Kosin Med J.
2023 Mar;38(1):36-42. 10.7180/kmj.22.137.
Comparison of circuit patency and exchange rates between the original and generic versions of nafamostat mesylate in critically ill adults receiving continuous renal replacement therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Renal, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Transplantation Research Institute, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2540760
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.22.137
Abstract
- Background
Nafamostat mesylate is widely used as an anticoagulant in continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). The generic versions of nafamostat mesylate have identical main components to the original product. However, it is questionable whether the generic versions have the same efficacy as the original. Therefore, we compared the circuit patency and exchange rates of the original nafamostat mesylate and a generic version to determine which is more efficient as an anticoagulant in CRRT.
Methods
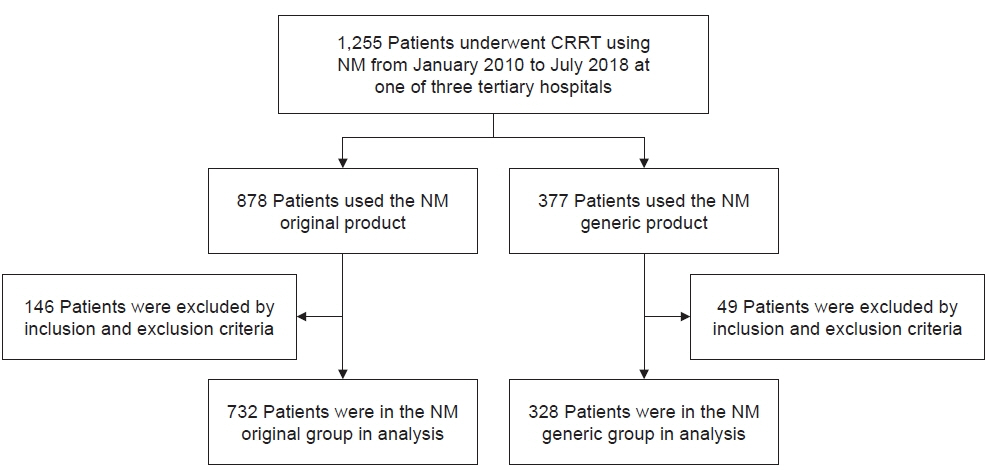
This retrospective study enrolled 1,255 patients hospitalized to receive CRRT who received the original version of nafamostat mesylate or a generic version between January 2010 and July 2018. We evaluated the filter lifespan, number of filters used per day, mean blood flow, and transmembrane pressure (TMP).
Results
The mean filter lifespan was 36.3±15.1 hours in the original product group and 22.2±16.2 hours in the generic product group, which was not a statistically significant difference (p=0.060). The mean TMP was 62.2±47.3 mmHg in the original product group and 74.5±45.6 mmHg in the generic product group (p=0.045).
Conclusions
This retrospective study suggests no meaningful difference in filter lifespan between the original and generic versions of nafamostat mesylate. However, TMP was lower in the original product group than in the generic product group.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Choi JY, Kang YJ, Jang HM, Jung HY, Cho JH, Park SH, et al. Nafamostat mesilate as an anticoagulant during continuous renal replacement therapy in patients with high bleeding risk: a randomized clinical trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e2392.2. Kim SY, Kim YN, Shin HS, Jung Y, Rim H. The influence of hypophosphatemia on outcomes of low- and high-intensity continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2017; 36:240–9.3. Legrand M, Tolwani A. Anticoagulation strategies in continuous renal replacement therapy. Semin Dial. 2021; 34:416–22.4. Brandenburger T, Dimski T, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D. Renal replacement therapy and anticoagulation. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017; 31:387–401.5. Raina R, Chakraborty R, Davenport A, Brophy P, Sethi S, McCulloch M, et al. Anticoagulation in patients with acute kidney injury undergoing kidney replacement therapy. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37:2303–30.6. Lee YK, Lee HW, Choi KH, Kim BS. Ability of nafamostat mesilate to prolong filter patency during continuous renal replacement therapy in patients at high risk of bleeding: a randomized controlled study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e108737.7. Zarbock A, Kullmar M, Kindgen-Milles D, Wempe C, Gerss J, Brandenburger T, et al. Effect of regional citrate anticoagulation vs systemic heparin anticoagulation during continuous kidney replacement therapy on dialysis filter life span and mortality among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020; 324:1629–39.8. Michel T, Ksouri H, Schneider AG. Continuous renal replacement therapy: understanding circuit hemodynamics to improve therapy adequacy. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018; 24:455–62.9. Razavi SA, Still MD, White SJ, Buchman TG, Connor MJ Jr. Comparison of circuit patency and exchange rates between 2 different continuous renal replacement therapy machines. J Crit Care. 2014; 29:272–7.10. Niwa H, Hashiba E, Ohkawa H. Comparative investigation on original product and generic version of nafamostat mesilate as an anticoagulant for continuous hemodiafiltration. Jap J Intensive Care Med 2009;33:575-9.11. Sansom B, Sriram S, Presneill J, Bellomo R. Circuit hemodynamics and circuit failure during continuous renal replacement therapy. Crit Care Med. 2019; 47:e872–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regional Citrate Anticoagulation in Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration: Report of Two Cases
- Vancomycin Dosing in Critically Ill Patients Receiving Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
- The role of nafamostat mesylate anticoagulation in continuous kidney replacement therapy for critically ill patients with bleeding tendencies: a retrospective study on patient outcomes and safety
- Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Children
- Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Pediatrics