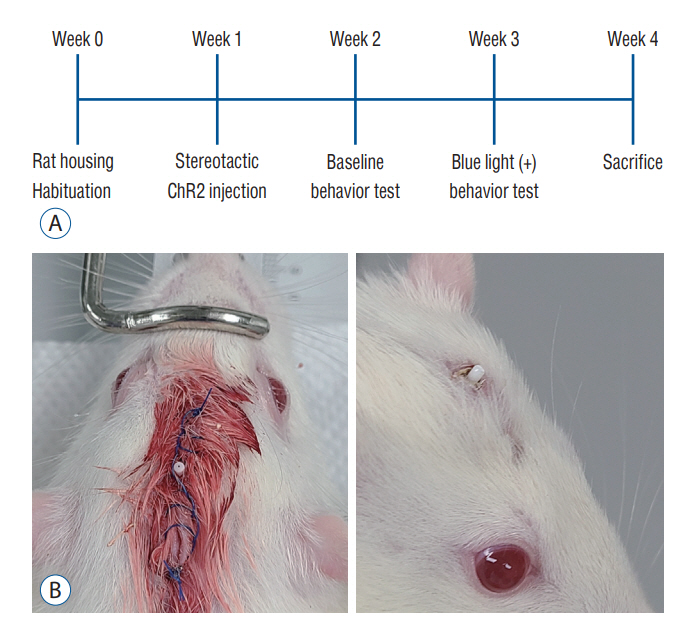
J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2023 Mar;66(2):121-132. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0106.
Hyperkinetic Rat Model Induced by Optogenetic Parafascicular Nucleus Stimulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- KMID: 2539873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0106
Abstract
Objective
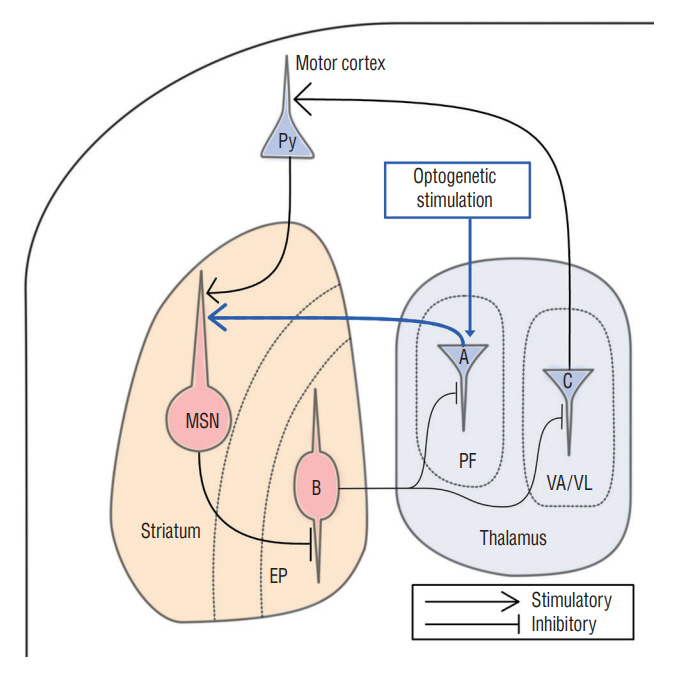
: The parafascicular nucleus (PF) plays important roles in controlling the basal ganglia. It is not well known whether the PF affects the development of abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs). This study was aimed to find a role of the PF in development of AIMs using optogenetic methods in an animal model.
Methods
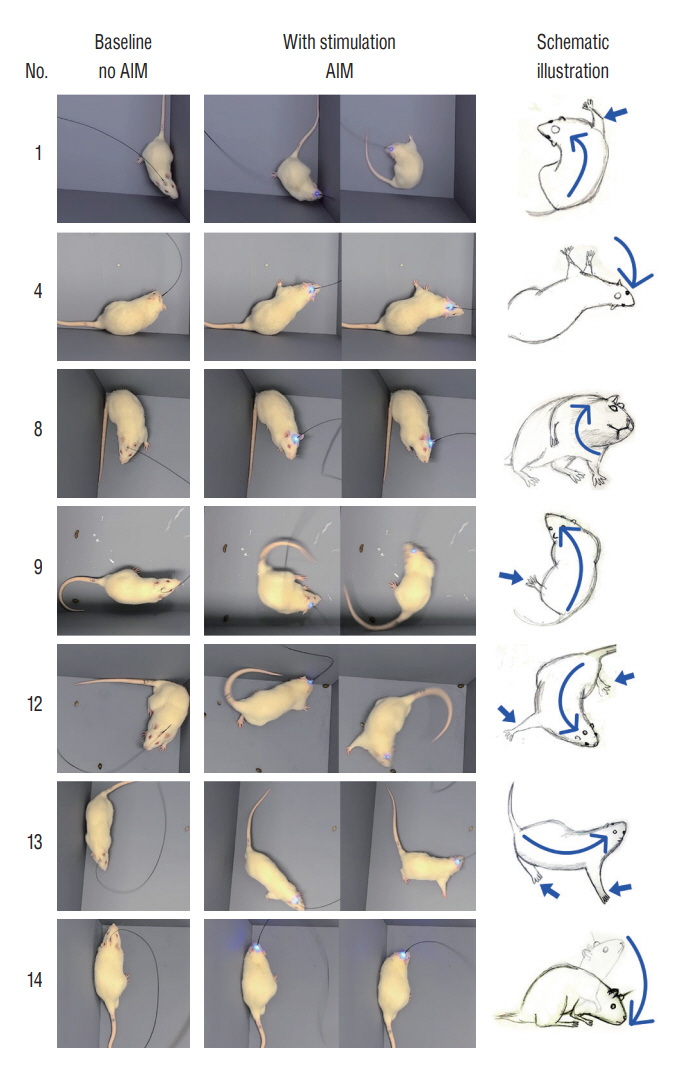
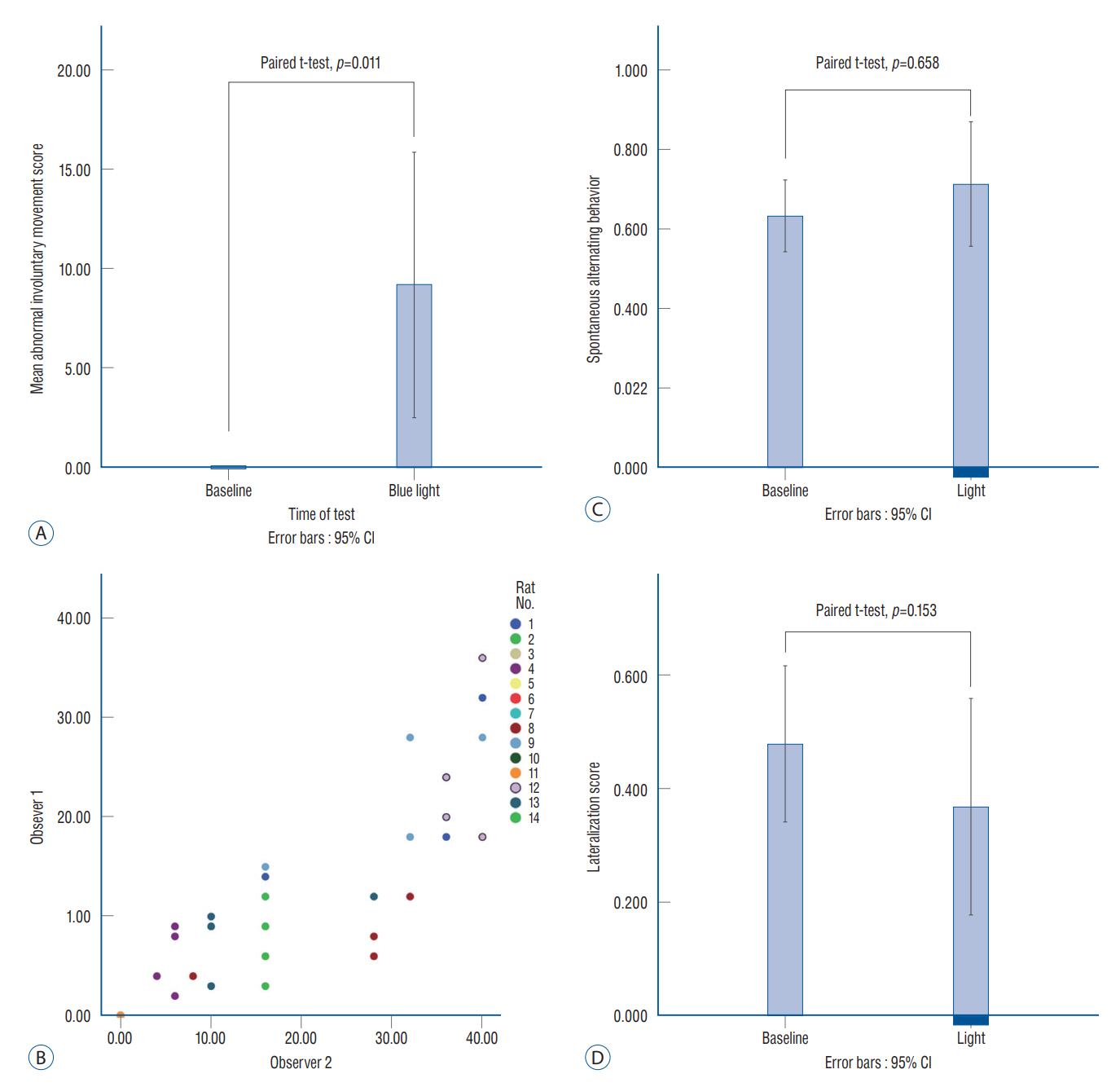
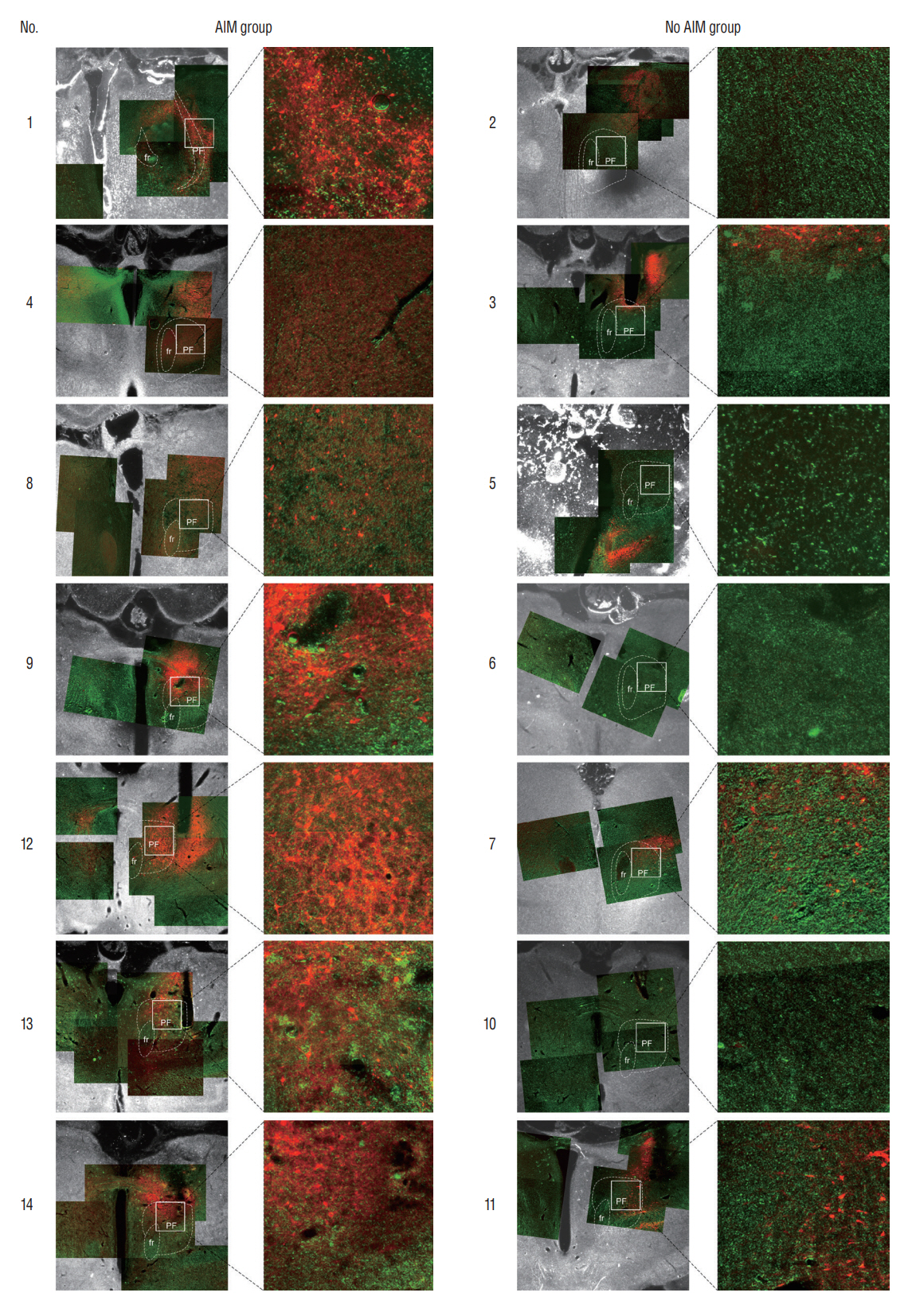
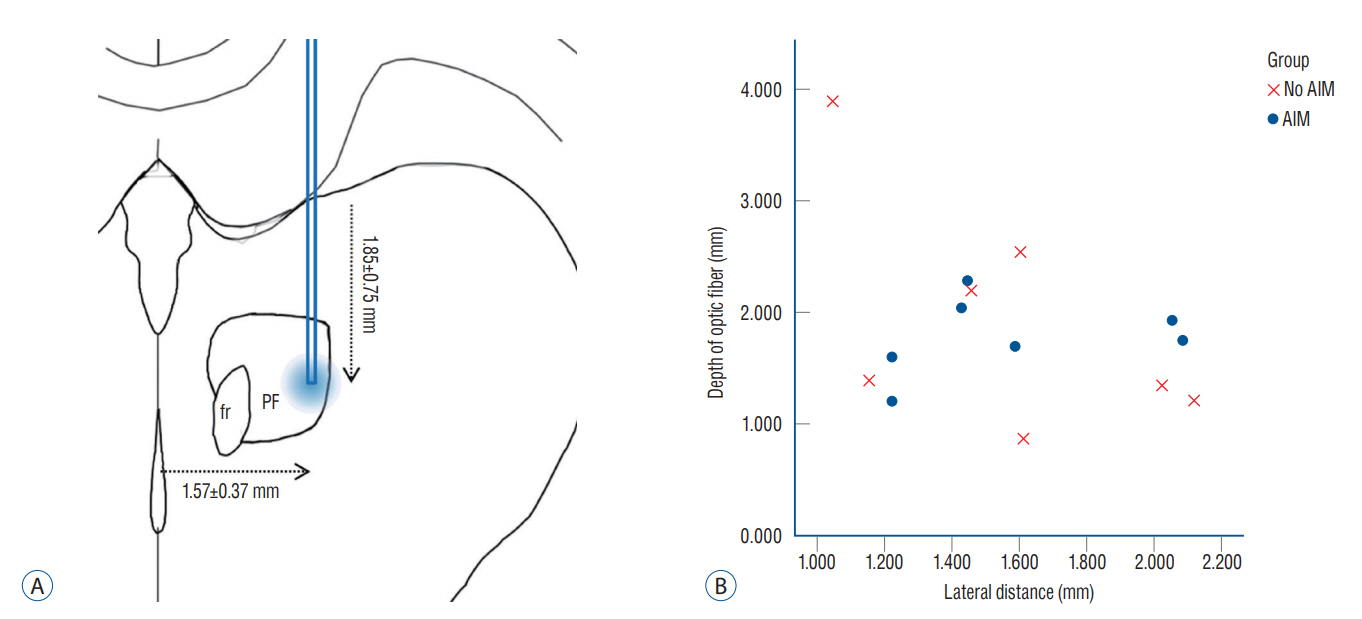
: Fourteen rats were underwent stereotactic operation, in which they were injected with an adeno-associated virus with channelrhodopsin (AAV2-hSyn-ChR2-mCherry) to the lateral one third of the PF. Behavior test was performed with and without optical stimulation 14 days after the injection of the virus. AIM of rat was examined using AIM score. After the behavior test, rat’s brain was carefully extracted and the section was examined using a fluorescence microscope to confirm transfection of the PF.
Results
: Of the 14 rats, seven rats displayed evident involuntary abnormal movements. AIM scores were increased significantly after the stimulation compared to those at baseline. In rats with AIMs, mCherry expression was prominent in the PF, while the rats without AIM lacked with the mCherry expression.
Conclusion
: AIMs could be reversibly induced by stimulating the PF through an optogenetic method.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Altenmüller E, Baur V, Hofmann A, Lim VK, Jabusch HC. Musician’s cramp as manifestation of maladaptive brain plasticity: arguments from instrumental differences. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1252:259–265. 2012.2. Barow E, Neumann WJ, Brücke C, Huebl J, Horn A, Brown P, et al. Deep brain stimulation suppresses pallidal low frequency activity in patients with phasic dystonic movements. Brain. 137:3012–3024. 2014.3. Dang MT, Yokoi F, McNaught KS, Jengelley TA, Jackson T, Li J, et al. Generation and characterization of Dyt1 DeltaGAG knock-in mouse as a model for early-onset dystonia. Exp Neurol. 196:452–463. 2005.4. de Hemptinne C, Ryapolova-Webb ES, Air EL, Garcia PA, Miller KJ, Ojemann JG, et al. Exaggerated phase-amplitude coupling in the primary motor cortex in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110:4780–4785. 2013.5. DeLong MR. Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trends Neurosci. 13:281–285. 1990.6. Fama R, Sullivan EV. Thalamic structures and associated cognitive functions: relations with age and aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 54:29–37. 2015.7. Ferbinteanu J. Memory systems 2018 - towards a new paradigm. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 157:61–78. 2019.8. French JD, Verzeano M, Magoun HW. An extralemniscal sensory system in the brain. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 69:505–518. 1953.9. Gradinaru V, Mogri M, Thompson KR, Henderson JM, Deisseroth K. Optical deconstruction of parkinsonian neural circuitry. Science. 324:354–359. 2009.10. Huh R, Chung M. Range of voluntary neck motility predicts outcome of pallidal DBS for cervical dystonia. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 161:2491–2498. 2019.11. Huh R, Song IU, Chung M. Neuropsychological consequences of pallidal deep brain stimulation altering brain networks. J Clin Neurosci. 54:50–56. 2018.12. Ilyas A, Pizarro D, Romeo AK, Riley KO, Pati S. The centromedian nucleus: anatomy, physiology, and clinical implications. J Clin Neurosci. 63:1–7. 2019.13. Jouve L, Salin P, Melon C, Kerkerian-Le Goff L. Deep brain stimulation of the center median-parafascicular complex of the thalamus has efficient anti-parkinsonian action associated with widespread cellular responses in the basal ganglia network in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci. 30:9919–9928. 2010.14. Koechlin E. Prefrontal executive function and adaptive behavior in complex environments. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 37:1–6. 2016.15. Krauss JK. Surgical treatment of dystonia. Eur J Neurol. 17:97–101. 2010.16. Kulkarni SK, Dhir A. Animal models of tardive dyskinesia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 98:265–287. 2011.17. LaLumiere RT. A new technique for controlling the brain: optogenetics and its potential for use in research and the clinic. Brain Stimul. 4:1–6. 2011.18. Mandelbaum G, Taranda J, Haynes TM, Hochbaum DR, Huang KW, Hyun M, et al. Distinct cortical-thalamic-striatal circuits through the parafascicular nucleus. Neuron. 102:636–652.e7. 2019.19. Mazzone P, Stocchi F, Galati S, Insola A, Altibrandi MG, Modugno N, et al. Bilateral implantation of centromedian-parafascicularis complex and GPi: a new combination of unconventional targets for deep brain stimulation in severe Parkinson disease. Neuromodulation. 9:221–228. 2006.20. McCairn KW, Iriki A, Isoda M. Deep brain stimulation reduces Tic-related neural activity via temporal locking with stimulus pulses. J Neurosci. 33:6581–6593. 2013.21. Meringolo M, Tassone A, Imbriani P, Ponterio G, Pisani A. Dystonia: are animal models relevant in therapeutics? Rev Neurol (Paris). 174:608–614. 2018.22. Miller EK, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 24:167–202. 2001.23. Mitchell AS, Sherman SM, Sommer MA, Mair RG, Vertes RP, Chudasama Y. Advances in understanding mechanisms of thalamic relays in cognition and behavior. J Neurosci. 34:15340–15346. 2014.24. Parent A, Hazrati LN. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 20:91–127. 1995.25. Paxinos G, Charles W. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 6th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier;2007.26. Penttinen AM, Suleymanova I, Albert K, Anttila J, Voutilainen MH, Airavaara M. Characterization of a new low-dose 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease in rat. J Neurosci Res. 94:318–328. 2016.27. Prashanth LK, Fox S, Meissner WG. l-Dopa-induced dyskinesia-clinical presentation, genetics, and treatment. Int Rev Neurobiol. 98:31–54. 2011.28. Quartarone A, Pisani A. Abnormal plasticity in dystonia: disruption of synaptic homeostasis. Neurobiol Dis. 42:162–170. 2011.29. Rabinovici GD, Stephens ML, Possin KL. Executive dysfunction. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 21:646–659. 2015.30. Sadikot AF, Rymar VV. The primate centromedian-parafascicular complex: anatomical organization with a note on neuromodulation. Brain Res Bull. 78:122–130. 2009.31. Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN. Disconnection syndromes of basal ganglia, thalamus, and cerebrocerebellar systems. Cortex. 44:1037–1066. 2008.32. Sewards TV, Sewards MA. The medial pain system: neural representations of the motivational aspect of pain. Brain Res Bull. 59:163–180. 2002.33. Sidibé M, Paré JF, Smith Y. Nigral and pallidal inputs to functionally segregated thalamostriatal neurons in the centromedian/parafascicular intralaminar nuclear complex in monkey. J Comp Neurol. 447:286–299. 2002.34. Smith Y, Raju DV, Pare JF, Sidibe M. The thalamostriatal system: a highly specific network of the basal ganglia circuitry. Trends Neurosci. 27:520–527. 2004.35. Tanimura A, Du Y, Kondapalli J, Wokosin DL, Surmeier DJ. Cholinergic interneurons amplify thalamostriatal excitation of striatal indirect pathway neurons in Parkinson’s disease models. Neuron. 101:444–458.e6. 2019.36. Tronci E, Shin E, Björklund A, Carta M. Amphetamine-induced rotation and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the rat 6-OHDA model: a correlation study. Neurosci Res. 73:168–172. 2012.37. Varela C. Thalamic neuromodulation and its implications for executive networks. Front Neural Circuits. 8:69. 2014.38. Vidailhet M, Grabli D, Roze E. Pathophysiology of dystonia. Curr Opin Neurol. 22:406–413. 2009.39. Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, et al. Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med. 352:459–467. 2005.40. Weigel R, Krauss JK. Center median-parafascicular complex and pain control. review from a neurosurgical perspective. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 82:115–126. 2004.41. Winkler C, Kirik D, Björklund A, Cenci MA. L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine model of parkinson's disease: relation to motor and cellular parameters of nigrostriatal function. Neurobiol Dis. 10:165–186. 2002.42. Wong YC, Luk K, Purtell K, Burke Nanni S, Stoessl AJ, Trudeau LE, et al. Neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease: should the focus be on axons and synaptic terminals? Mov Disord. 34:1406–1422. 2019.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulse-train Stimulation of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Blocks Pain Perception in Tail Clip Test
- The neural mechanism of apomorphine-induced erection: an experimental study by the comparison with electrostimulation-induced erection of the rat model
- Effect of Chronic Alcohol Intake on Vasopressin and Oxytocin-containing Neurons in the Paraventricular and Supraoptic Nucleus of the Rat Hypothalamus
- The Effect and the Mechanism of Action of High Frequency Electrical Stimulation of Subthalamic Nucleus on Status Epilepticus Induced by Lithium-Pilocarpine of Rat
- Hemiballism as First Isolated Manifestation Following Caudate Infarction