Korean J Pain.
2023 Apr;36(2):230-241. 10.3344/kjp.22336.
Prevalence of chronic pain and contributing factors: a cross-sectional population-based study among 2,379 Iranian adolescents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Community Based Psychiatric Care Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
- 2Nursing Department, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
- KMID: 2541031
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.22336
Abstract
- Background
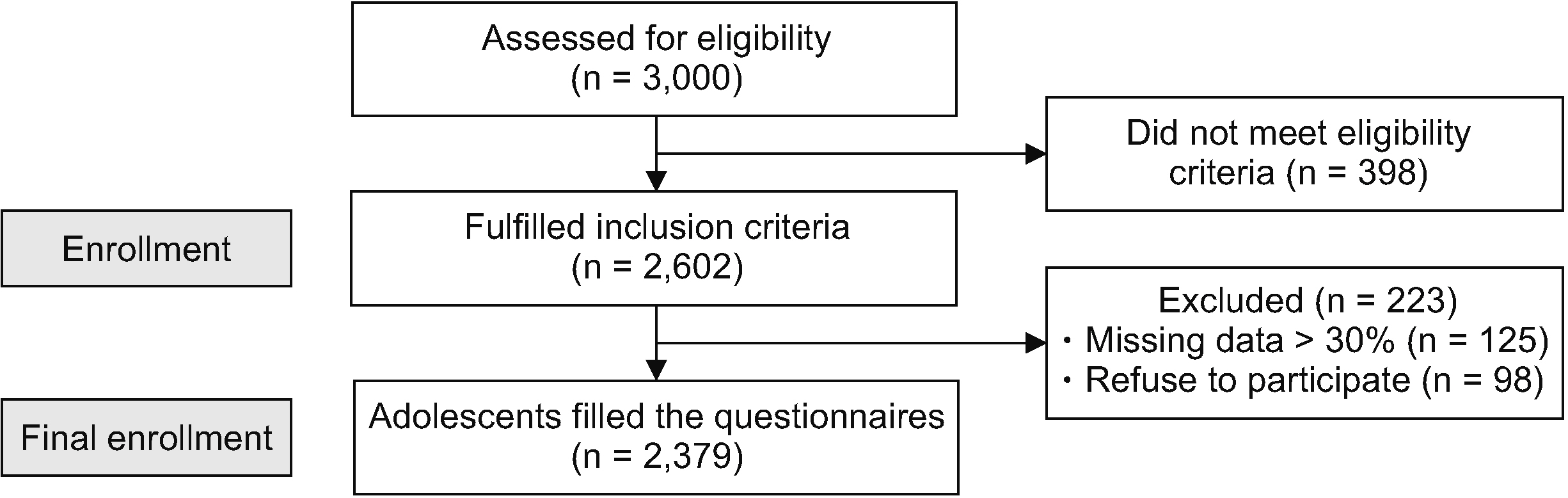
This study aimed to determine the prevalence of chronic pain and its contributing factors among teenagers aged 12–21 years in Shiraz, Iran.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted on adolescents aged 12–21 years. Demographic variables of the adolescents and their parents as well as the pain characteristics were assessed. Descriptive statistics, multinomial logistic regression, and regression models were used to describe the characteristics of the pain and its predictive factors.
Results
The prevalence of chronic pain was 23.7%. The results revealed no significant difference between the male and female participants regarding the pain characteristics, except for the home medications used for pain relief. The results of a chi-square test showed that the mother’s pain, education, and occupation, and the father’s education were associated significantly with chronic pain in adolescents (P < 0.05). Multinomial logistic regression also showed the mother’s history of pain played a significant role in the incidence of adolescents’ chronic pain.
Conclusions
The prevalence of chronic pain was relatively high in these adolescents. The results also provided basic and essential information about the contributing factors in this area. However, consideration of factors such as anxiety, depression, school problems, sleep, and physical activity are suggested in future longitudinal studies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Treede RD, Rief W, Barke A, Aziz Q, Bennett MI, Benoliel R, et al. 2015; A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain. 156:1003–7. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000160. PMID: 25844555. PMCID: PMC4450869.2. Groenewald CB, Palermo TM. 2015; The price of pain: the economics of chronic adolescent pain. Pain Manag. 5:61–4. DOI: 10.2217/pmt.14.52. PMID: 25806898. PMCID: PMC4562402.3. Luntamo T, Sourander A, Rihko M, Aromaa M, Helenius H, Koskelainen M, et al. 2012; Psychosocial determinants of headache, abdominal pain, and sleep problems in a community sample of Finnish adolescents. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 21:301–13. DOI: 10.1007/s00787-012-0261-1. PMID: 22350133.4. Dobe M, Zernikow B. 2019. Practical treatment options for chronic pain in children and adolescents: an interdisciplinary therapy manual. 2nd ed. Springer;Cham: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-19201-3. PMCID: PMC6619685.5. Swain MS, Henschke N, Kamper SJ, Gobina I, Ottová-Jordan V, Maher CG. 2014; An international survey of pain in adolescents. BMC Public Health. 14:447. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-447. PMID: 24885027. PMCID: PMC4046513.6. Alotaibi K, Higgins I, Day J, Chan S. 2018; Paediatric pain management: knowledge, attitudes, barriers and facilitators among nurses - integrative review. Int Nurs Rev. 65:524–33. DOI: 10.1111/inr.12465. PMID: 29956310.7. Agyemang JB, Diji AKA, Afaya RA, Boakye H, Oduro E, Amagyei A, et al. 2020; Nursing and midwifery students' knowledge and attitudes regarding children's pain. J Res Dev Nurs Midwifery. 17:7–10. DOI: 10.52547/jgbfnm.17.2.7.8. World Health Organization. 2020. Guidelines on the management of chronic pain in children. WHO;Geneva: DOI: 10.1891/9780826153425.0003b.9. Hurley-Wallace A, Wood C, Franck LS, Howard RF, Liossi C. 2019; Paediatric pain education for health care professionals. Pain Rep. 4:e701. DOI: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000701. PMID: 30801042. PMCID: PMC6370141. PMID: f6f8042eb4ef45958d6a65bda5b8d952.10. Walther-Larsen S, Aagaard GB, Friis SM, Petersen T, Møller-Sonnergaard J, Rømsing J. 2016; Structured intervention for management of pain following day surgery in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 26:151–7. DOI: 10.1111/pan.12811. PMID: 26559643.11. Faccioli SC, Tacla MTGM, Rossetto EG, Collet N. 2020; The management of pediatric pain and the perception of the nursing team in light of the Social Communication Model of Pain. Braz J Pain. 3:37–41. DOI: 10.5935/2595-0118.20200009.12. Abazari P, Namnabati M. 2017; Nurses' experiences from pain management in children in Iranian culture: a phenomenology study. J Educ Health Promot. 6:74. DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1_16. PMID: 28852664. PMCID: PMC5561679.13. Wrona S, Czarnecki ML. 2021; Pediatric pain management - an individualized, multimodal, and interprofessional approach is key for success. Am Nurse J. 16:6–13.14. Leseman PP. 2020; The power of ethnotheories in changing societies: commentary on cross-cultural research on parents: applications to the care and education of children. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2020:195–200. DOI: 10.1002/cad.20342. PMID: 32463552. PMCID: PMC7383620.15. Skrove M, Romundstad P, Indredavik MS. 2015; Chronic multisite pain in adolescent girls and boys with emotional and behavioral problems: the Young-HUNT study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 24:503–15. DOI: 10.1007/s00787-014-0601-4. PMID: 25138145.16. Donnelly TJ, Palermo TM, Newton-John TR. 2020; Parent cognitive, behavioural, and affective factors and their relation to child pain and functioning in pediatric chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. 161:1401–19. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001833. PMID: 32132395.17. Hechler T, Vervoort T, Hamann M, Tietze AL, Vocks S, Goubert L, et al. 2011; Parental catastrophizing about their child's chronic pain: are mothers and fathers different? Eur J Pain. 15:515.e1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.09.015. PMID: 20971665.18. Hoftun GB, Romundstad PR, Rygg M. 2012; Factors associated with adolescent chronic non-specific pain, chronic multisite pain, and chronic pain with high disability:. the Young-HUNT Study 2008. J Pain. 13:874–83. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.06.001. PMID: 22832694.19. Gheysvandi E, Dianat I, Heidarimoghadam R, Tapak L, Karimi-Shahanjarini A, Rezapur-Shahkolai F. 2019; Neck and shoulder pain among elementary school students: prevalence and its risk factors. BMC Public Health. 19:1299. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-7706-0. PMID: 31619204. PMCID: PMC6796365. PMID: 02944983684643e38bcca678b5309003.20. Kazemi S. 2020; The prevalence and risk factors of low back pain in children and adolescents in Iran: a systematic review. Int J Musculoskelet Pain Prev. 5:301–9. DOI: 10.52547/ijmpp.5.1.301.21. Shaygan M, Karami Z. 2020; Chronic pain in adolescents: the predictive role of emotional intelligence, self-esteem and parenting style. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 8:253–63. DOI: 10.30476/ijcbnm.2020.83153.1129. PMID: 32656277. PMCID: PMC7334746. PMID: ab5382375d574c35995c1a010003ed95.22. Gobina I, Villberg J, Välimaa R, Tynjälä J, Whitehead R, Cosma A, et al. 2019; Prevalence of self-reported chronic pain among adolescents: evidence from 42 countries and regions. Eur J Pain. 23:316–26. DOI: 10.1002/ejp.1306. PMID: 30098106.23. Klinger R, Hasenbring M, Pfingsten M. Klinger R, Hasenbring M, Pfingsten M, editors. 2019. The multiaxial classification of pain: psychosocial dimension (MACPainP). MACPainP multiaxial classification of pain psychosocial dimension: systematic approach to classify biopsychosocial aspects of pain disorders. Springer;Cham: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-00425-5.24. Beitel M, Stults-Kolehmainen M, Cutter CJ, Schottenfeld RS, Eggert K, Madden LM, et al. 2016; Physical activity, psychiatric distress, and interest in exercise group participation among individuals seeking methadone maintenance treatment with and without chronic pain. Am J Addict. 25:125–31. DOI: 10.1111/ajad.12336. PMID: 26824197.25. Hairi NN, Cumming RG, Blyth FM, Naganathan V. 2013; Chronic pain, impact of pain and pain severity with physical disability in older people--is there a gender difference? Maturitas. 74:68–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2012.10.001. PMID: 23103063.26. Rutherford C, Nixon JE, Brown JM, Briggs M, Horton M. 2016; The Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs Scale (LANSS) is not an adequate outcome measure of pressure ulcer-related neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain. 20:1710–20. DOI: 10.1002/ejp.894. PMID: 27172978.27. VanDenKerkhof EG, Mann EG, Torrance N, Smith BH, Johnson A, Gilron I. 2016; An epidemiological study of neuropathic pain symptoms in Canadian adults. Pain Res Manag. 2016:9815750. DOI: 10.1155/2016/9815750. PMID: 27445636. PMCID: PMC4904601. PMID: 70f3a1682a6c497eb00a27012a29bfd0.28. Akbari-Chehrehbargh Z, Tavafian SS, Montazeri A. 2018; Assessing back pain, healthy back behavior and its cognitive determinants among pupils in Iran. Int J Musculoskelet Pain Prev. 3:114–21.29. Hatefi M, Abdi A, Tarjoman A, Borji M. 2019; Investigating the prevalence of musculoskeletal pain among Iranian children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pediatr Rev. 7:191–8. DOI: 10.32598/jpr.7.4.191.30. Dianat I, Alipour A, Jafarabadi MA. 2017; Prevalence and risk factors of low back pain among school age children in Iran. Health Promot Perspect. 7:223–9. DOI: 10.15171/hpp.2017.39. PMID: 29085800. PMCID: PMC5647358. PMID: bf2c83c1dbef44778cdb246a74750c90.31. Haraldstad K, Sørum R, Eide H, Natvig GK, Helseth S. 2011; Pain in children and adolescents: prevalence, impact on daily life, and parents' perception, a school survey. Scand J Caring Sci. 25:27–36. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2010.00785.x. PMID: 20409061.32. Wager J, Brown D, Kupitz A, Rosenthal N, Zernikow B. 2020; Prevalence and associated psychosocial and health factors of chronic pain in adolescents: differences by sex and age. Eur J Pain. 24:761–72. DOI: 10.1002/ejp.1526. PMID: 31889351.33. Zhang Y, Deng G, Zhang Z, Zhou Q, Gao X, Di L, et al. 2015; A cross sectional study between the prevalence of chronic pain and academic pressure in adolescents in China (Shanghai). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 16:219. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-015-0625-z. PMID: 26296558. PMCID: PMC4546215.34. Pollock CM, Harries RL, Smith AJ, Straker LM, Kendall GE, O'Sullivan PB. 2011; Neck/shoulder pain is more strongly related to depressed mood in adolescent girls than in boys. Man Ther. 16:246–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.math.2010.10.010. PMID: 21094075.35. Widmalm SE, McKay DC, Radke JC, Zhang Y, Wang X, Wang M. 2013; Gender differences in low and high pain palpation thresholds in the TMJ and neck areas. Cranio. 31:92–9. Erratum in: Cranio 2013; 31: A-5. DOI: 10.1179/crn.2013.016. PMID: 23795398.36. Shaygan M, Jaberi A. 2021; The effect of a smartphone-based pain management application on pain intensity and quality of life in adolescents with chronic pain. Sci Rep. 11:6588. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86156-8. PMID: 33758322. PMCID: PMC7988051. PMID: 460a7679b19a45418fc406ca5c91d8ea.37. Rezapur-Shahkolai F, Gheysvandi E, Tapak L, Dianat I, Karimi-Shahanjarini A, Heidarimoghadam R. 2020; Risk factors for low back pain among elementary school students in western Iran using penalized logistic regression. Epidemiol Health. 42:e2020039. DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2020039. PMID: 32512660. PMCID: PMC7871161.38. Lynch-Jordan AM, Kashikar-Zuck S, Szabova A, Goldschneider KR. 2013; The interplay of parent and adolescent catastrophizing and its impact on adolescents' pain, functioning, and pain behavior. Clin J Pain. 29:681–8. DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3182757720. PMID: 23370064. PMCID: PMC3730260.39. Logan DE, Simons LE, Carpino EA. 2012; Too sick for school? Parent influences on school functioning among children with chronic pain. Pain. 153:437–43. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.11.004. PMID: 22169177. PMCID: PMC3884564.40. Vervoort T, Huguet A, Verhoeven K, Goubert L. 2011; Mothers' and fathers' responses to their child's pain moderate the relationship between the child's pain catastrophizing and disability. Pain. 152:786–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.12.010. PMID: 21272996.41. Stevens BJ, Hathway G, Zempsky WT. 2021. Oxford textbook of pediatric pain. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press;Oxford: DOI: 10.1093/med/9780198818762.001.0001.42. Boerner KE, Chambers CT, McGrath PJ, LoLordo V, Uher R. 2017; The effect of parental modeling on child pain responses: the role of parent and child sex. J Pain. 18:702–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2017.01.007. PMID: 28161474.43. Welkom JS, Hwang WT, Guite JW. 2013; Adolescent pain catastrophizing mediates the relationship between protective parental responses to pain and disability over time. J Pediatr Psychol. 38:541–50. DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jst011. PMID: 23471361. PMCID: PMC3666120.44. Sieberg CB, Williams S, Simons LE. 2011; Do parent protective responses mediate the relation between parent distress and child functional disability among children with chronic pain? J Pediatr Psychol. 36:1043–51. DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsr043. PMID: 21742755.45. Hoftun GB, Romundstad PR, Rygg M. 2013; Association of parental chronic pain with chronic pain in the adolescent and young adult: family linkage data from the HUNT Study. JAMA Pediatr. 167:61–9. DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2013.422. PMID: 23403843.46. Palermo TM, Valrie CR, Karlson CW. 2014; Family and parent influences on pediatric chronic pain: a developmental perspective. Am Psychol. 69:142–52. DOI: 10.1037/a0035216. PMID: 24547800. PMCID: PMC4056332.47. Grimby-Ekman A, Åberg M, Torén K, Brisman J, Hagberg M, Kim JL. 2018; Pain could negatively affect school grades - Swedish middle school students with low school grades most affected. PLoS One. 13:e0208435. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208435. PMID: 30521591. PMCID: PMC6283606. PMID: 3097a13770f04a538f0ce630eff06e92.48. Kosola S, Mundy LK, Sawyer SM, Canterford L, van der Windt DA, Dunn KM, et al. 2017; Pain and learning in primary school: a population-based study. Pain. 158:1825–30. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000984. PMID: 28738407.49. Tegethoff M, Belardi A, Stalujanis E, Meinlschmidt G. 2015; Comorbidity of mental disorders and chronic pain: chronology of onset in adolescents of a national representative cohort. J Pain. 16:1054–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.06.009. PMID: 26168877.50. Koh MJ, Park SY, Woo YS, Kang SH, Park SH, Chun HJ, et al. 2012; Assessing the prevalence of recurrent neck and shoulder pain in Korean high school male students: a cross-sectional observational study. Korean J Pain. 25:161–7. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.3.161. PMID: 22787546. PMCID: PMC3389320.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Risk Factors of Suicidal Ideation according to Age Groups among the Adolescents in Korea
- Thoracic Kyphosis and Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Male Adolescents
- Decomposing gender disparity in total physical activity among Iranian adults
- Trends in Allergic Sensitization and Diseases in the Korean General Population Over a 9-Year Period
- Suicidal Thinking Among Patients With Spinal Conditions in South Korea: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study