Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Mar;56(1):1-8. 10.5115/acb.22.166.
Anatomy acts concerning body and organ donations across the globe: past, present and future with a special emphasis on the indian scenario
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
- KMID: 2540978
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.166
Abstract
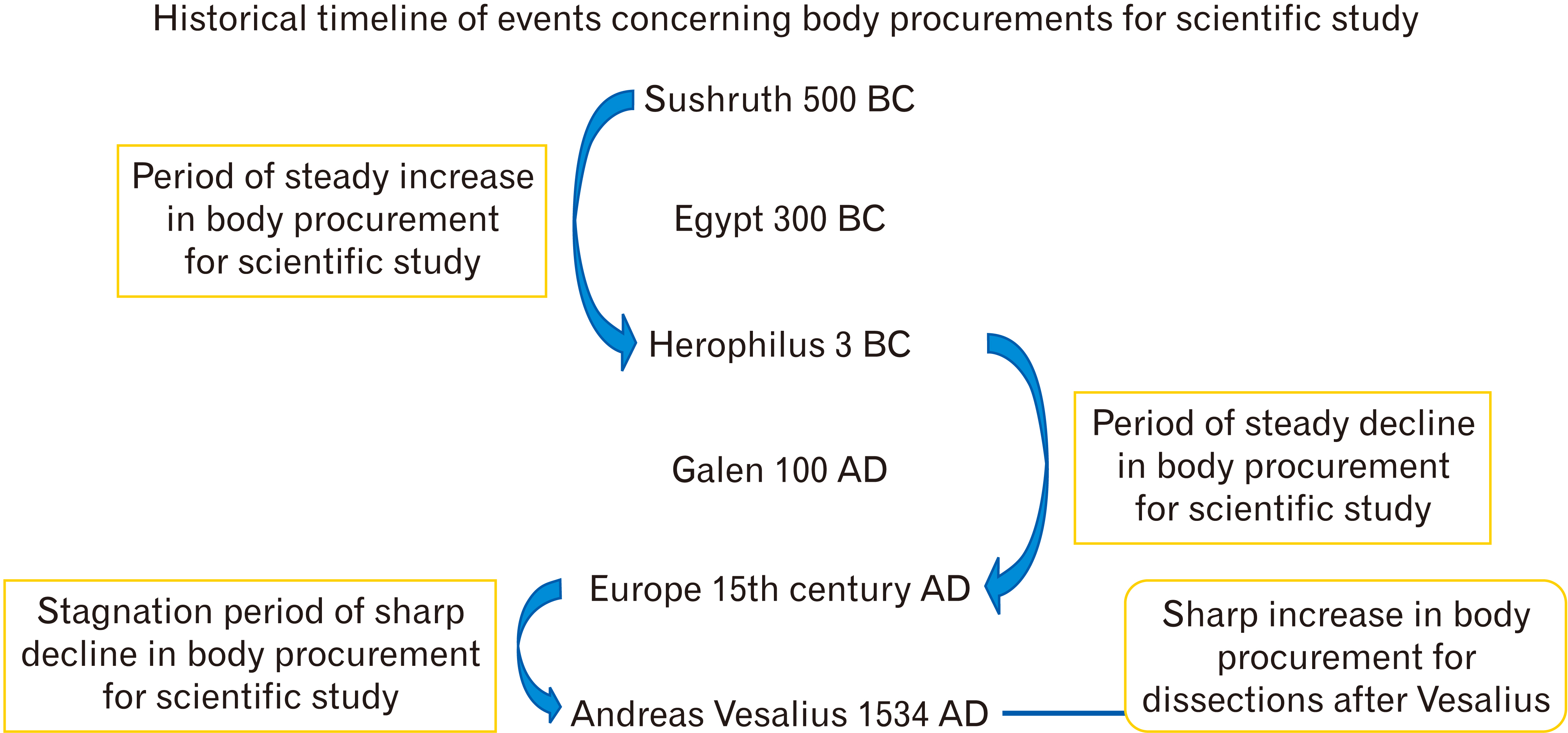
- From the era of pre-historic times, the ancient Indians and the Greeks highlighted the importance of body and organ donations thereby emphasizing the need for anatomical sciences in medicine through the use of effective dissections for the same. However, after the Renaissance, there was a surge in dissections throughout the world, particularly in Europe, as a result of which various laws were enacted by governments concerning the procurement of bodies for the purpose of scientific dissections, which were later promulgated throughout the world through various anatomical acts. The situation in India was quite similar to that of Britain until its independence in 1947, after which different Indian states formulated their own anatomy acts that had their own merits and pitfalls. Hence, this literature review serves to highlight the various acts throughout history and would serve as a guide to emphasize the future perspectives of formulating a centralized unified anatomy act for the Indian nation that could possibly be the need of the hour.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Narayana A. 1995; Medical science in ancient Indian culture with special reference to Atharvaveda. Bull Indian Inst Hist Med Hyderabad. 25:100–10. PMID: 11618829. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0029420793&origin=inward.2. Mitra J. 1995; Glimpses of the advancement of medical science as depicted in the Mahäbhärata. Bull Indian Inst Hist Med Hyderabad. 25:20–37. PMID: 11618838. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0029420179&origin=inward.3. Prasad PV. 2000; Atharvaveda and its materia medica. Bull Indian Inst Hist Med Hyderabad. 30:83–92. PMID: 12577897.4. Mukherjee PK, Nema NK, Venkatesh P, Debnath PK. 2012; Changing scenario for promotion and development of Ayurveda--way forward. J Ethnopharmacol. 143:424–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.036. PMID: 22885133.5. Magee R. 2001; Art macabre: resurrectionists and anatomists. ANZ J Surg. 71:377–80. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.2001.02127.x. PMID: 11409024.
Article6. Ghosh SK. 2015; Human cadaveric dissection: a historical account from ancient Greece to the modern era. Anat Cell Biol. 48:153–69. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2015.48.3.153. PMID: 26417475. PMCID: PMC4582158.
Article7. Yammine K. 2014; The current status of anatomy knowledge: where are we now? Where do we need to go and how do we get there? Teach Learn Med. 26:184–8. DOI: 10.1080/10401334.2014.883985. PMID: 24702556.
Article8. Tamuli RP, Sarmah S, Saikia B. 2019; Organ donation - "attitude and awareness among undergraduates and postgraduates of North-East India". J Family Med Prim Care. 8:130–6. DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_206_18. PMID: 30911493. PMCID: PMC6396593.
Article9. Sahu SK, Rath B, Rath S, Panigrahi S. 2017; Knowledge and attitude of educated people towards organ and body donation: a cross-sectional study in Southern Odisha. Sch J Appl Med Sci. 5:2456–62.10. Bharambe V, Puranam V, Manvikar PR, Bajpayee P. 2019; Anatomy acts in India: a review. Eur J Anat. 23:469–77.11. Habbal O. 2017; The science of anatomy: a historical timeline. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 17:e18–22. DOI: 10.18295/squmj.2016.17.01.004. PMID: 28417023. PMCID: PMC5380415.
Article12. Lalwani R, Kotgirwar S, Athavale SA. 2020; Changing medical education scenario: a wakeup call for reforms in Anatomy Act. BMC Med Ethics. 21:63. DOI: 10.1186/s12910-020-00507-0. PMID: 32711534. PMCID: PMC7382862. PMID: cacbbe7b1a9e42c7bf84e8bdbeab243d.
Article13. Dope SA, Bhusari PA, Kulkarni PR, Diwan CV. 2015; Body donation-the life after death. MedPulse. 2:216–20.14. 2013. Guidelines for cadaver and whole body deceased donation, 2014. No. 14/02/Misc/H & FW/2013/8110-20(5.9.14) [Internet]. Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi;New Delhi: Available from: https://dshm.delhi.gov.in/mis/(S(mr4go54ormtlapcdwm1vhxux))/orders/Guidelines_for_cadaver.pdf. cited 2014 Jan 18.15. 2005. Rules and Regulation for transfer of cadaver from one college to another Medical College, 2005. No. 183/MSF/2005/17.09.2005. Government of Karnataka;Karnataka:16. Ajita R, Singh YI. 2007; Body donation and its relevance in anatomy learning: a review. J Anat Soc India. 56:44–7.17. FICEM Federative International Committee for Ethics and Medical Humanities of the International Federation of Associations of anatomists (IFAA). 2012; Recommendations of good practice for the donation and study of human bodies and tissues for anatomical examination. Plexus. 2012:4–5.18. Champney TH, Hildebrandt S, Gareth Jones D, Winkelmann A. 2019; Bodies R US: ethical views on the commercialization of the dead in medical education and research. Anat Sci Educ. 12:317–25. DOI: 10.1002/ase.1809. PMID: 30240149.
Article19. 1957. The Uttar Pradesh anatomy act, 1956. Act no. 6 of 1957. The Uttar Pradesh Gazette, Extraordinary;Uttar Pradesh: DOI: 10.1002/ase.1809.20. c2011. The Gujarat anatomy act, 2011. Act no. 10 of 2011. The Gujarat Government Gazette [Internet]. Government of Gujarat;Gujarat: Available from: https://www.indiacode.nic.in/bitstream/123456789/6148/1/gaz.ex-iv-10_dt.11-4-2011vd.pdf. cited 2014 Jan 23.21. Jones DG, Whitaker MI. 2012; Anatomy's use of unclaimed bodies: reasons against continued dependence on an ethically dubious practice. Clin Anat. 25:246–54. DOI: 10.1002/ca.21223. PMID: 21800367.22. Bøgh L, Madsen M. 2005; Attitudes, knowledge, and proficiency in relation to organ donation: a questionnaire-based analysis in donor hospitals in northern Denmark. Transplant Proc. 37:3256–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.09.063. PMID: 16298563.
Article23. Winkelmann A, Güldner FH. 2004; Cadavers as teachers: the dissecting room experience in Thailand. BMJ. 329:1455–7. Erratum in: BMJ 2005;330:82. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.329.7480.1455. PMID: 15604182. PMCID: PMC535977.
Article24. Park JT, Jang Y, Park MS, Pae C, Park J, Hu KS, Park JS, Han SH, Koh KS, Kim HJ. 2011; The trend of body donation for education based on Korean social and religious culture. Anat Sci Educ. 4:33–8. DOI: 10.1002/ase.198. PMID: 21265035.
Article25. Sehirli US, Saka E, Sarikaya O. 2004; Attitudes of Turkish anatomists toward cadaver donation. Clin Anat. 17:677–81. DOI: 10.1002/ca.20056. PMID: 15495167.
Article26. Conesa C, Ríos A, Ramírez P, del Mar Rodríguez M, Rivas P, Parrilla P. 2004; Socio-personal factors influencing public attitude towards living donation in south-eastern Spain. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 19:2874–82. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfh466. PMID: 15316100.
Article27. Karau PB, Wamachi A, Ndede K, Mwamisi J, Ndege P. 2014; Perception to cadaver dissection and views on anatomy as a subject between two pioneer cohorts in a Kenyan Medical School. Anat J Afr. 3:318–23.28. Manzanares-Céspedes MC, Dalmau-Pastor M, Simon de Blas C, Vázquez-Osorio MT. 2021; Body donation, teaching, and research in dissection rooms in Spain in times of COVID-19. Anat Sci Educ. 14:562–71. DOI: 10.1002/ase.2093. PMID: 33891806. PMCID: PMC8250704.
Article29. Park HJ, Ahn H, Ki E, Lee JS, Choi Y, Hu KS, Chun YM, Kim HJ. 2021; Body donation trends in Yonsei University: a statistical analysis of donor records. Anat Cell Biol. 54:59–64. DOI: 10.5115/acb.20.261. PMID: 33424016. PMCID: PMC8017449.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Willingness and attitude of the Arab world population towards solid organ
- Intraoral HIV-associated Burkitt's lymphoma: a rare case report with special emphasis on differential diagnosis
- Cases of inadequate donation in the operating room
- Effects of the register to become an organ donor on the organ donation agreement rate
- Vision of Thyroid Surgery: Past, Present and Future