Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Feb;38(1):104-116. 10.3803/EnM.2023.1669.
A Comprehensive Assessment of the Harms of Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2539824
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1669
Abstract
- Background
There have concerns related with the potential harms of fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB). We aimed to summarize the clinical complications and evaluate the safety of FNAB.
Methods
Studies related with the harms of FNAB were searched on MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane library, and KoreaMed from 2012 to 2022. Also, studies reviewed in the previous systematic reviews were evaluated. Included clinical complications were postprocedural pain, bleeding events, neurological symptoms, tracheal puncture, infections, post-FNAB thyrotoxicosis, and needle tract implantation of thyroid cancers.
Results
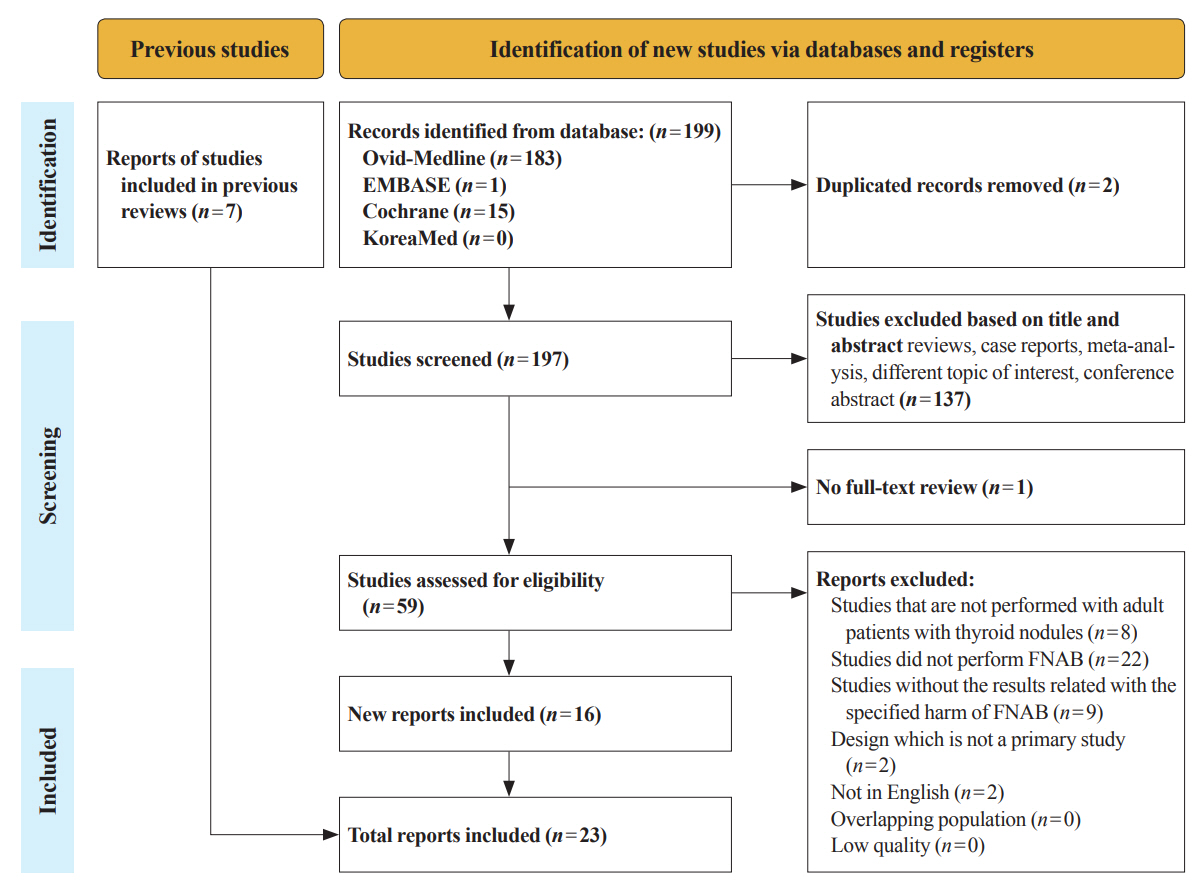
Twenty-three cohort studies were included in this review. Nine studies which were related with FNAB-related pain showed that most of the subjects had no or mild discomfort. The 0% to 6.4% of the patients had hematoma or hemorrhage after FNAB, according to 15 studies. Vasovagal reaction, vocal cord palsy, and tracheal puncture have rarely described in the included studies. Needle tract implantation of thyroid malignancies was described in three studies reporting 0.02% to 0.19% of the incidence rate.
Conclusion
FNAB is considered to be a safe diagnostic procedure with rare complications, which are mainly minor events. Thorough assessement of the patients’ medical condition when deciding to perform FNABs would be advisable to lower potential complications.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):75-77. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.105.To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):69-71. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.104.Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Part II. Follow-up Surveillance after Initial Treatment 2024
Mijin Kim, Ji-In Bang, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Young Joo Park, Youngduk Seo, Young Shin Song, So Won Oh, Sang-Woo Lee, Eun Kyung Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Ari Chong, Yun Jae Chung, Chae Moon Hong, Min Kyoung Lee, Bo Hyun Kim
Int J Thyroidol. 2024;17(1):115-146. doi: 10.11106/ijt.2024.17.1.115.
Reference
-
1. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2016; 26:1–133.
Article2. Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW. Charboneau JW. Diagnostic ultrasound. Vol. 1. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby;2005. p. 736–43.3. Russ G, Bonnema SJ, Erdogan MF, Durante C, Ngu R, Leenhardt L. European Thyroid Association guidelines for ultrasound malignancy risk stratification of thyroid nodules in adults: the EU-TIRADS. Eur Thyroid J. 2017; 6:225–37.
Article4. Ha EJ, Chung SR, Na DG, Ahn HS, Chung J, Lee JY, et al. 2021 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol. 2021; 22:2094–123.
Article5. Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG, Hoang JK, Berland LL, Teefey SA, et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): white paper of the ACR TI-RADS committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017; 14:587–95.
Article6. Polyzos SA, Kita M, Avramidis A. Thyroid nodules: stepwise diagnosis and management. Hormones (Athens). 2007; 6:101–19.7. Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD. Clinical complications following thyroid fine-needle biopsy: a systematic review. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009; 71:157–65.
Article8. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for thyroid cancer: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017; 317:1882–7.9. Lee YH, Baek JH, Jung SL, Kwak JY, Kim JH, Shin JH. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: a consensus statement by the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:391–401.
Article10. Kim DW, Choo HJ, Park JS, Lee EJ, Kim SH, Jung SJ, et al. Ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology for thyroid nodules: an emphasis on one-sampling and biopsy techniques. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012; 40 Suppl 1:E48–54.
Article11. Birgi E, Ergun O, Turkmenoglu TT, Gunes Tatar I, Durmaz HA, Hekimoglu B. The contribution of vacuum-assisted modified Menghini type needle to diagnosis of US-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2016; 22:173–7.
Article12. Lee YJ, Kim DW, Shin GW, Heo YJ, Baek JW, Choo HJ, et al. Comparison of cytological adequacy and pain scale score in ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid thyroid nodules for liquid-based cytology with 23- and 25-gauge needles: a single-center prospective study. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:7027.13. Jung SJ, Kim DW, Baek HJ. Comparison study of the adequacy and pain scale of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid thyroid nodules with a 21- or 23-gauge needle for liquid-based cytology: a single-center study. Endocr Pathol. 2018; 29:30–4.
Article14. Cordes M, Schmidkonz C, Horstrup K, Weppler M, Kuwert T. Fine-needle aspiration biopsies of thyroid nodules. Nuklearmedizin. 2018; 57:211–5.
Article15. Toman H, Ozkul F, Erbag G, Erbas M, Simsek T, Adam G, et al. Effects of fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) nodule depth on pain score. Ir J Med Sci. 2016; 185:673–6.
Article16. Lee YJ, Kim DW, Jung SJ. Comparison of sample adequacy, pain-scale ratings, and complications associated with ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules between two radiologists with different levels of experience. Endocrine. 2013; 44:696–701.
Article17. Gursoy A, Ertugrul DT, Sahin M, Tutuncu NB, Demirer AN, Demirag NG. Needle-free delivery of lidocaine for reducing the pain associated with the fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules: time-saving and efficacious procedure. Thyroid. 2007; 17:317–21.
Article18. Gursoy A, Ertugrul DT, Sahin M, Tutuncu NB, Demirer AN, Demirag NG. The analgesic efficacy of lidocaine/prilocaine (EMLA) cream during fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007; 66:691–4.
Article19. Kavanagh J, McVeigh N, McCarthy E, Bennett K, Beddy P. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: factors affecting diagnostic outcomes and confounding variables. Acta Radiol. 2017; 58:301–6.
Article20. Newkirk KA, Ringel MD, Jelinek J, Mark A, Wartofsky L, Deeb ZE, et al. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and thyroid disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 123:700–5.
Article21. Cappelli C, Pirola I, Agosti B, Tironi A, Gandossi E, Incardona P, et al. Complications after fine-needle aspiration cytology: a retrospective study of 7449 consecutive thyroid nodules. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017; 55:266–9.
Article22. Ahn HS, Youn I, Na DG, Kim SJ, Lee MY. Diagnostic performance of core needle biopsy as a first-line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules according to ultrasound patterns: comparison with fine needle aspiration using propensity score matching analysis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2021; 94:494–503.
Article23. Kim HJ, Kim YK, Moon JH, Choi JY, Choi SI. Thyroid core needle biopsy: patients’ pain and satisfaction compared to fine needle aspiration. Endocrine. 2019; 65:365–70.
Article24. Chae IH, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Yoon JH, Park VY, Kwak JY. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy: comparison of post-biopsy hematoma rates and risk factors. Endocrine. 2017; 57:108–14.
Article25. Khoo TK, Baker CH, Hallanger-Johnson J, Tom AM, Grant CS, Reading CC, et al. Comparison of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy with core-needle biopsy in the evaluation of thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract. 2008; 14:426–31.
Article26. Chen BT, Jain AB, Dagis A, Chu P, Vora L, Maghami E, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy versus fine-needle aspiration for evaluating thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract. 2015; 21:128–35.
Article27. Uchida T, Himuro M, Komiya K, Goto H, Takeno K, Honda A, et al. Evanescent hyperechoic changes after fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid in a series with a low overall prevalence of complications. J Ultrasound Med. 2016; 35:599–604.
Article28. Khadra H, Kholmatov R, Monlezun D, Kandil E. Do anticoagulation medications increase the risk of haematoma in ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of thyroid lesions? Cytopathology. 2018; 29:565–8.
Article29. Abu-Yousef MM, Larson JH, Kuehn DM, Wu AS, Laroia AT. Safety of ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of neck lesions in patients taking antithrombotic/anticoagulant medications. Ultrasound Q. 2011; 27:157–9.
Article30. Tomoda C, Takamura Y, Ito Y, Miya A, Miyauchi A. Transient vocal cord paralysis after fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid tumor. Thyroid. 2006; 16:697–9.
Article31. Ito Y, Tomoda C, Uruno T, Takamura Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, et al. Needle tract implantation of papillary thyroid carcinoma after fine-needle aspiration biopsy. World J Surg. 2005; 29:1544–9.
Article32. Ito Y, Asahi S, Matsuzuka F, Nakamura Y, Amino N, Miyauchi A. Needle tract implantation of follicular neoplasm after fine-needle aspiration biopsy: report of a case. Thyroid. 2006; 16:1059–62.
Article33. Hayashi T, Hirokawa M, Higuchi M, Kudo T, Ito Y, Miyauchi A. Needle tract implantation following fine-needle aspiration of thyroid cancer. World J Surg. 2020; 44:378–84.
Article34. Tangpricha V, Chen BJ, Swan NC, Sweeney AT, de las Morenas A, Safer JD. Twenty-one-gauge needles provide more cellular samples than twenty-five-gauge needles in fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid but may not provide increased diagnostic accuracy. Thyroid. 2001; 11:973–6.
Article35. Bonsignore A, Drommi M, Frigiolini F, Roncallo A, Ventura F, Buffelli F, et al. A rare case of fatal thyroid hemorrhage after fine-needle aspiration: case report and review of the literature. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2022; 43:291–5.
Article36. Katagiri H, Lefor AK, Kubota T, Mizokami K, Kishida A. Massive hematoma after fine-needle aspiration of the thyroid. Surgery. 2016; 160:245–6.
Article37. Noordzij JP, Goto MM. Airway compromise caused by hematoma after thyroid fine-needle aspiration. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005; 26:398–9.
Article38. Yoshida M, Miyata M, Maeda H, Oiso Y. Massive thyroid hematoma developing after a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Intern Med. 2012; 51:3223–4.
Article39. Donatini G, Masoni T. Is fine-needle aspiration cytology for thyroid nodules a routine and safe procedure? A series of emergency cervicotomies following FNAC. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010; 395:873–6.
Article40. Park MH, Yoon JH. Anterior neck hematoma causing airway compression following fine needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid nodule: a case report. Acta Cytol. 2009; 53:86–8.41. Lee YS, Baek HS, Park TS, Jin HY. Bilateral intrathyroidal hemorrhage after fine needle aspiration completely resolved by compression without thyroidectomy. Endocrine. 2013; 43:460–1.
Article42. Roh JL. Intrathyroid hemorrhage and acute upper airway obstruction after fine needle aspiration of the thyroid gland. Laryngoscope. 2006; 116:154–6.
Article43. Hor T, Lahiri SW. Bilateral thyroid hematomas after fine-needle aspiration causing acute airway obstruction. Thyroid. 2008; 18:567–9.
Article44. Kakiuchi Y, Idota N, Nakamura M, Ikegaya H. A fatal case of cervical hemorrhage after fine needle aspiration and core needle biopsy of the thyroid gland. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2015; 36:207–9.
Article45. Strachan MW, Dalvi M, Ainsworth R, Gibb FW, Horsfall H, Patel D. Fatal haemorrhage following fine needle aspiration of the thyroid. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2016; 46:166–7.
Article46. Park JK, Jeon EJ. Infection of thyroid cyst occurring 1 month after fine-needle aspiration in an immunocompetent patient. Int J Thyroidol. 2018; 11:182–8.
Article47. Wang YC, Yeh TS, Lin JD. Gram-negative thyroid abscess resulting from fine-needle aspiration in an immunosuppressed patient. Clin Infect Dis. 1997; 25:745–6.
Article48. Isenberg SF. Thyroid abscess resulting from fine-needle aspiration. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; 111:832–3.
Article49. Nishihara E, Miyauchi A, Matsuzuka F, Sasaki I, Ohye H, Kubota S, et al. Acute suppurative thyroiditis after fine-needle aspiration causing thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 2005; 15:1183–7.
Article50. Sun JH, Chang HY, Chen KW, Lin KD, Lin JD, Hsueh C. Anaerobic thyroid abscess from a thyroid cyst after fine-needle aspiration. Head Neck. 2002; 24:84–6.
Article51. Unluturk U, Ceyhan K, Corapcioglu D. Acute suppurative thyroiditis following fine-needle aspiration biopsy in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Ultrasound. 2014; 42:215–8.
Article52. Orrego JJ. Thyrotoxicosis following fine-needle aspiration biopsy of a thyroid nodule: case report. Rev Colomb Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017; 3:40–1.
Article53. Kobayashi A, Kuma K, Matsuzuka F, Hirai K, Fukata S, Sugawara M. Thyrotoxicosis after needle aspiration of thyroid cyst. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992; 75:21–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Indications for Fine Needle Aspiration in Thyroid Nodules
- Thyroid Nodules with Nondiagnostic FNA Results: Role of Core Needle Biopsy
- Natural Course of Cytologically Diagnosed Benign Thyroid Nodules
- Arterial Bleeding of a Thyroid Mass After Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: A Case Report
- A clinical analysis of fine needle aspiration biopsy cytologic diagnosis on thyroid nodules