J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2023 Mar;27(1):17-23. 10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.1.17.
Toe-in Gait, Associated Complications, and Available Conservative Treatments: A Systematic Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthotics and Prosthetics, Faculty of Rehabilitation, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
- KMID: 2540402
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.1.17
Abstract
- Purpose
Toe-in gait is defined as a style of walking in which the foot turns inward. It may be caused by an increase in femoral bone anteversion, tibia torsion, and metatarsus adductus. There are some conservative treatment approaches used to correct this condition. This review aimed to determine the effects of the toe-in gait on joint loading, kinematics, and kinetic parameters while walking. Moreover, it sought to determine the efficiency of various conservative treatments used to correct the condition.
Materials and Methods
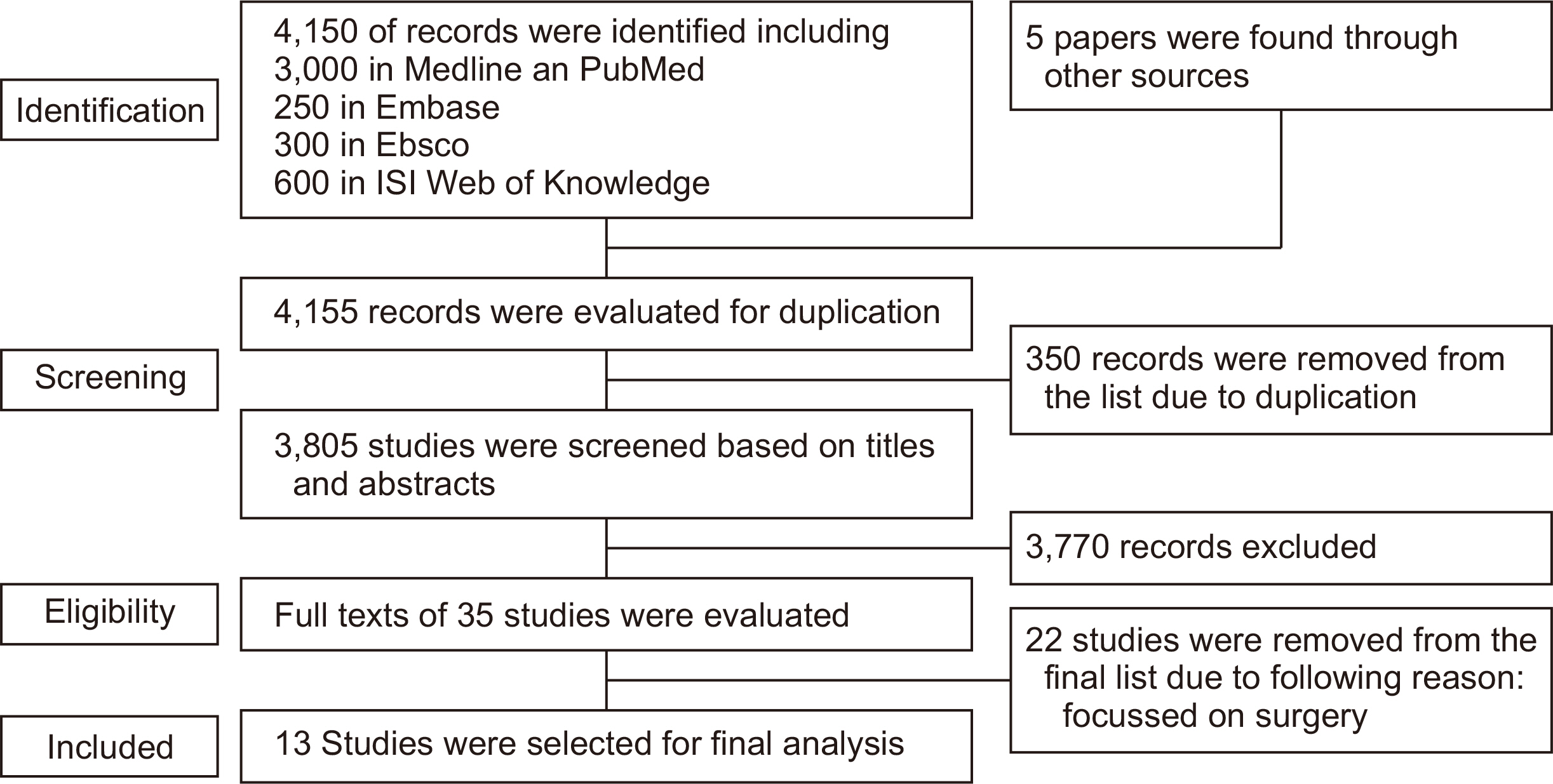
A literature search was conducted in the following databases: PubMed, Institute for Scientific Information (ISI), Web of Science database, EBSCO, and Embase, using the following keywords in toe, toe-in, toeing, in-toe, pigeon toe, and conservative treatment published between 1950 and 2021. The quality of the studies was evaluated using the Down and Black tool.
Results
A total of 13 papers on the impact of toe-in gait on joint contact force, kinematics, kinetic parameters, and conservative approaches to management were found. The quality of the studies varied between a score of 11 and 22. The toe-in gait influences the joint contact forces and kinematics of the joints, especially the hip and pelvis. The effects of conservative treatment on the toe-in gait appear to be controversial.
Conclusion
As the toe-in gait influences the joint contact force, it may increase the incidence of degenerative joint diseases. Therefore, treatment is recommended. However, there is no strong evidence on the efficacy of conservative treatments, and there are no recommendations for the use of these treatments in subjects with toe-in gait.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Staheli LT, Corbett M, Wyss C, King H. 1985; Lower-extremity rotational problems in children. Normal values to guide management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 67:39–47. doi: 10.2106/00004623-198567010-00006. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-198567010-00006.
Article2. Sass P, Hassan G. 2003; Lower extremity abnormalities in children. Am Fam Physician. 68:461–8. Erratum in: Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:1049.3. Yeo A, James K, Ramachandran M. 2015; Normal lower limb variants in children. BMJ. 350:h3394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h3394. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.h3394. PMID: 26152216.
Article4. Nourai MH, Fadaei B, Rizi AM. 2015; In-toeing and out-toeing gait conservative treatment; hip anteversion and retroversion: 10-year follow-up. J Res Med Sci. 20:1084–7. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.172833. DOI: 10.4103/1735-1995.172833. PMID: 26941813. PMCID: PMC4755096.
Article5. Kamegaya M, Shinohara Y. 2002; Gait disorders and leg deformities in children. J Orthop Sci. 7:154–9. doi: 10.1007/s776-002-8439-9. DOI: 10.1007/s776-002-8439-9. PMID: 11819150.
Article6. Blackmur JP, Murray AW. 2010; Do children who in-toe need to be referred to an orthopaedic clinic? J Pediatr Orthop B. 19:415–7. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0b013e3283339067. DOI: 10.1097/BPB.0b013e3283339067. PMID: 20520580.
Article7. Naqvi G, Stohr K, Rehm A. 2017; Proximal femoral derotation osteotomy for idiopathic excessive femoral anteversion and intoeing gait. SICOT J. 3:49. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2017033. DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017033. PMID: 28675371. PMCID: PMC5496450.
Article8. Zandi B, Hozhabri H. 2015; Correlation between femoral neck anteversion in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and normal controls. J Patient Saf Qual Improv. 3:206–10. doi: 10.22038/PSJ.2015.4173. DOI: 10.22038/PSJ.2015.4173.9. Sielatycki JA, Hennrikus WL, Swenson RD, Fanelli MG, Reighard CJ, Hamp JA. 2016; In-toeing is often a primary care orthopedic condition. J Pediatr. 177:297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.06.022. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.06.022. PMID: 27470689.
Article10. Ahn JK, Kwon DR, Park GY, Lee KH, Rim JH, Jung WB, et al. 2017; Therapeutic effect of microcurrent therapy in children with in-toeing gait caused by increased femoral anteversion: a pilot study. Ann Rehabil Med. 41:104–12. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.1.104. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.1.104. PMID: 28289642. PMCID: PMC5344811.
Article11. Radler C, Kranzl A, Manner HM, Höglinger M, Ganger R, Grill F. 2010; Torsional profile versus gait analysis: consistency between the anatomic torsion and the resulting gait pattern in patients with rotational malalignment of the lower extremity. Gait Posture. 32:405–10. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.06.019. DOI: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.06.019. PMID: 20655226.
Article12. Bruderer-Hofstetter M, Fenner V, Payne E, Zdenek K, Klima H, Wegener R. 2015; Gait deviations and compensations in pediatric patients with increased femoral torsion. J Orthop Res. 33:155–62. doi: 10.1002/jor.22746. DOI: 10.1002/jor.22746. PMID: 25284013.
Article13. Nyland J, Kuzemchek S, Parks M, Caborn DN. 2004; Femoral anteversion influences vastus medialis and gluteus medius EMG amplitude: composite hip abductor EMG amplitude ratios during isometric combined hip abduction-external rotation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 14:255–61. doi: 10.1016/S1050-6411(03)00078-6. DOI: 10.1016/S1050-6411(03)00078-6. PMID: 14962778.
Article14. Bosmans L, Jansen K, Wesseling M, Molenaers G, Scheys L, Jonkers I. 2016; The role of altered proximal femoral geometry in impaired pelvis stability and hip control during CP gait: a simulation study. Gait Posture. 44:61–7. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2015.11.010. DOI: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2015.11.010. PMID: 27004634.
Article15. Karabicak GO, Balcı NC, Gulsen M, Ozturk B, Cetin N. 2016; The effect of postural control and balance on femoral anteversion in children with spastic cerebral palsy. J Phys Ther Sci. 28:1696–700. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.1696. DOI: 10.1589/jpts.28.1696. PMID: 27390397. PMCID: PMC4932038.
Article16. Carriero A, Zavatsky A, Stebbins J, Theologis T, Shefelbine SJ. 2009; Correlation between lower limb bone morphology and gait characteristics in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 29:73–9. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e31819224d. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e31819224d. PMID: 19098651.
Article17. Carriero A, Jonkers I, Shefelbine SJ. 2011; Mechanobiological prediction of proximal femoral deformities in children with cerebral palsy. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 14:253–62. doi: 10.1080/10255841003682505. DOI: 10.1080/10255841003682505. PMID: 20229379.
Article18. Heller MO, Bergmann G, Deuretzbacher G, Claes L, Haas NP, Duda GN. 2001; Influence of femoral anteversion on proximal femoral loading: measurement and simulation in four patients. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 16:644–9. doi: 10.1016/s0268-0033(01)00053-5. DOI: 10.1016/S0268-0033(01)00053-5. PMID: 11535345.
Article19. Amichai T, Harries N, Dvir Z, Patish H, Copeliovitch L. 2009; The effects of femoral derotation osteotomy in children with cerebral palsy: an evaluation using energy cost and functional mobility. J Pediatr Orthop. 29:68–72. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181924331. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181924331. PMID: 19098650.
Article20. Redmond AC. 1998; An evaluation of the use of gait plate inlays in the short-term management of the intoeing child. Foot Ankle Int. 19:144–8. doi: 10.1177/107110079801900305. DOI: 10.1177/107110079801900305. PMID: 9542984.
Article21. Ehlert R, Manfio EF, Heidrich RO, Goldani R. 2017; Cerebral palsy: influence of TheraTogs® on gait, posture and in functional performance. Fisioter Mov. 30:307–17. doi: 10.1590/1980-5918.030.002.AO11. DOI: 10.1590/1980-5918.030.002.ao11.22. Schumacher C, Grimmer M, Scherf A, Zhao G, Beckerle P, Seyfarth A. A movement manipulator to introduce temporary and local perturbations in human hopping. Paper presented at: 7th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob). 2018 Aug 26-29; Enschede, Netherlands. p. 940–7.23. Abd El-Kafy EM. 2014; The clinical impact of orthotic correction of lower limb rotational deformities in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 28:1004–14. doi: 10.1177/0269215514533710. DOI: 10.1177/0269215514533710. PMID: 24837141.
Article24. Naseri A, Grimmer M, Seyfarth A, Sharbafi MA. 2020; Neuromechanical force-based control of a powered prosthetic foot. Wearable Technol. 1:E6. doi: 10.1017/wtc.2020.6. DOI: 10.1017/wtc.2020.6.
Article25. Cimolin V, Piccinini L, Turconi AC, Crivellini M, Galli M. 2010; Are knee kinematic anomalies in swing due to rectus femoris spasticity different from those due to femoral anteversion in children with cerebral palsy? A quantitative evaluation using 3D gait analysis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 19:221–5. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0b013e32833390ca. DOI: 10.1097/BPB.0b013e32833390ca. PMID: 20093956.
Article26. Brand RA. 2005; Joint contact stress: a reasonable surrogate for biological processes? Iowa Orthop J. 25:82–94.27. Meireles S, Wesseling M, Smith CR, Thelen DG, Verschueren S, Jonkers I. 2017; Medial knee loading is altered in subjects with early osteoarthritis during gait but not during step-up-and-over task. PLoS One. 12:e0187583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187583. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187583. PMID: 29117248. PMCID: PMC5678707.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of Gait Features in Healthy Adolescents and Adults
- Reconstruction of a soft tissue defect in the toe using a serratus anterior fascia free flap: a case report
- Treatment of the Resistant Idiopathic Clubfoot with Toe-in Gait
- Characteristics of Gait in the Elderly: Normal vs. Abnormal
- Treatment of Lesser Toe Deformities