Nutr Res Pract.
2023 Apr;17(2):356-370. 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.2.356.
Causal relationship among quality factors, emotional responses, and satisfaction of school food service in Henan province, China
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hotel Management, Changzhou Vocational Institute of Textile and Garment, Changzhou 213164, China
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Human Ecology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 28644, Korea
- KMID: 2541371
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2023.17.2.356
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
School food service has played an important role in promoting the health and physical condition of students by providing students with a balanced and nutritious diet. Therefore, boosting the quality of school food service and improving the students’ satisfaction is critical. For this purpose, this study examined the structural causal relationship among the quality of school food service factors, emotional responses, and satisfaction in China.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
This study was conducted with 4th–6th-grade students from 6 junior high schools in Henan province of China, with 590 questionnaire responses (87.3%) collected and statistically analyzed.
RESULTS
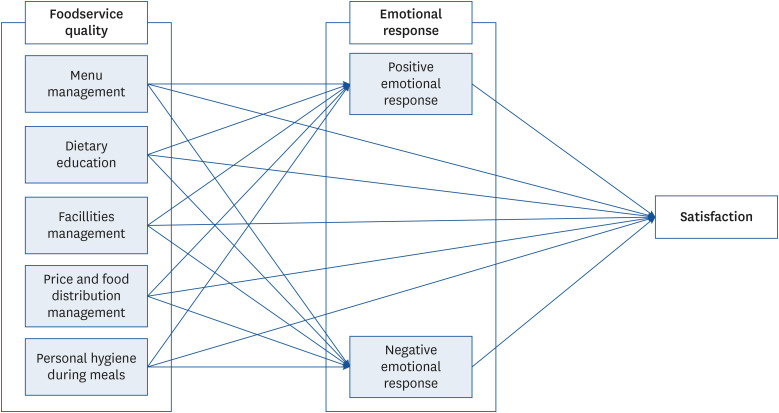
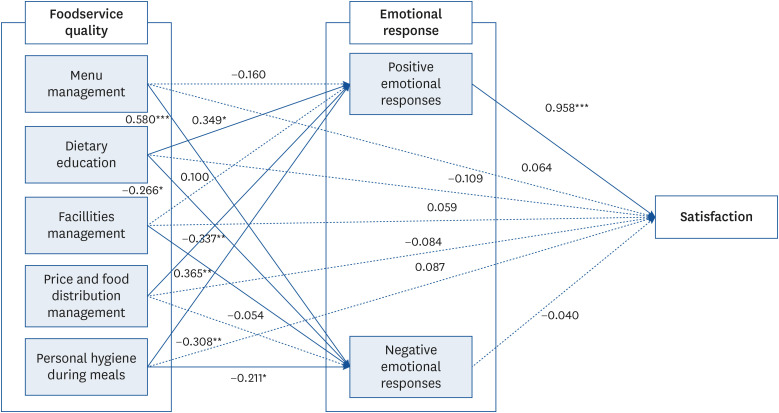
The school food service quality factors (including menu management, dietary education, facilities management, price and food distribution management, and personal hygiene during meals) must be enhanced to boost the students’ satisfaction. In addition, the study used questionnaire survey data to validate the full mediation of students’ emotional responses between school food service quality factors and student satisfaction.
CONCLUSIONS
Students’ emotions also play an important role in influencing the quality of school food service, all of which affect the emotional responses of students. Therefore, students’ positive emotions are an important indicator for improving the quality of school food service. A national support policy is necessary for the ongoing maintenance and development of various programs that drive students' satisfaction and promote the adoption of education guidelines for school food service in China.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Analysis of hotspots and emerging trends in school foodservice research using CiteSpace
Miaomiao Li, Young Eun Lee
Nutr Res Pract. 2024;18(6):910-923. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.6.910.
Reference
-
1. Liu Y, Cheng S, Liu X, Cao X, Xue L, Liu G. Plate waste in school lunch programs in Beijing, China. Sustainability (Basel). 2016; 8:1288.2. Huang Z, Gao R, Bawuerjiang N, Zhang Y, Huang X, Cai M. Food and nutrients intake in the school lunch program among school children in Shanghai, China. Nutrients. 2017; 9:582. PMID: 28590431.3. Tang HM, Fang H, Xu HL. Diet and nutrition survey among primary and secondary school students in Minhang district of Shanghai city. Chin J Public Health. 2013; 29:1143–1146.4. Ministry of the Health People’s Republic of China. WS/T 100-1998. Amount of Nutritional Provision for School Lunch [Internet]. Beijing: Ministry of the Health People’s Republic of China;1998. cited 2021 May 10. Available from: https://www.renrendoc.com/paper/112965121.html.5. Zhai FY, Cao RX, Fu JJ, Wang ZH, Zhang LW. Current status of nutritional lunch in primary and high schools of Beijing. Can J Public Health. 2007; 1:7–12.6. Min K, Wang J, Liao W, Astell-Burt T, Feng X, Cai S, Liu Y, Zhang P, Su F, Yang K, et al. Dietary patterns and their associations with overweight/obesity among preschool children in Dongcheng district of Beijing: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2021; 21:223. PMID: 33504346.7. Zhang F, Hu X, Tian Z, Zhang Q, Ma G. Literature research of the nutrition improvement program for rural compulsory education students in China. Public Health Nutr. 2015; 18:936–943. PMID: 24866472.8. Zhou L, Wang JX, Jiang B. The impact of rural compulsory education nutrition improvement program on students’ health. Chin Rural Surv. 2021; 2:97–100.9. Liu J. Building educational community for left-behind children in rural China: a case study of a small rural school in Hubei province. Peddie F, Liu J, editors. Economics, Law, and Institutions in Asia Pacific. Singapore: Springer;2021. p. 15–39.10. Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. The nationwide school canteen rate reached 84% [Internet]. Beijing: Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China;2019. cited 2021 May 10. Available from: http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/xw_fbh/moe_2606/2019/tqh20191125/sfcl/201911/t20191125_409551.html.11. Duan JL, Pan YP, Teng LX, Zhao R, Qin Y. Nutrition quality of self-feeding lunch in the primary and secondary schools in Beijing. Chin J Sch Health. 2012; 33:651–653.12. Cheng SK, Gao LW, Xu ZR, Tang CC, Wang L, Dhruba Bijaya GC. Food waste in catering industry and its impacts on resources and environment in China. Chin Soft Sci. 2012; 7:106–114.13. Kim HC. A study on the causal model of students’ perceived service quality, affect and satisfaction in college and university foodservices. Korean J Tourism Res. 2006; 20:245–262.14. Clemes MD, Gan C, Sriwongrat C. Consumers’ choice factors of an upscale ethnic restaurant. J Food Prod Mark. 2013; 19:413–438.15. Liljander V, Strandvik T. Emotions in service satisfaction. Int J Serv Ind Manage. 1997; 8:148–169.16. Oh HM, Cho HJ, Jeong C. An effect of servicescape on emotional response and satisfaction: focusing on Incheon International Airport. J Tourism Leis Res. 2018; 30:119–141.17. Lee KA, Park SY, Lyu ES. Relationship between foodservice satisfaction and customer loyalty of university dormitory foodservice in Gyeongsangbuk-do area. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2017; 38:1271–1278.18. Jani D, Han H. Influence of environmental stimuli on hotel customer emotional loyalty response: testing the moderating effect of the big five personality factors. Int J Hospit Manag. 2015; 44:48–57.19. Moon HS. A study on the influences of restaurant choice attributes on the customers emotional response and satisfaction - focusing on the differences in types of restaurants. J Hosp Tourism Stud. 2015; 17:203–218.20. Park MH, Choi YS, Kim YJ. Comparison of dietary attitudes and attitudes to the school lunch service of elementary and middle school students living in the same region. Korean J Community Nutr. 2002; 7:3–13.21. Cha SS, Shin MH. The effect of delivery food on customer emotional response and repurchase intention. Korean J Food Health Converg. 2021; 7:1–10.22. People’s Government of Henan Province. Henan Province Information [Internet]. Zhengzhou: People’s Government of Henan Province;2018. cited 2021 May 10. Available from: https://baike.baidu.com/reference/132980/26168qZVMe8xb9sgkCMDcPtQA0GDjNhjlFAHCFJa8vBaYSwIKFi3RnlNEVLcnvWM4Ci3GFwULI5lyGOdrwcBa2zQR3LKZmi_CCQ.23. People’s Government of Henan Province. In 2019, the province’s economic operation was generally stable, with steady progress [Internet]. Zhengzhou: People’s Government of Henan Province;2020. Available from: https://baike.baidu.com/reference/132980/4093rTbyJ7jlfgmRo8wbxvoAhXnWi5hgIjYB8x6nmu3O9eLzKGgsfC7WGzxkIEi5Uum43UhNd9ZImorWYNI6eaq-T14Ez4W2sHk4zZA.24. People’s Government of Henan Province. Implementation of the pilot work of the nutrition improvement plan for rural compulsory education students in Henan Province [Internet]. Zhengzhou: People’s Government of Henan Province;2012. cited 2021 May 10. Available from: http://jyt.henan.gov.cn/2012/02-29/1654292.html.25. Din N, Rani AA, Ridzuan FHF, Zulkifli CN, Tarmizi SAA, Ghazali N, Abdullah D, Kamal SBM. Gauging students’ perception and attitudes towards Halal products and logos. Radzi SM, Mohd Hanafiah MH, Sumarjan N, Mohi Z, Sukyadi D, Suryadi K, Purnawarman P, editors. Heritage, Culture and Society: Research Agenda and Best Practices in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry. London: CRC Press;2016. p. 729–733.26. Abdullah D, Hamir N, Nor NM, Krishnaswamy J, Rostum AMM. Food quality, service quality, price fairness and restaurant re-patronage intention: the mediating role of customer satisfaction. Int J Acad Res Bus Soc Sci. 2018; 8:211–226.27. Krishna M, Lim EC, Ooi CY, Ooi SY, Ooi YW, Tan MW. Customer loyalty to newly opened cafés and restaurants in Malaysia. J Foodserv Bus Res. 2017; 20:525–541.28. Park SH. The effects of school feeding service quality on students’ practice and satisfaction of school feeding - focusing on high school students in Daegu. Korean J Tourism Res. 2015; 29:69–82.29. Lee JU, Lee YK, Ahn SM. Effects of experiential value and emotional responses on brand satisfaction and brand loyalty in the family restaurant context. Food Serv Ind J. 2017; 13:123–140.30. Kim WG, Lee YK, Yoo YJ. Predictors of relationship quality and relationship outcomes in luxury restaurants. J Hosp Tour Res (Wash DC). 2006; 30:143–169.31. Kamal S, Bukhari N, Abdullah D, Din N. Tourists’ satisfaction and loyalty towards food tourism in Georgetown, Penang. Radzi SM, Mohd Hanafiah MH, Sumarjan N, Mohi Z, Sukyadi D, Suryadi K, Purnawarman P, editors. Heritage, Culture and Society: Research Agenda and Best Practices in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry. London: CRC Press;2016. p. 393.32. Leninkumar V. The relationship between customer satisfaction and customer trust on customer loyalty. Int J Acad Res Bus Soc Sci. 2017; 7:450–465.33. Lee YC, Ahn SH. The influence of foodservice servicescape on customers’ emotional reaction and behavioral intention. J Foodserv Manag. 2016; 19:61–78.34. Kim YK. A study on the relationship between physical servicescape and social servicescape, positive emotion of customer and satisfaction in coffee shop. J Foodserv Manag. 2017; 20:25–55.35. Jung MW, Son ES, Lee JH. Effects of coffee shop servicescape on the emotional reaction and behavioral intention of customers and the moderating effect of background music. J Hosp Tour Res (Wash DC). 2016; 40:69–86.36. Moon HS. A study on the Influences of restaurant choice attributes on the customers’ emotional response and satisfaction - Focusing on the differences in types of restaurants. J Hosp Tour Res (Wash DC). 2015; 17:203–218.37. Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. Structural equation modeling in practice: a review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol Bull. 1988; 103:411–423.38. Kline RB. Software review: Software programs for structural equation modeling: AMOS, EQS, and LISREL. J Psychoed Assess. 1998; 16:343–364.39. Lee SY. A study on effect of customer emotion and satisfaction by hotel employee’s nonverbal communication. J Hotel Resort. 2011; 10:139–150.40. Lee JR, Yoo D, Lee YK. The effect of web interactivity of e-brand on relationship quality and customer loyalty. J Korean Oper Res Manag Sci Soc. 2004; 29:73–93.41. Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986; 51:1173–1182. PMID: 3806354.42. Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 2004; 36:717–731. PMID: 15641418.43. Heo J. Heo Jun’s Easily Follow to Structural Equation Modeling MOS. Seoul: Hanara Publishing;2013. p. 104–111.44. Yim HR, Kim HS. A study on the quality and image of school meal service and student satisfaction with the service: focused on moderating effect of distribution types. Korean J Culinary Res. 2013; 11:11–22.45. Park JE, Choi KS. Improving perception and satisfaction on middle and high school foodservice: the role of student participation program in serving school meals. Korean J Community Nutr. 2018; 23:243–256.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence, Occupational WellBeing, and Work Engagement Among Chinese Clinical Nurses
- The Effects of Customer Expectations & Satisfaction on Customer Loyalty in Restaurants
- Relationship among Nursing Service Quality, Medical Service Satisfaction, and Hospital Revisit Intent
- Identifying the Quality Attributes Affecting Customer Satisfaction of School Foodservice by City and Province: Students, Parents, and Faculty
- The Improvement of Hospital Food Service in Quality and Customer Satisfaction by Using 6-sigma Strategy