Acute Crit Care.
2022 Nov;37(4):672-673. 10.4266/acc.2022.00920.
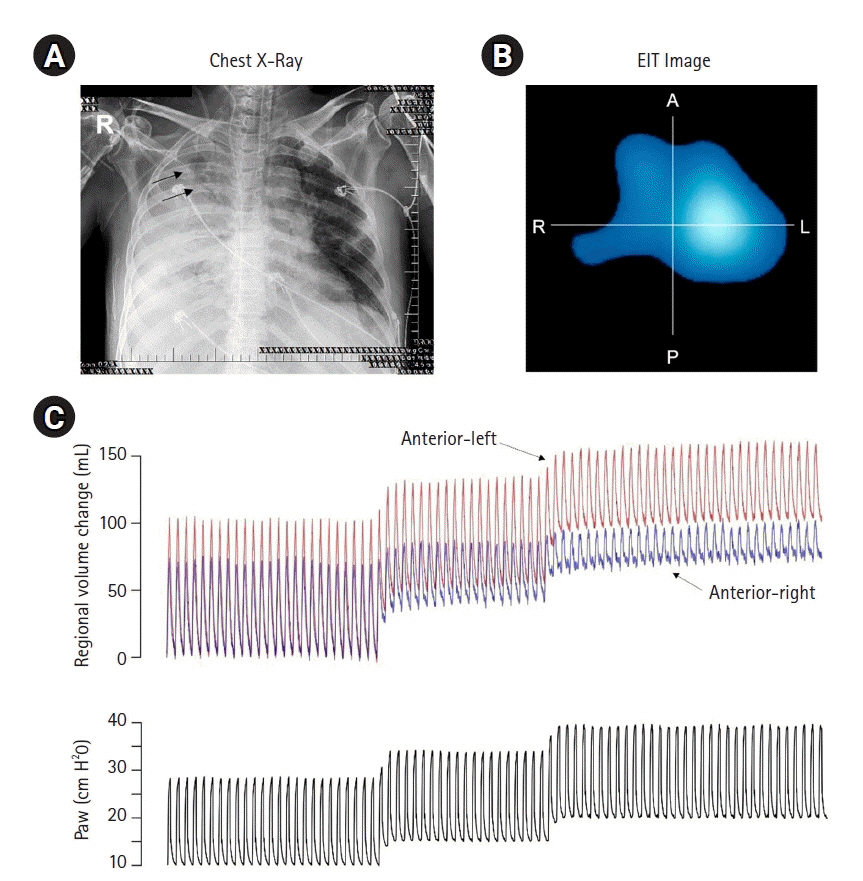
Real-time distinct visualization of barotrauma risk monitored by electrical impedance tomography in a COVID-19 and latent tuberculosis case
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiotherapy, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil
- KMID: 2540157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2022.00920
Figure
Reference
-
1. Muñoz L, Stagg HR, Abubakar I. Diagnosis and management of latent tuberculosis infection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015; 5:a017830.2. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020 [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020 [cited 2022 Jul 12]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131.3. Tofigh AM, Shojaei S, Bagherpour JZ, Mirkheshti A, Tahmasebi H. Subcutaneous emphysema as an ominous side effect in COVID-19 patients under mechanical ventilation, report of 7 cases. J Cell Mol Anesth. 2020; 5:202–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Excluding Participants With Mycobacteria Infections From Clinical Trials: A Critical Consideration in Evaluating the Efficacy of BCG Against COVID-19
- Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea
- Cardiovascular Imaging in the Era of the COVID-19 Outbreak
- Comparison Study of Molecular Diagnostic Reagents for COVID-19 Pooling Test
- Current laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019