J Korean Med Sci.
2023 May;38(18):e134. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e134.
Concurrent Subacute Thyroiditis and Graves’ Disease After COVID-19: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2542027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e134
Abstract
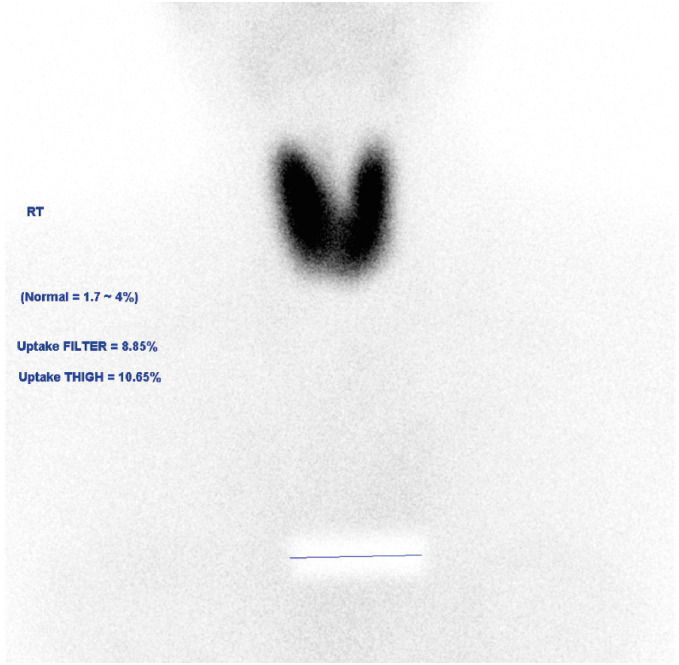
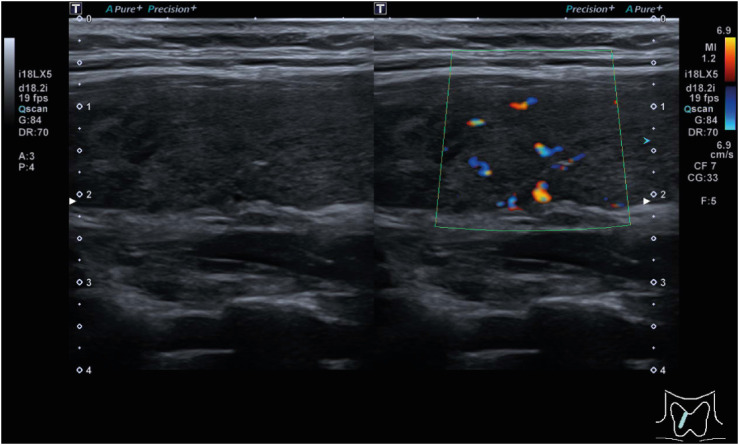
- There are many reports of subacute thyroiditis (SAT) that occurred after the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but no such case has been reported in Korea. Moreover, the simultaneous occurrence of SAT and Graves’ disease (GD) is rare. Here, we describe a patient who developed SAT and GD after the second episode of COVID-19. A 27-year-old woman with no known history of thyroid disease presented with fever, upper respiratory tract symptoms, and painful neck swelling. Thyroid function tests revealed thyrotoxicosis, and thyroid ultrasound showed heterogeneous echogenicity of enlarged thyroid glands. Her initial clinical presentation was consistent with SAT after viral infection, with typical neck tenderness and spontaneous improvement of thyrotoxicosis without antithyroid drug use. However, this case had some atypical features, such as an elevated thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin level, relapse of thyrotoxicosis in short-term follow-up, and increased Tc-99m pertechnetate uptake, suggesting the coexistence of GD. About two months after methimazole (15 mg/day) was prescribed, she was lost to follow up again. We report the first case of unusual co-occurrence of SAT and GD following COVID-19.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Desailloud R, Hober D. Viruses and thyroiditis: an update. Virol J. 2009; 6(1):5. PMID: 19138419.
Article2. Brancatella A, Ricci D, Cappellani D, Viola N, Sgrò D, Santini F, et al. Is subacute thyroiditis an underestimated manifestation of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Insights from a case series. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 105(10):dgaa537. PMID: 32780854.
Article3. Campos-Barrera E, Alvarez-Cisneros T, Davalos-Fuentes M, Usui T. Subacute thyroiditis associated with COVID-19. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2020; 2020:8891539. PMID: 33005461.
Article4. Chakraborty U, Ghosh S, Chandra A, Ray AK. Subacute thyroiditis as a presenting manifestation of COVID-19: a report of an exceedingly rare clinical entity. BMJ Case Rep. 2020; 13(12):e239953.
Article5. Mattar SA, Koh SJ, Rama Chandran S, Cherng BP. Subacute thyroiditis associated with COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2020; 13(8):e237336.
Article6. Mehmood MA, Bapna M, Arshad M. A case of post-COVID-19 subacute thyroiditis. Cureus. 2020; 12(12):e12301. PMID: 33510992.
Article7. Davoodi L, Oladi Z, Jafarpour H, Zakariaei Z, Soleymani E, Razavi A. A 33-year-old man with COVID-19 presented with subacute thyroiditis: a rare case report and literature review. New Microbes New Infect. 2021; 41:100871. PMID: 33777402.
Article8. Dworakowska D, Morley S, Mulholland N, Grossman AB. COVID-19-related thyroiditis: a novel disease entity? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2021; 95(3):369–377. PMID: 33650180.
Article9. Feghali K, Atallah J, Norman C. Manifestations of thyroid disease post COVID-19 illness: report of Hashimoto thyroiditis, Graves’ disease, and subacute thyroiditis. J Clin Transl Endocrinol Case Rep. 2021; 22:100094. PMID: 34462717.
Article10. Khatri A, Charlap E, Kim A. Subacute thyroiditis from COVID-19 infection: a case report and review of literature. Eur Thyroid J. 2021; 9(6):324–328. PMID: 33708634.
Article11. Ruggeri RM, Campennì A, Siracusa M, Frazzetto G, Gullo D. Subacute thyroiditis in a patient infected with SARS-COV-2: an endocrine complication linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. Hormones (Athens). 2021; 20(1):219–221. PMID: 32676935.
Article12. Sato D, Nishiguchi S, Tanaka E. Successful management of subacute thyroiditis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Intern Med. 2021; 60(22):3573–3576. PMID: 34511569.
Article13. Al-Shammaa MS, Abdlkadir AS. A case of post COVID-19 subacute thyroiditis. Clin Case Rep. 2022; 10(7):e6092. PMID: 35865769.
Article14. Jhon M, Lee SH, Oh TH, Kang HC. Subacute thyroiditis after receiving the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Moderna): the first case report and literature review in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(6):e39. PMID: 35166076.
Article15. Choi YS. Two cases of subacute thyroiditis following COVID-19 vaccination. Clin Ultrasound. 2022; 7(1):32–36.
Article16. Mateu-Salat M, Urgell E, Chico A. SARS-COV-2 as a trigger for autoimmune disease: report of two cases of Graves’ disease after COVID-19. J Endocrinol Invest. 2020; 43(10):1527–1528. PMID: 32686042.
Article17. Hoang TD, Mai VQ, Clyde PW, Shakir MK. Simultaneous occurrence of subacute thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Thyroid. 2011; 21(12):1397–1400. PMID: 22136271.
Article18. Scappaticcio L, Pitoia F, Esposito K, Piccardo A, Trimboli P. Impact of COVID-19 on the thyroid gland: an update. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021; 22(4):803–815. PMID: 33241508.
Article19. Knack RS, Hanada T, Knack RS, Mayr K. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2021; 14(8):e244909.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Graves' Disease Following Subacute Thyroiditis
- Two Cases of Subacute Thyroiditis Following COVID-19 Vaccination
- Graves' Disease Following Recurrent Subacute Thyroiditis
- A case of an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule combined with subacute thyroiditis
- A Case of Graves' Disease Following Subacute Thyroiditis Presented with Creeping