Healthc Inform Res.
2023 Jan;29(1):16-22. 10.4258/hir.2023.29.1.16.
Application of a Multi-Layer Perceptron in Preoperative Screening for Orthognathic Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Advanced General Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2Department of General Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Srinakharinwirot University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 4Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- KMID: 2539394
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2023.29.1.16
Abstract
Objectives
Orthognathic surgery is used to treat moderate to severe occlusal discrepancies. Examinations and measurements for preoperative screening are essential procedures. A careful analysis is needed to decide whether cases require orthognathic surgery. This study developed screening software using a multi-layer perceptron to determine whether orthognathic surgery is required.
Methods
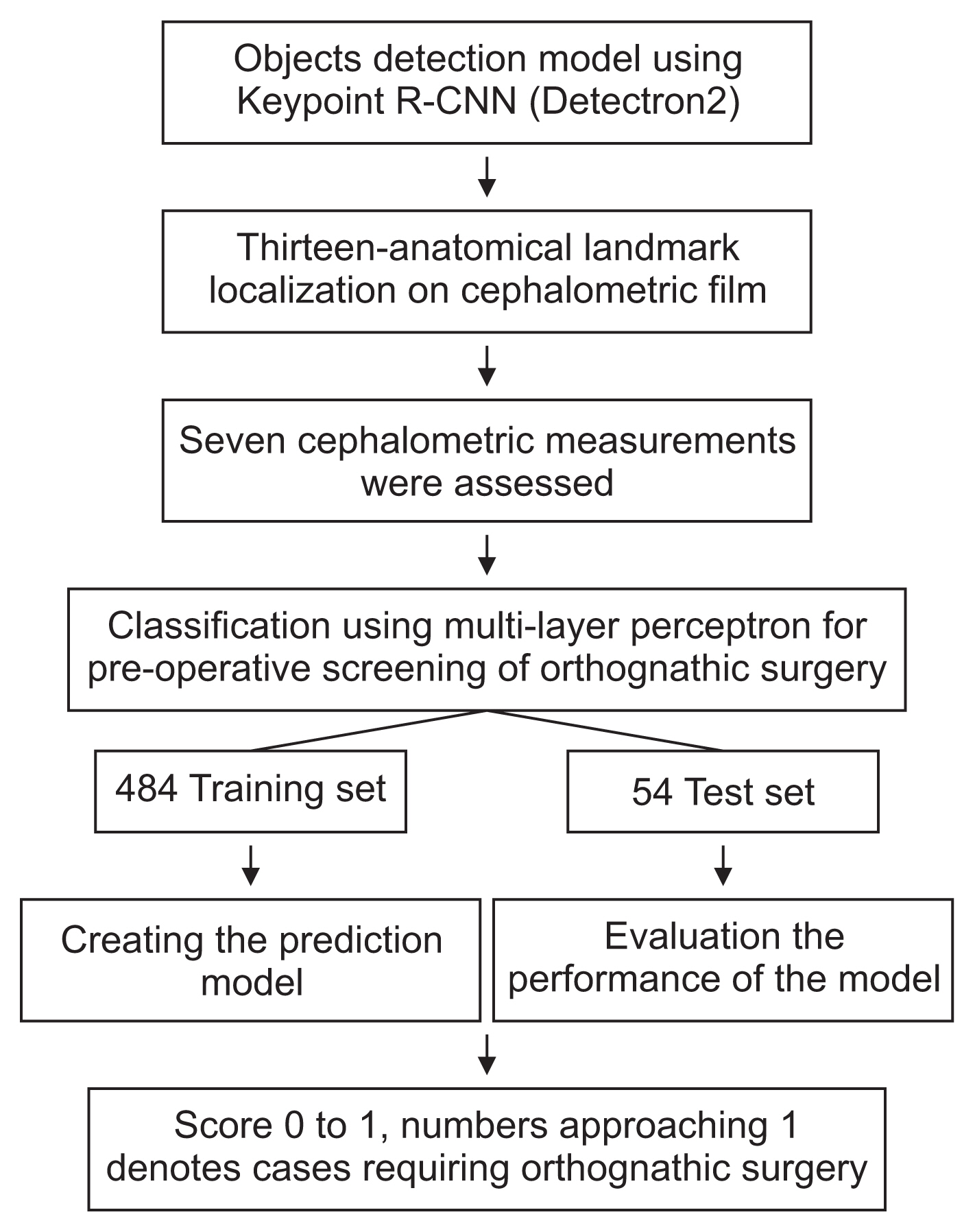
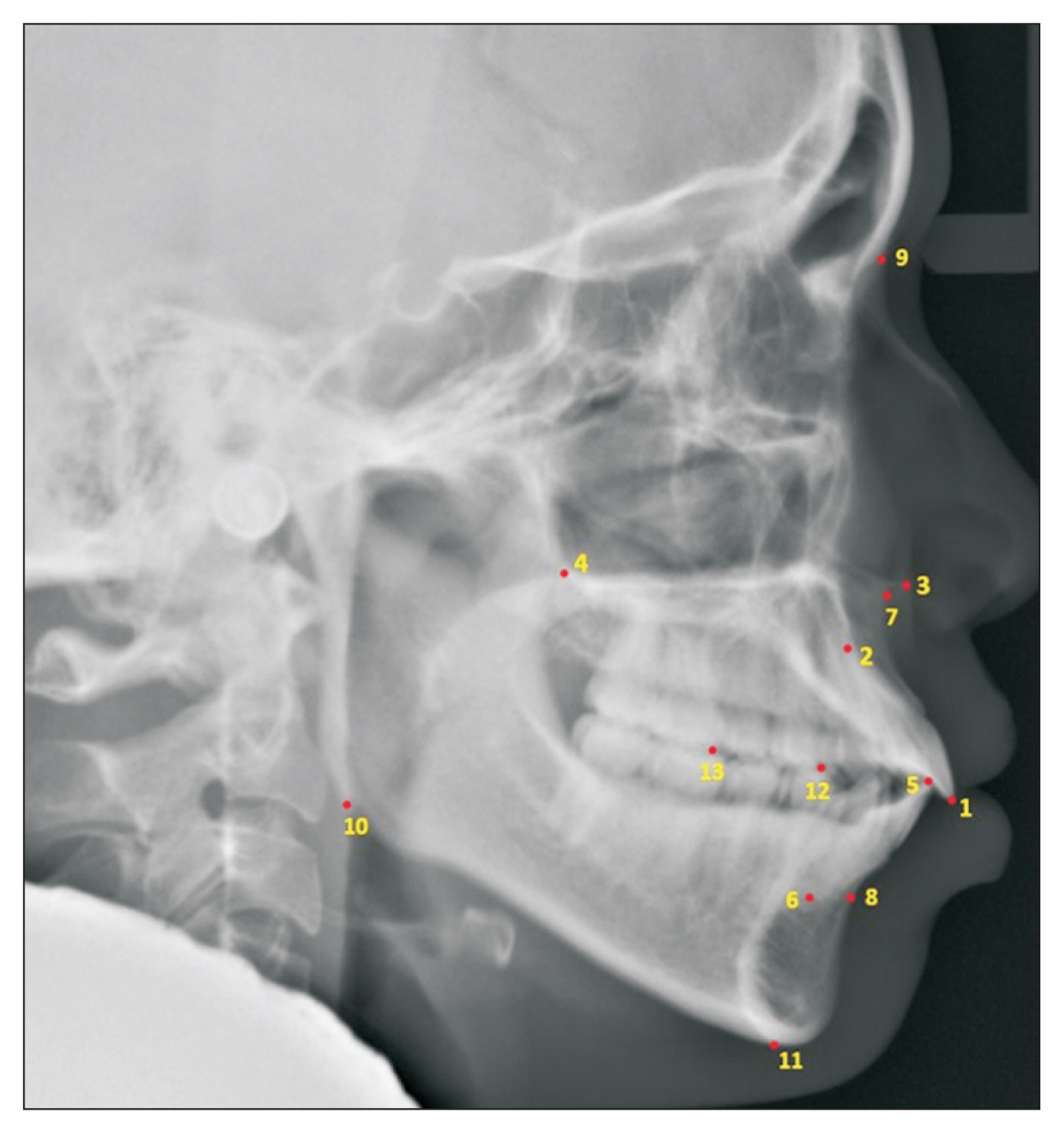
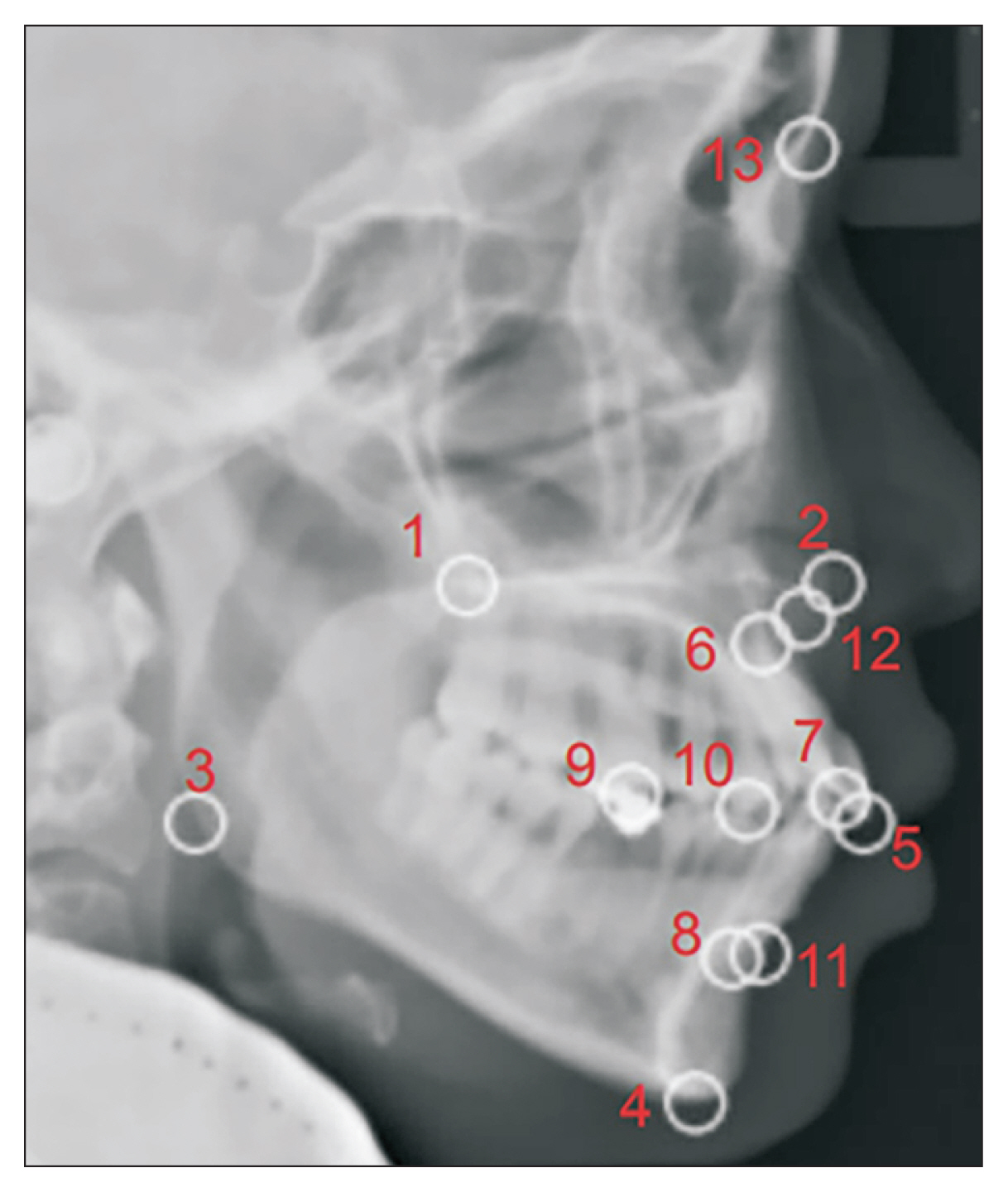
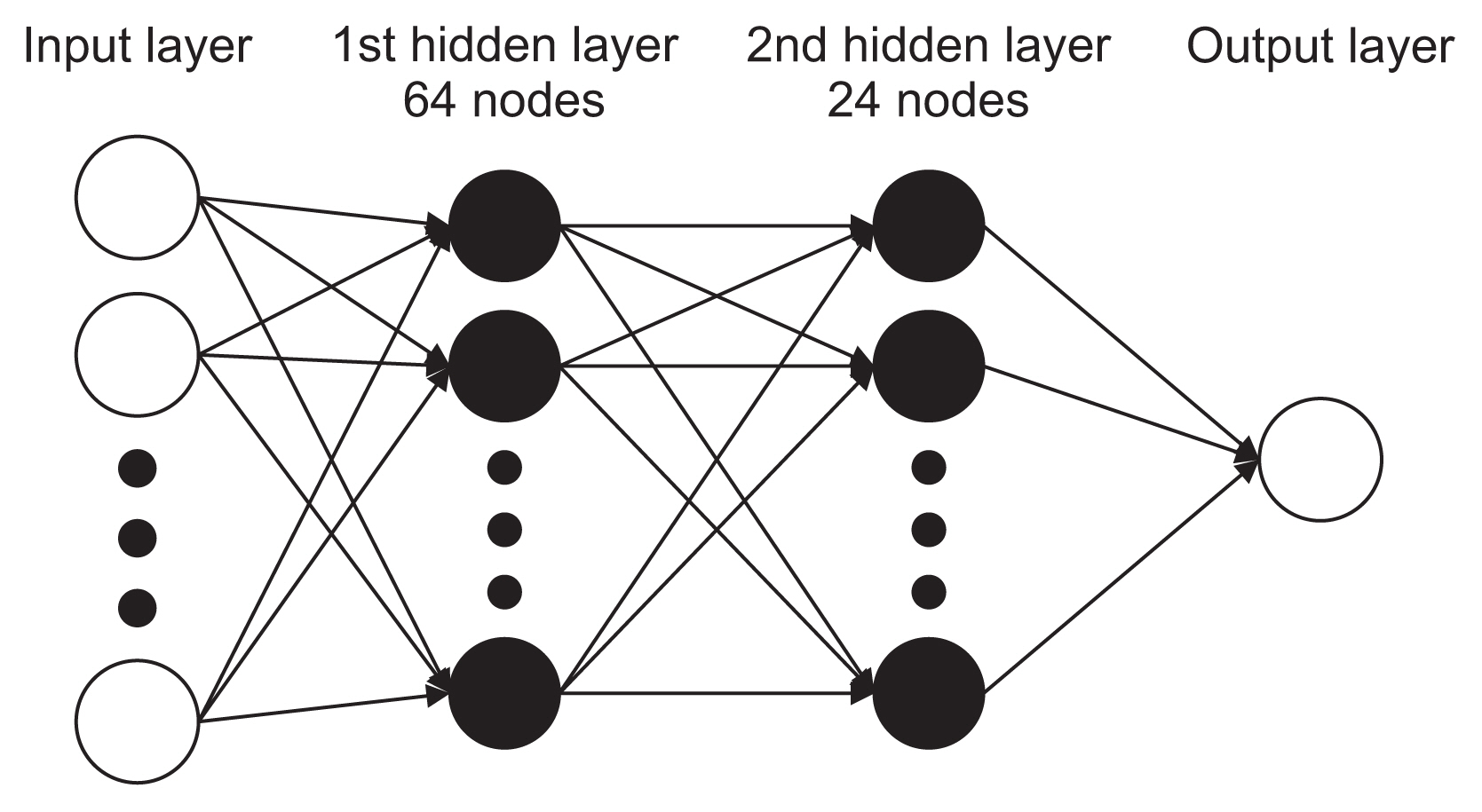
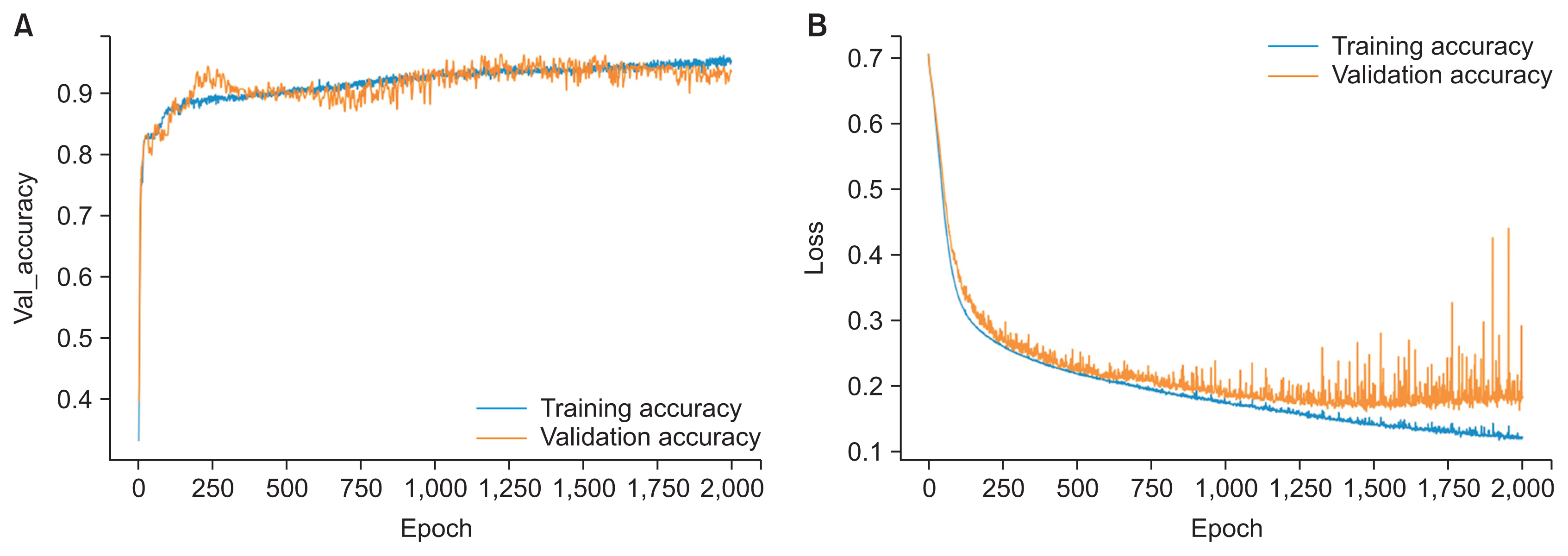
In total, 538 digital lateral cephalometric radiographs were retrospectively collected from a hospital data system. The input data consisted of seven cephalometric variables. All cephalograms were analyzed by the Detectron2 detection and segmentation algorithms. A keypoint region-based convolutional neural network (R-CNN) was used for object detection, and an artificial neural network (ANN) was used for classification. This novel neural network decision support system was created and validated using Keras software. The output data are shown as a number from 0 to 1, with cases requiring orthognathic surgery being indicated by a number approaching 1.
Results
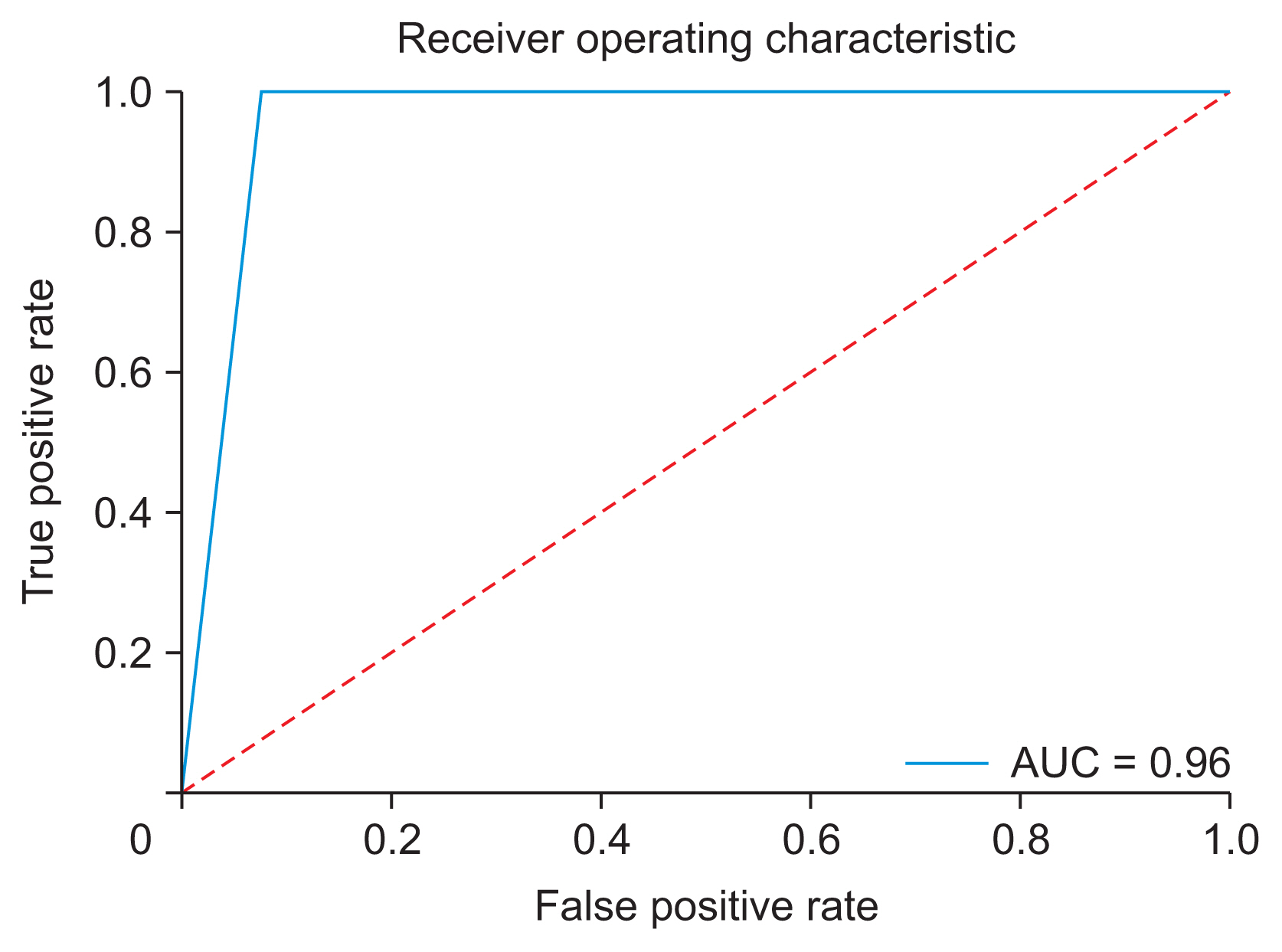
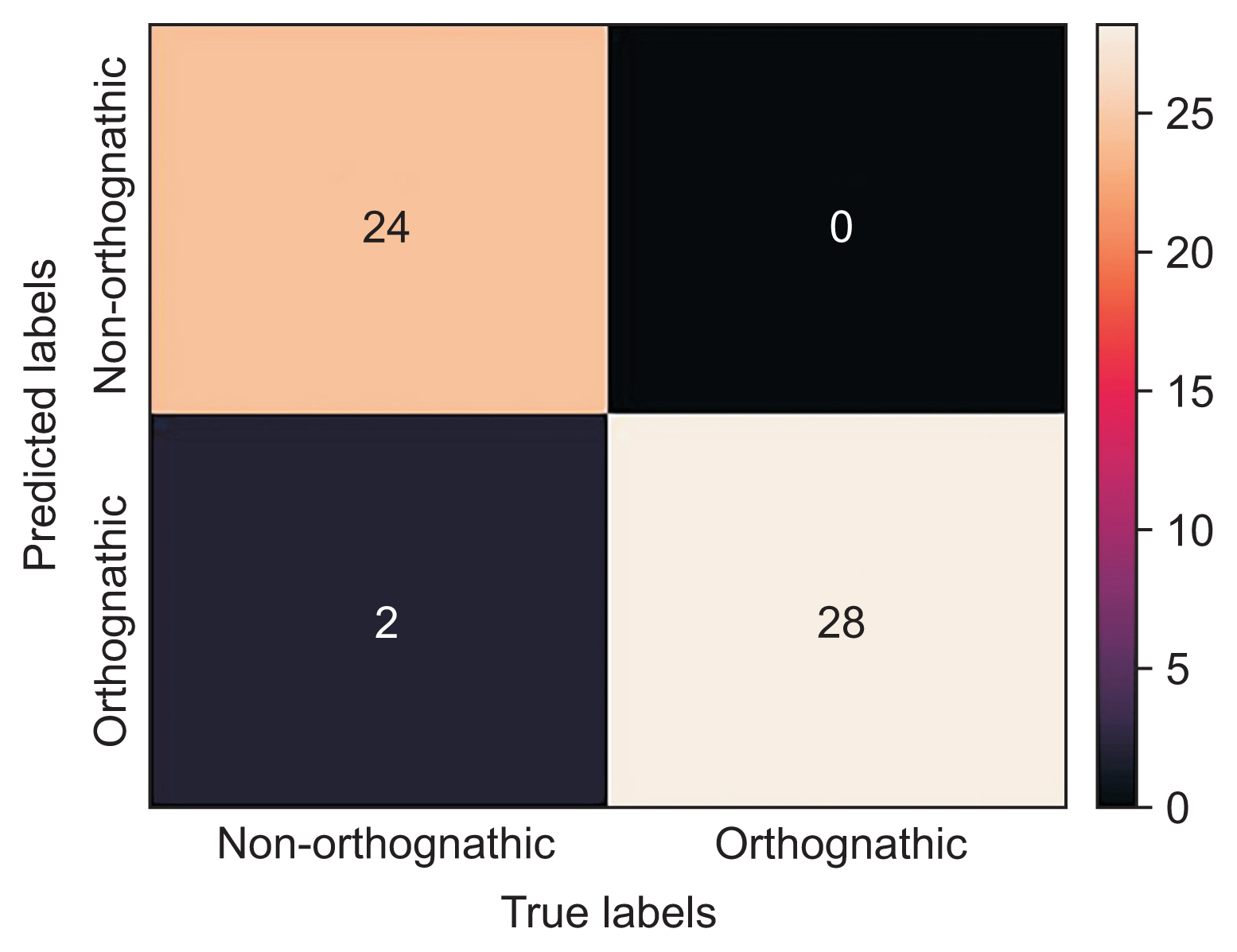
The screening software demonstrated a diagnostic agreement of 96.3% with specialists regarding the requirement for orthognathic surgery. A confusion matrix showed that only 2 out of 54 cases were misdiagnosed (accuracy = 0.963, sensitivity = 1, precision = 0.93, F-value = 0.963, area under the curve = 0.96).
Conclusions
Orthognathic surgery screening with a keypoint R-CNN for object detection and an ANN for classification showed 96.3% diagnostic agreement in this study.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Graber TM, Vanarsdall RL. Orthodontics: current principles & techniques. 3rd ed. St. Louis (MO): Mosby;2000.2. Proffit WR, Fields HW. Contemporary orthodontics. 3rd ed. St. Louis (MO): Mosby;2000.3. Jung SK, Kim TW. New approach for the diagnosis of extractions with neural network machine learning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016; 149(1):127–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2015.07.030 .4. Wehle HD. Machine learning, deep learning and AI: what’s the difference. In : Proceedings of the Annual Data Scientist Innovation Day Conference; 2017 Mar 28; Brussels, Belgium.5. Min S, Lee B, Yoon S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform. 2017; 18(5):851–69. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw068 .6. Ding X, Li Q, Cheng Y, Wang J, Bian W, Jie B. Local keypoint-based Faster R-CNN. Appl Intell. 2020; 50(10):3007–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01665-9 .7. Wolford L, Stevao E, Alexander CA, Goncalves JR. Orthodontics for orthognathic surgery. Miloro M, editor. Peterson’s principles of oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2nd ed. Ontario, Canada: BC Decker Inc;2004. p. 1111–34.8. Wu Y, Kirillov A, Massa F, Lo WY, Girshick R. Detectron2 [Internet]. San Francisco (CA): github.com;2019. [cited at 2022 Oct 10]. Available from: https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2 .9. Wen H, Huang C, Guo S. The application of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to recognize defects in 3D-printed parts. Materials (Basel). 2021; 14(10):2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102575 .10. Wu Y, Kirillov A, Massa F, Lo WY, Girshick R. Detectron2: a PyTorch-based modular object detection library [Internet]. Menlo Park (CA): Facebook;2019. [cited at 2022 Oct 10]. Available from: https://ai.facebook.com/blog/-detectron2-a-pytorch-based-modular-objectdetection-library-/ .11. Toshev A, Szegedy C. DeepPose: human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In : Proceeding of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2014 Jun 23–28; Columbus, OH. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.214 .12. Agarap AF. Deep learning using rectified linear units (ReLU) [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;2018. [cited at 2022 Oct 10]. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08375 .13. Gulli A, Pal S. Deep learning with Keras. Birmingham, UK: Packt Publishing Ltd;2017.14. Noorbakhsh-Sabet N, Zand R, Zhang Y, Abedi V. Artificial intelligence transforms the future of health care. Am J Med. 2019; 132(7):795–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.01.017 .15. Han J, Pei J, Kamber M. Data mining: concepts and techniques. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier;2011.16. Chen YW, Stanley K, Att W. Artificial intelligence in dentistry: current applications and future perspectives. Quintessence Int. 2020; 51(3):248–57. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.qi.a43952 .17. Zhang WC, Fu C, Zhu M. Joint object contour points and semantics for instance segmentation [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;2020. [cited at 2022 Oct 10]. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00460 .18. Uzair M, Jamil N. Effects of hidden layers on the efficiency of neural networks. In : Proceedings of 2020 IEEE 23rd International Multitopic Conference (INMIC); 2020 Nov 5–7; Bahawalpur, Pakistan. p. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/INMIC50486.2020.9318195 .19. Ide H, Kurita T. Improvement of learning for CNN with ReLU activation by sparse regularization. In : Proceedings of 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN); 2017 May 14–19; Anchorage, AK. p. 2684–2691. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2017.7966185 .20. Lee KS, Ryu JJ, Jang HS, Lee DY, Jung SK. Deep convolutional neural networks based analysis of cephalometric radiographs for differential diagnosis of orthognathic surgery indications. Appl Sci. 2020; 10(6):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124 .21. Choi HI, Jung SK, Baek SH, Lim WH, Ahn SJ, Yang IH, et al. Artificial intelligent model with neural network machine learning for the diagnosis of orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2019; 30(7):1986–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005650 .22. Poedjiastoeti W, Suebnukarn S. Application of convolutional neural network in the diagnosis of jaw tumors. Healthc Inform Res. 2018; 24(3):236–41. https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.3.236 .23. Schabel BJ, McNamara JA Jr, Franchi L, Baccetti T. Qsort assessment vs visual analog scale in the evaluation of smile esthetics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009; 135(4 Suppl):S61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.08.019 .24. Ludlow JB, Gubler M, Cevidanes L, Mol A. Precision of cephalometric landmark identification: cone-beam computed tomography vs conventional cephalometric views. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009; 136(3):312.e1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.12.018 .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prediction of oculocardiac reflex in strabismus surgery using neural networks
- Surgical Stent Fabrication and Clinical Application for Orthognathic Surgery Using Cone-Beam CT
- Current trends in orthognathic surgery
- A clinical study of the blood loss and transfusion on orthognathic surger
- The relationship between the symptoms of the patients and post-surgical application of antibiotics in orthognathic surgery