases, PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar, and crossed references were queried for cerebral chondrosarcoma metastases. Extracted variables included demographics, risk factors, tumor characteristics, interventions, and outcomes. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed.
Results
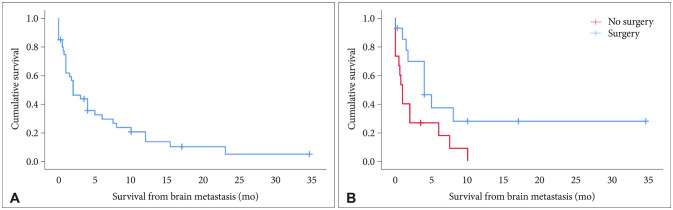
Fifty-six patients were included from 1,489 literature results. The average age at brain metastasis was 46.6±17.6 years and occurred at a median of 24±2.8 months from primary diagnosis. Primary tumor histology (dedifferentiated 5.0±1.5 months, mesenchymal 24±3.0 months, conventional 41±7.4 months, p<0.05) and grade (low grade 54±16.7 months vs. high-grade 10±6.4 months, p<0.001) correlated with time interval until brain metastasis. A multiple enchondromatosis syndrome occurred in 13.2% of cases. At time of brain metastases diagnosis, extracranial metastases were identified in 76.2% of cases. Median survival after the development of brain metastasis was 2.0±0.78 months with a 1-year survival of 10.0%. On regression analysis, surgery reduced brain metastasis mortality risk and radiation trended towards reduced mortality risk (surgery: hazard ratio [HR] 0.22, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.064–0.763, p=0.017; radiation: HR 0.31, 95% CI 0.091–1.072, p=0.064).
Conclusion
We present a systematic review of cerebral chondrosarcoma metastases. Primary tumor histology and grade correlate with time until cerebral metastasis. Following cerebral metastasis, these tumors have poor prognosis and modestly benefit from surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gelderblom H, Hogendoorn PC, Dijkstra SD, van Rijswijk CS, Krol AD, Taminiau AH, et al. The clinical approach towards chondrosarcoma. Oncologist. 2008; 13:320–329. PMID: 18378543.2. Giuffrida AY, Burgueno JE, Koniaris LG, Gutierrez JC, Duncan R, Scully SP. Chondrosarcoma in the United States (1973 to 2003): an analysis of 2890 cases from the SEER database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:1063–1072. PMID: 19411454.3. Evans HL, Ayala AG, Romsdahl MM. Prognostic factors in chondrosarcoma of bone: a clinicopathologic analysis with emphasis on histologic grading. Cancer. 1977; 40:818–831. PMID: 890662.4. Ozaki T, Hillmann A, Lindner N, Blasius S, Winkelmann W. Metastasis of chondrosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1996; 122:625–628. PMID: 8879261.5. Wang Z, Chen G, Chen X, Huang X, Liu M, Pan W, et al. Predictors of the survival of patients with chondrosarcoma of bone and metastatic disease at diagnosis. J Cancer. 2019; 10:2457–2463. PMID: 31258751.6. Bekiesinska-Figatowska M, Duczkowska A, Duczkowski M, Bragoszewska H, Romaniuk-Doroszewska A, Iwanowska B, et al. CNS metastases from bone and soft tissue sarcomas in children, adolescents, and young adults: are they really so rare? Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:1456473. PMID: 28243595.7. Shweikeh F, Bukavina L, Saeed K, Sarkis R, Suneja A, Sweiss F, et al. Brain metastasis in bone and soft tissue cancers: a review of incidence, interventions, and outcomes. Sarcoma. 2014; 2014:475175. PMID: 24757391.8. Postovsky S, Ash S, Ramu IN, Yaniv Y, Zaizov R, Futerman B, et al. Central nervous system involvement in children with sarcoma. Oncology. 2003; 65:118–124. PMID: 12931017.9. Ogose A, Morita T, Hotta T, Kobayashi H, Otsuka H, Hirata Y, et al. Brain metastases in musculoskeletal sarcomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1999; 29:245–247. PMID: 10379335.10. Ahmad O, Chan M, Savage P, Watabe K, Lo HW, Qasem S. Biology and treatment of metastasis of sarcoma to the brain. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2016; 8:233–244. PMID: 26709659.11. Al Sannaa G, Watson KL, Olar A, Wang WL, Fuller GN, McCutcheon I, et al. Sarcoma brain metastases: 28 years of experience at a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; 23(Suppl 5):962–967. PMID: 27646022.12. Kokkali S, Vini L, Stergioula A, Kyriazoglou A, Vassos N, Boukovinas I. Brain metastases from adult sarcomas: a retrospective cohort study from the Hellenic group of sarcomas and rare cancers (HGSRC). J Clin Med. 2021; 10:5978. PMID: 34945275.13. Yoshida S, Morii K, Watanabe M, Saito T. Brain metastasis in patients with sarcoma: an analysis of histological subtypes, clinical characteristics, and outcomes. Surg Neurol. 2000; 54:160–164. PMID: 11077098.14. Chou YS, Liu CY, Chen WM, Chen TH, Chen PC, Wu HT, et al. Brain, the last fortress of sarcoma: similar dismal outcome but discrepancy of timing of brain metastasis in bone and soft tissue sarcoma. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:765–770. PMID: 21714120.15. Grossman R, Ram Z. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) classification predicts survival in patients with brain metastases from sarcoma. World Neurosurg. 2014; 82:1291–1294. PMID: 25102368.16. Xu G, Wu H, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Lin F, Baklaushev VP, et al. Homogenous and heterogenous prognostic factors for patients with bone sarcoma. Orthop Surg. 2021; 13:134–144. PMID: 33305494.17. Santos GC, Carvalho KC, Falzoni R, Simoes AC, Rocha RM, Lopes A, et al. Glial fibrillary acidic protein in tumor types with cartilaginous differentiation. Mod Pathol. 2009; 22:1321–1327. PMID: 19668151.18. Nakagawa M, Sekimizu M, Endo M, Kobayashi E, Iwata S, Fukushima S, et al. Prognostic impact of IDH mutations in chondrosarcoma. J Orthop Sci. 2022; 27:1315–1322. PMID: 34531086.19. Shyamasunder AH, Rajan R, Cherian KE, Kapoor N, Jebasingh F, Paul T, et al. Pituitary metastases - management and outcome of three cases from a tertiary care centre. Rev Argent Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 58(Suppl 1):227.20. Flint JH, Conley AP, Rubin ML, Feng L, Lin PP, Moon B, et al. Clear cell chondrosarcoma: clinical characteristics and outcomes in 15 patients. Sarcoma. 2020; 2020:2386191.21. Hussain NS, Ahmed SH. Metastatic intracerebral chondrosarcoma: case report and literature review of endocrine effects and management paradigms. Cureus. 2020; 12:e8417. PMID: 32642333.22. Zoccali C, Baldi J, Anelli V, Annovazzi A, Scotto di Uccio A, Arrigoni F, et al. The giant aggressive chondroma: a rare entity, a difficult approach. J Orthop. 2020; 18:181–184. PMID: 32042223.23. Agarwal C, Bhardwaj M, Agarwal P, Ahuja A. Intracranial chondrosarcoma: series of three cases with varied and unusual presentations. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018; 61:294–296. PMID: 29676384.24. Ghosh AK, Barma RD, Sharma TN, Chakrabarty M. A rare case of brain metastasis. Open Access J Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 1:43–45.25. Lee CT, Tsai CC, Chang HT, Hsu YL. Primary pulmonary mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: a case report with clinical course and response to radiation. Thorac Med. 2016; 31:108–114.26. Lo W, Feeney V, Carey M, Grimer R, Albanese E. Cerebral metastatic chondrosarcoma and breast carcinoma–Report of a rare case and literature review. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015; 41:S279.27. Lo WB, Feeney V, Carey M, Grimer R, Albanese E. Cerebral metastatic chondrosarcoma and breast carcinoma–Report of a rare case and literature review. Neuro Oncol. 2015; 17(Suppl 8):viii14.28. Niazi OT, Alhaj E, Rahman IU, Waller A, Ghesani N, Klapholz M. Detection of cardiac metastasis by F-18 fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 65(10S):A1285.29. Chow LT. Femur chondrosarcoma misdiagnosed as acute knee arthritis and osteomyelitis--further developing a hitherto unreported complication of tumor embolic ischemic ileal perforation after arthroscopic lavage. Pathol Res Pract. 2014; 210:1095–1099. PMID: 25242025.30. Jiang B, Veeravagu A, Feroze AH, Lee M, Harsh GR, Soltys SG, et al. CyberKnife radiosurgery for the management of skull base and spinal chondrosarcomas. J Neurooncol. 2013; 114:209–218. PMID: 23748573.31. Frances-Munoz E, Gallego-Pinazo R, Pardo-Lopez D, Diaz-Llopis M. Choroidal metastasis from chondrosarcoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:949–951. PMID: 21713532.32. Kawaguchi T, Yamanouchi Y, Numa Y, Sakurai Y, Yamahara T, Seno T, et al. A case of metastatic brain tumor causing multifocal cerebral embolism. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2012; 29:63–67. PMID: 21935684.33. Pontes HA, Pontes FS, de Abreu MC, de Carvalho PL, de Brito Kato AM, Fonseca FP, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of head and neck chondrosarcoma: three case reports and literature review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:203–210. PMID: 22055262.34. Tseng YA, Youn T, Eisenkraft B, Drexler S. A case report: primary cutaneous chondrosarcoma metastatic to the brain. Am J Clin Pathol. 2012; 138(suppl 2):A126.35. Tam ACW, Chan ATS, Lee JCK, Cheung FMF. Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma in the scapula. Hong Kong J Radiol. 2011; 14:229–233.36. Flannery T, Kano H, Niranjan A, Monaco EA 3rd, Flickinger JC, Kofler J, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery as a therapeutic strategy for intracranial sarcomatous metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76:513–519. PMID: 19467792.37. Goda JS, Ferguson PC, O’Sullivan B, Catton CN, Griffin AM, Wunder JS, et al. High-risk extracranial chondrosarcoma: long-term results of surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer. 2011; 117:2513–2519. PMID: 21246520.38. Tsutsumi S, Yasumoto Y, Oizumi H, Ito M. Chondrosarcoma with atypical clinical presentation treated by gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010; 50:502–505. PMID: 20587980.39. Bruns J, Fiedler W, Werner M, Delling G. Dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma--a fatal disease. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005; 131:333–339. PMID: 15785935.40. Kawanishi C, Onishi H, Kato D, Yamada T, Onose M, Hirayasu Y. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome in cancer treatment. Palliat Support Care. 2005; 3:51–53. PMID: 16594195.41. Patil S, de Silva MV, Crossan J, Reid R. Chondrosarcoma of the bones of the feet. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003; 42:290–295. PMID: 14566721.42. Yoshida K, Miyashita N, Nakajima M, Niki Y, Matsushima T. [A case of sternal chondrosarcoma with multiple pulmonary embolisms]. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2002; 40:166–170. Japanese. PMID: 11974874.43. Bovée JV, van Roggen JF, Cleton-Jansen AM, Taminiau AH, van der Woude HJ, Hogendoorn PC. Malignant progression in multiple enchondromatosis (Ollier’s disease): an autopsy-based molecular genetic study. Hum Pathol. 2000; 31:1299–1303. PMID: 11070122.44. Kim HB, Jung SE, Kim HH, Choi KH, Lee YS, Kang SJ. Metastatic brain tumor from cardiac chondrosarcoma: a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999; 40:657–660.45. Rushing EJ, Armonda RA, Ansari Q, Mena H. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: a clinicopathologic and flow cytometric study of 13 cases presenting in the central nervous system. Cancer. 1996; 77:1884–1891. PMID: 8646689.46. Sans M, Nubiola D, Alejo M, Diaz F, Anglada A, Autonell J, et al. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the foot, an unusual location: case report and review of the literature. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996; 26:139–142. PMID: 8531853.47. Wroński M, Arbit E, Burt M, Perino G, Galicich JH, Brennan MF. Resection of brain metastases from sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 1995; 2:392–399. PMID: 7496833.48. Konishi H, Isetani K, Satoh T, Fukuda S, Kodama T, Kashima K. A case of metastatic chondrosarcoma of the stomach. J Gastroenterol. 1994; 29:495–500. PMID: 7951861.49. Moran CA, Suster S, Carter D. Laryngeal chondrosarcomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993; 117:914–917. PMID: 8368904.50. Jallu A, Kanaan I, Agarwal S. Metastatic chondrosarcoma of the brain: a case report. Ann Saudi Med. 1992; 12:307–308. PMID: 17586975.51. Salminen US, Halttunen P, Taskinen E, Mattila S. Recurrence and malignant transformation of endotracheal chondroma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 49:830–832. PMID: 2339945.52. Bertoni F, Present D, Bacchini P, Picci P, Pignatti G, Gherlinzoni F, et al. Dedifferentiated peripheral chondrosarcomas. A report of seven cases. Cancer. 1989; 63:2054–2059. PMID: 2702574.53. Perry BE, McQueen DA, Lin JJ. Synovial chondromatosis with malignant degeneration to chondrosarcoma. Report of a case. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:1259–1261. PMID: 3417715.54. Bertoni F, Unni KK, Beabout JW, Sim FH. Chondrosarcomas of the synovium. Cancer. 1991; 67:155–162. PMID: 1985712.55. Liu J, Hudkins PG, Swee RG, Unni KK. Bone sarcomas associated with Ollier’s disease. Cancer. 1987; 59:1376–1385. PMID: 3815310.56. Reif J, Graf N. Intraspinal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma in a three-year-old boy. Neurosurg Rev. 1987; 10:311–314. PMID: 3506147.57. Johnson S, Tetu B, Ayala AG, Chawla SP. Chondrosarcoma with additional mesenchymal component (dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma). I. A clinicopathologic study of 26 cases. Cancer. 1986; 58:278–286. PMID: 3719521.58. Sherr DL, Fountain KS, Piro JD. Chondrosarcoma metastatic to the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985; 59:622–626. PMID: 3859824.59. Templeton PA, Gellad FE, Wood C. Computed tomography of metastatic chondrosarcoma to the brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985; 9:829–834. PMID: 4019850.60. Pialat J, Bejui-Thivolet F, Perrin G. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: two cases and review of the literature. Lyon Med. 1980; 243:603–607.61. Unni KK, Dahlin DC, Beabout JW, Sim FH. Chondrosarcoma: clear-cell variant. A report of sixteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58:676–683. PMID: 932066.62. Gercovich FG, Luna MA, Gottlieb JA. Increased incidence of cerebral metastases in sarcoma patients with prolonged survival from chemotherapy. Report of cases of leiomysarcoma and chondrosarcoma. Cancer. 1975; 36:1843–1851. PMID: 1192369.63. Talerman A. Chondrosarcoma with long-delayed metastasis of unusual distribution. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967; 93:348–350. PMID: 6029772.64. Cowan WK. Malignant change and multiple metastases in Ollier’s disease. J Clin Pathol. 1965; 18:650–653. PMID: 5835448.65. Damron TA, Ward WG, Stewart A. Osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma: national cancer data base report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 459:40–47. PMID: 17414166.66. Fromm J, Klein A, Baur-Melnyk A, Knosel T, Lindner L, Birkenmaier C, et al. Survival and prognostic factors in conventional central chondrosarcoma. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:849. PMID: 30143018.67. Amer KM, Munn M, Congiusta D, Abraham JA, Basu Mallick A. Survival and prognosis of chondrosarcoma subtypes: SEER database analysis. J Orthop Res. 2020; 38:311–319. PMID: 31498474.68. Vuong HG, Ngo TNM, Dunn IF. Prognostic importance of IDH mutations in chondrosarcoma: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2021; 10:4415–4423. PMID: 34085407.69. Andreou D, Ruppin S, Fehlberg S, Pink D, Werner M, Tunn PU. Survival and prognostic factors in chondrosarcoma: results in 115 patients with long-term follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82:749–755. PMID: 22066552.70. Verdegaal SH, Bovee JV, Pansuriya TC, Grimer RJ, Ozger H, Jutte PC, et al. Incidence, predictive factors, and prognosis of chondrosarcoma in patients with Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome: an international multicenter study of 161 patients. Oncologist. 2011; 16:1771–1779. PMID: 22147000.71. Bovee J, Bloem J, Flanagan AM. Enchondroma. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours: soft tissue and bone tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2020. p. 353–355.72. El Abiad JM, Robbins SM, Cohen B, Levin AS, Valle DL, Morris CD, et al. Natural history of Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome: patient survey and review of clinical literature. Am J Med Genet A. 2020; 182:1093–1103. PMID: 32144835.73. Flanagan AM, Blay JY, Bovee J, Bredella MA, Cool P, Nielsen GP. Bone tumours: introduction. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours: soft tissue and bone tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2020. p. 340–344.74. Bustinza-Linares E, Socola F, Ernani V, Miller SA, Trent JC. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma with small bowel metastasis causing bowel obstruction. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2012; 2012:621025. PMID: 23213584.75. Damas O, Betesh A, Deshpande A. An unknown cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding: metastatic extraskeletal chondrosarcoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:S362–S363.76. Geyer HL, Karlin N. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the heart and review of current literature. Curr Oncol. 2010; 17:58–62. PMID: 20975880.77. Enzinger FM, Shiraki M. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. An analysis of 34 cases. Hum Pathol. 1972; 3:421–435. PMID: 4261659.78. Ganguly R, Mukherjee A. Maxillo-facial extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma: a case report and discussion. Korean J Pathol. 2011; 45:639–643.79. Bhalla A, Osipov V. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the nasopharynx. Pathology. 2011; 43:507–509. PMID: 21753718.80. Horvai AE, Agaram NP, Lucas DR. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. WHO classification of tumours: soft tissue and bone tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2020. p. 303–305.81. Bovee J, BA A. Enchondromatosis. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumours: soft tissue and bone tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2020. p. 506–509.82. Italiano A, Mir O, Cioffi A, Palmerini E, Piperno-Neumann S, Perrin C, et al. Advanced chondrosarcomas: role of chemotherapy and survival. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:2916–2922. PMID: 24099780.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medulloblastoma with Extracranial Metastates: Case Report
- A Case of Intracranial Meningeal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma: A Case Report
- Primary Intracranial Malignant Melanoma with Extracranial Metastasis
- Chondrosarcoma with Intratumoral Hemorrhage: Case Report
- Primary Intracranial Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature