J Korean Med Sci.
2023 May;38(18):e138. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e138.
Case 10: A 30-Year-Old Woman With Breast Mass and Family History of Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Clinical Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2542030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e138
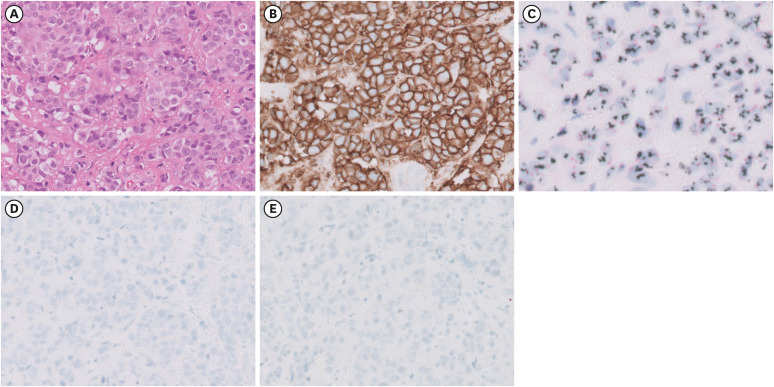
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kumamoto T, Yamazaki F, Nakano Y, Tamura C, Tashiro S, Hattori H, et al. Medical guidelines for Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2019, version 1.1. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021; 26(12):2161–2178. PMID: 34633580.
Article2. Chompret A, Brugières L, Ronsin M, Gardes M, Dessarps-Freichey F, Abel A, et al. P53 germline mutations in childhood cancers and cancer risk for carrier individuals. Br J Cancer. 2000; 82(12):1932–1937. PMID: 10864200.3. Gradishar WJ, Moran MS, Abraham J, Aft R, Agnese D, Allison KH, et al. Breast cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022; 20(6):691–722. PMID: 35714673.4. Weiss JM, Gupta S, Burke CA, Axell L, Chen LM, Chung DC, et al. NCCN guidelines(r) insights: genetic/familial high-risk assessment: colorectal, version 1.2021. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021; 19(10):1122–1132. PMID: 34666312.5. Trombetta MG, Dragun A, Mayr NA, Pierce LJ. Astro radiation therapy summary of the asco-astro-sso guideline on management of hereditary breast cancer. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020; 10(4):235–242. PMID: 32471709.6. Tung N, Lin NU, Kidd J, Allen BA, Singh N, Wenstrup RJ, et al. Frequency of germline mutations in 25 cancer susceptibility genes in a sequential series of patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34(13):1460–1468. PMID: 26976419.
Article7. Sidransky D, Tokino T, Helzlsouer K, Zehnbauer B, Rausch G, Shelton B, et al. Inherited p53 gene mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992; 52(10):2984–2986. PMID: 1581912.8. Gonzalez KD, Noltner KA, Buzin CH, Gu D, Wen-Fong CY, Nguyen VQ, et al. Beyond Li Fraumeni syndrome: clinical characteristics of families with p53 germline mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27(8):1250–1256. PMID: 19204208.
Article9. Silwal-Pandit L, Vollan HK, Chin SF, Rueda OM, McKinney S, Osako T, et al. TP53 mutation spectrum in breast cancer is subtype specific and has distinct prognostic relevance. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20(13):3569–3580. PMID: 24803582.
Article10. Mai PL, Best AF, Peters JA, DeCastro RM, Khincha PP, Loud JT, et al. Risks of first and subsequent cancers among TP53 mutation carriers in the National Cancer Institute Li-Fraumeni syndrome cohort. Cancer. 2016; 122(23):3673–3681. PMID: 27496084.
Article11. Kappel S, Janschek E, Wolf B, Rudas M, Teleky B, Jakesz R, et al. TP53 germline mutation may affect response to anticancer treatments: analysis of an intensively treated Li-Fraumeni family. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 151(3):671–678. PMID: 25981898.
Article12. Masciari S, Dillon DA, Rath M, Robson M, Weitzel JN, Balmana J, et al. Breast cancer phenotype in women with TP53 germline mutations: a Li-Fraumeni syndrome consortium effort. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 133(3):1125–1130. PMID: 22392042.
Article13. Kamihara J, Rana HQ, Garber JE. Germline TP53 mutations and the changing landscape of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2014; 35(6):654–662. PMID: 24706533.
Article14. Kuba MG, Lester SC, Bowman T, Stokes SM, Taneja KL, Garber JE, et al. Histopathologic features of breast cancer in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Mod Pathol. 2021; 34(3):542–548. PMID: 32636452.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interactions of Family History of Breast Cancer with Radiotherapy in Relation to the Risk of Breast Cancer Recurrence
- Usefulness of Ultrasonography for Detection of Breast Cancer in Patients under 30 Years of Age
- Relapse of Biphenotypic Acute Leukemia as a Breast Mass
- Case Report of Desmoid Fibromatosis as a Rare Disease Entity of the Breast
- Clinical Review of Familial and Hereditary Breast Cancer